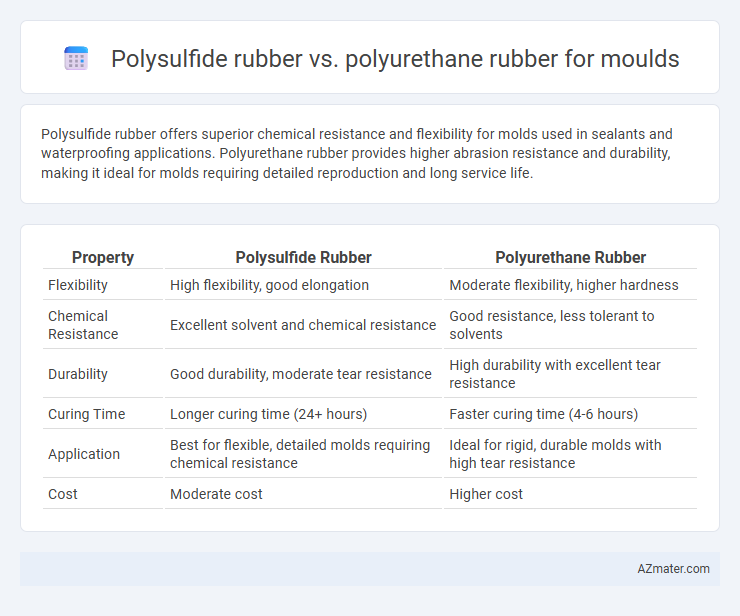
Polysulfide rubber offers superior chemical resistance and flexibility for molds used in sealants and waterproofing applications. Polyurethane rubber provides higher abrasion resistance and durability, making it ideal for molds requiring detailed reproduction and long service life.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfide Rubber | Polyurethane Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High flexibility, good elongation | Moderate flexibility, higher hardness |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent solvent and chemical resistance | Good resistance, less tolerant to solvents |
| Durability | Good durability, moderate tear resistance | High durability with excellent tear resistance |
| Curing Time | Longer curing time (24+ hours) | Faster curing time (4-6 hours) |
| Application | Best for flexible, detailed molds requiring chemical resistance | Ideal for rigid, durable molds with high tear resistance |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Mold-Making Rubbers
Polysulfide rubber is renowned for its excellent chemical resistance, flexibility, and longevity, making it ideal for molds requiring high durability and precision. Polyurethane rubber offers superior tear strength and abrasion resistance, suited for detailed molds and applications demanding high resilience and faster curing times. Both materials provide unique advantages in mold-making, where selecting between polysulfide and polyurethane depends on specific requirements like flexibility, chemical exposure, and production speed.
Overview of Polysulfide Rubber
Polysulfide rubber is a synthetic elastomer known for its exceptional chemical resistance, flexibility, and durability, making it ideal for mold-making applications that require resistance to oils, solvents, and moisture. Its unique polysulfide linkages enable superior elongation and tear strength, ensuring precise detail reproduction and longevity in the molding process. Compared to polyurethane rubber, polysulfide offers enhanced resistance to environmental degradation and is especially suited for marine, aerospace, and industrial sealing molds.
Overview of Polyurethane Rubber
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and high tensile strength compared to polysulfide rubber, making it ideal for mold applications requiring durability and precise detail. This elastomer exhibits excellent mechanical properties, including resistance to oils, solvents, and chemicals, extending the lifespan of molds in industrial casting. Its faster curing time and ability to replicate fine surface details provide significant advantages in prototyping and small-scale production.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Polysulfide rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance and flexibility with elongation rates typically between 250-400%, making it ideal for molds requiring durability against solvents and fuel exposure. Polyurethane rubber offers higher tensile strength, ranging from 20 to 40 MPa, and greater abrasion resistance, suitable for molds demanding toughness and wear resistance. Both materials vary significantly in hardness; polysulfide generally measures Shore A 20-50, while polyurethane ranges from Shore A 70 to Shore D 70, influencing mold performance based on specific application needs.
Chemical Resistance and Compatibility
Polysulfide rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance to solvents, oils, and fuels, making it ideal for molds exposed to harsh chemicals and environmental degradation. Polyurethane rubber offers excellent mechanical strength and abrasion resistance but is less resistant to strong acids, bases, and certain solvents compared to polysulfide. When selecting a mold material, polysulfide is preferable for chemical compatibility with aggressive substances, while polyurethane is suited for applications requiring toughness and wear resistance.
Flexibility and Durability in Use
Polysulfide rubber offers excellent flexibility with remarkable elongation, making it ideal for molds requiring intricate detail and stretch without cracking. Polyurethane rubber provides superior durability and abrasion resistance, ensuring long-lasting performance under repetitive use and mechanical stress. For applications demanding a balance of flexibility and toughness, polyurethane is favored, while polysulfide excels in scenarios prioritizing flexibility and chemical resistance.
Curing and Processing Differences
Polysulfide rubber cures through a condensation reaction involving mercaptan groups and formaldehyde, requiring longer curing times and the use of specific curing agents like aromatic or aliphatic crosslinkers, whereas polyurethane rubber polymerizes via the reaction between isocyanate and polyol components, resulting in faster curing and room-temperature vulcanization options. Processing polysulfide rubber demands precise control of moisture and temperature due to its sensitivity during curing, while polyurethane rubber offers greater processing flexibility with varied formulations allowing for cast, injection, or spray molding techniques. The differences in curing mechanisms influence the mold production cycle, with polyurethane typically enabling quicker turnaround compared to the more chemically sensitive polysulfide formulations.
Cost and Availability
Polysulfide rubber generally offers lower initial costs compared to polyurethane rubber, making it a budget-friendly option for mold-making projects. Availability of polysulfide is widespread in many regions, while polyurethane rubber, although slightly more expensive, can vary significantly in cost depending on the specific formulation and supplier. Polyurethane rubber often provides enhanced mechanical properties but may face limited availability in some markets, impacting procurement timelines and overall project budgeting.
Typical Applications for Each Rubber
Polysulfide rubber excels in applications requiring exceptional chemical resistance and airtight sealing, commonly used in aerospace fuel tanks, marine sealants, and construction expansion joints. Polyurethane rubber is preferred for its high abrasion resistance, flexibility, and durability, making it ideal for industrial rollers, wheels, gaskets, and casting molds in manufacturing processes. Each rubber type optimizes performance based on specific environmental exposure and mechanical stress conditions in molding applications.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Project
Polysulfide rubber offers excellent chemical resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for molds requiring durability and flexibility in applications like sealants and gaskets. Polyurethane rubber provides superior abrasion resistance and tensile strength, suitable for molds demanding high impact resilience and long-lasting performance in industrial parts production. Choosing the right rubber depends on the specific project requirements, including exposure conditions, mechanical stress, and desired mold longevity.
Infographic: Polysulfide rubber vs Polyurethane rubber for Mould
 azmater.com
azmater.com