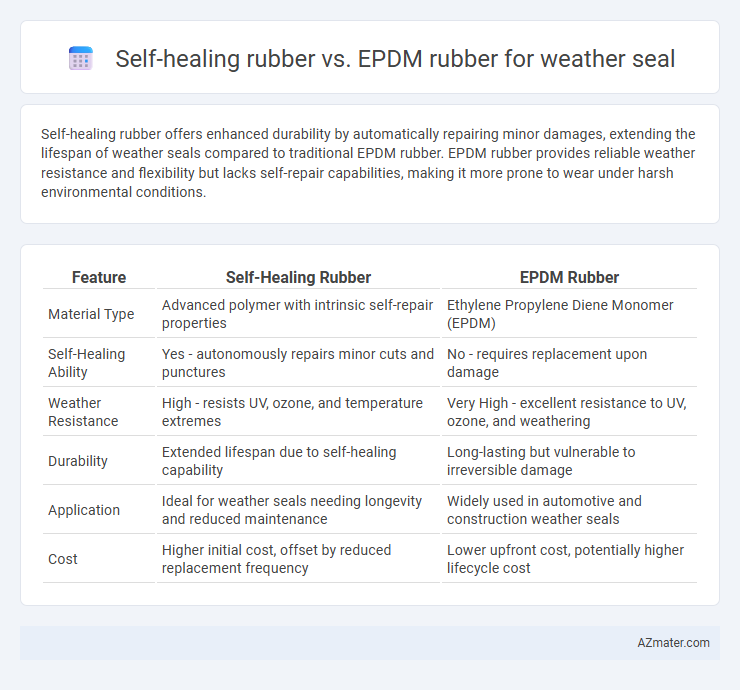
Self-healing rubber offers enhanced durability by automatically repairing minor damages, extending the lifespan of weather seals compared to traditional EPDM rubber. EPDM rubber provides reliable weather resistance and flexibility but lacks self-repair capabilities, making it more prone to wear under harsh environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Self-Healing Rubber | EPDM Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Advanced polymer with intrinsic self-repair properties | Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) |
| Self-Healing Ability | Yes - autonomously repairs minor cuts and punctures | No - requires replacement upon damage |
| Weather Resistance | High - resists UV, ozone, and temperature extremes | Very High - excellent resistance to UV, ozone, and weathering |
| Durability | Extended lifespan due to self-healing capability | Long-lasting but vulnerable to irreversible damage |
| Application | Ideal for weather seals needing longevity and reduced maintenance | Widely used in automotive and construction weather seals |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, offset by reduced replacement frequency | Lower upfront cost, potentially higher lifecycle cost |
Introduction to Weather Seals: Importance and Materials
Weather seals play a crucial role in preventing water, air, and dust infiltration in buildings and vehicles, ensuring energy efficiency and durability. Self-healing rubber offers advanced resilience by repairing minor damages autonomously, extending the lifespan of seals under harsh environmental conditions. EPDM rubber is widely used for weather seals due to its excellent resistance to UV rays, ozone, and temperature extremes, providing reliable and cost-effective protection.
What is EPDM Rubber? Key Properties and Applications
EPDM rubber, or ethylene propylene diene monomer, is a synthetic elastomer known for excellent resistance to heat, ozone, UV rays, and weathering, making it ideal for weather seals. Key properties include outstanding elasticity, durability, and water resistance, enabling effective sealing in automotive, roofing, and window applications. Its versatility and long lifespan make EPDM a preferred choice for preventing leaks and maintaining airtight environments in various industrial and residential settings.
Understanding Self-Healing Rubber: How It Works
Self-healing rubber contains microcapsules or reversible bonds that enable it to automatically repair damage when exposed to heat or pressure, restoring its integrity and extending its lifespan. EPDM rubber, known for its excellent weather resistance, flexibility, and durability, does not possess self-repair capabilities but provides long-lasting protection against UV rays, ozone, and extreme temperatures. The self-healing mechanism in rubber seals improves maintenance efficiency and reduces replacement frequency, making it advantageous for high-performance weather sealing applications where durability and rapid recovery are essential.
Comparative Weather Resistance: Self-Healing vs EPDM Rubber
Self-healing rubber exhibits superior weather resistance compared to EPDM rubber due to its intrinsic ability to repair micro-cracks caused by UV exposure, ozone, and temperature fluctuations, thus extending the seal's lifespan. EPDM rubber, while highly resistant to UV rays, ozone, and extreme temperatures, cannot restore damage once compromised, leading to degradation and reduced sealing efficiency over time. The comparative advantage of self-healing rubber lies in maintaining consistent weather-tight performance under harsh environmental conditions, making it a more durable choice for weather seal applications.
Durability and Longevity: Performance Over Time
Self-healing rubber exhibits superior durability by autonomously repairing micro-cracks, extending the weather seal's lifespan significantly compared to traditional EPDM rubber. EPDM rubber, while resistant to UV, ozone, and extreme temperatures, can develop wear over time without repair capability, leading to diminished sealing performance. The self-healing property enhances longevity by maintaining structural integrity and preventing seal failure in harsh environmental conditions.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Maintenance
Self-healing rubber offers a higher initial investment compared to EPDM rubber due to advanced material technology and specialized manufacturing processes. Maintenance costs for self-healing rubber are typically lower, as the material can autonomously repair minor damages, reducing the need for frequent replacements or repairs. EPDM rubber, while more affordable upfront, incurs higher long-term maintenance expenses because of its susceptibility to cracking and degradation in harsh weather conditions.
Installation and Flexibility: Which Rubber is Easier to Use?
Self-healing rubber offers superior flexibility due to its ability to autonomously repair small cuts and abrasions, making it easier to handle during installation without risking premature damage. EPDM rubber, known for its excellent weather resistance and durability, maintains consistent flexibility over a wide temperature range but can be less forgiving to installation stress or minor surface damage. For weather seal applications, self-healing rubber simplifies installation processes by reducing maintenance needs, while EPDM requires careful handling to preserve its long-term sealing effectiveness.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability and Eco-Friendliness
Self-healing rubber demonstrates superior sustainability in weather seal applications due to its ability to autonomously repair damage, significantly extending product lifespan and reducing waste compared to EPDM rubber. EPDM, while durable and recyclable, typically requires replacement after damage, leading to higher material consumption and environmental burden. The lower environmental impact of self-healing rubber aligns with eco-friendly goals by minimizing landfill waste and resource extraction through enhanced durability and reusability.
Common Applications: Where Each Rubber Excels
Self-healing rubber is ideal for applications requiring extended durability and rapid damage recovery, such as automotive gaskets and electronic device seals, where minor cuts or punctures are common. EPDM rubber excels in outdoor weather seals for windows, doors, and roofing due to its superior resistance to UV rays, ozone, and extreme temperatures. Both materials are widely used in HVAC systems, but EPDM's long-term weather resistance makes it the preferred choice for outdoor sealing solutions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Weather Seal Material
Self-healing rubber offers superior durability and long-term performance for weather seals by automatically repairing minor damages, reducing maintenance costs and extending seal lifespan. EPDM rubber provides excellent resistance to UV rays, ozone, and extreme temperatures, making it a reliable and cost-effective choice for traditional weather sealing applications. Selecting the best material depends on specific application needs, with self-healing rubber ideal for high-performance, maintenance-sensitive environments, while EPDM remains a trusted standard for general weather sealing.
Infographic: Self-healing rubber vs EPDM rubber for Weather seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com