Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for O-rings in automotive and industrial sealing applications. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides enhanced chemical resistance and durability under high temperatures and aggressive fluids, suitable for oil and fuel system O-rings.
Table of Comparison
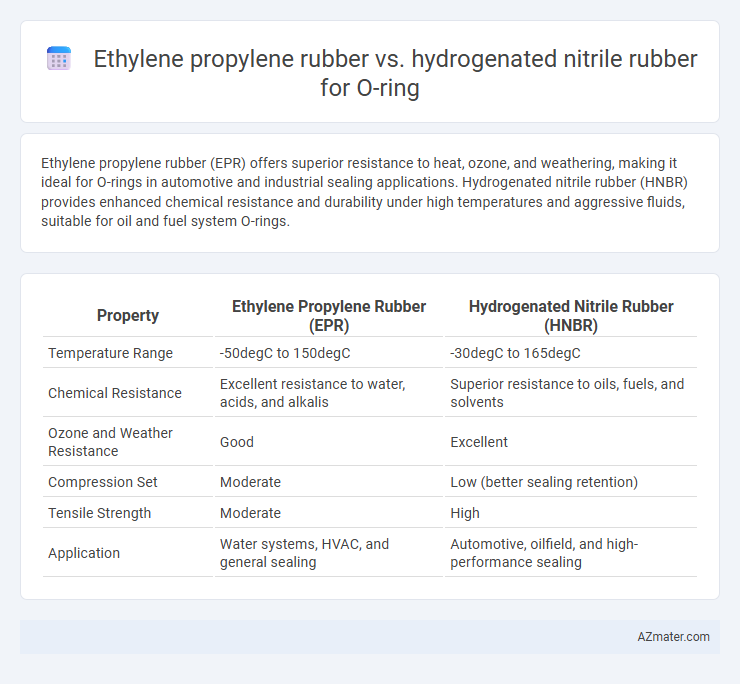
| Property | Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR) | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 150degC | -30degC to 165degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to water, acids, and alkalis | Superior resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents |
| Ozone and Weather Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Compression Set | Moderate | Low (better sealing retention) |
| Tensile Strength | Moderate | High |
| Application | Water systems, HVAC, and general sealing | Automotive, oilfield, and high-performance sealing |
Introduction to O-Ring Materials
O-ring materials like Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR) and Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) offer distinct properties tailored for sealing applications. EPR provides excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it suitable for outdoor and electrical environments. HNBR excels in oil, fuel, and chemical resistance while maintaining high mechanical strength and thermal stability, ideal for automotive and industrial sealing solutions.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPDM)
Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPDM) is a synthetic elastomer known for its exceptional resistance to heat, weathering, ozone, and a broad range of chemicals, making it ideal for O-ring applications in automotive, HVAC, and industrial settings. EPDM exhibits excellent flexibility at low temperatures and strong electrical insulating properties, which enhance its performance in dynamic sealing environments. Compared to Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR), EPDM offers superior resistance to steam and polar chemicals but lower resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels.
Overview of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, oil, and chemical degradation compared to Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR), making it ideal for demanding O-ring applications in automotive and industrial settings. Its enhanced thermal stability enables operation in temperatures ranging from -40degC to 150degC, while maintaining excellent mechanical properties and abrasion resistance. HNBR's hydrogenation process significantly improves its durability against ozone, oxidation, and aggressive fluids, delivering extended service life for sealing components.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) exhibits excellent resistance to water, steam, and oxygenated solvents but shows poor resistance to hydrocarbons and oils, limiting its use in petroleum-based applications. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance to fuels, oils, and aliphatic hydrocarbons, making it ideal for automotive and industrial sealing applications exposed to aggressive fluids. Both materials provide good heat resistance; however, HNBR's enhanced oil and chemical resistance give it a distinct advantage for O-rings in demanding chemical environments.
Temperature Performance: EPDM vs HNBR
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPDM) offers excellent low-temperature flexibility, remaining effective down to -40degC, and performs well in high temperatures up to 150degC, making it ideal for outdoor and automotive sealing applications. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior thermal resistance withstanding continuous temperatures up to 160degC and short peaks up to 175degC while maintaining mechanical properties and chemical resistance in demanding environments. EPDM's thermal range excels in weather-resistant applications, whereas HNBR is preferred for high-temperature oil and fuel exposure due to its robust heat aging stability.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) O-rings exhibit excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making them highly durable in outdoor and high-temperature environments. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) O-rings provide superior mechanical properties including higher tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and excellent resistance to oils and chemicals, resulting in enhanced durability under harsh mechanical and chemical conditions. Compared to EPR, HNBR offers better compression set resistance and longer service life in dynamic sealing applications exposed to aggressive fluids and elevated temperatures.
Compatibility with Fluids and Oils
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers excellent resistance to water, steam, and many chemicals but has limited compatibility with petroleum-based oils and fuels, making it less suitable for applications involving hydrocarbon fluids. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) demonstrates superior compatibility with a wide range of oils, fuels, and hydraulic fluids, maintaining elasticity and sealing performance under exposure to aggressive petroleum products. For O-rings exposed to fuels, lubricants, and oils, HNBR provides enhanced durability and chemical resistance compared to EPR.
Typical Applications in Industry
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) is widely used in automotive and electrical industries for O-rings due to its excellent resistance to heat, weathering, and ozone, making it ideal for sealing in engine components and electrical insulation. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) O-rings are preferred in oil and gas, aerospace, and chemical processing industries because of their superior resistance to oils, fuels, and aggressive chemicals, as well as high mechanical strength and thermal stability. EPR suits applications with exposure to water and steam, while HNBR excels in hydraulic systems and dynamic sealing in harsh chemical environments.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) generally offers higher cost efficiency due to its lower raw material and production expenses, making it a preferred choice for standard O-ring applications where chemical resistance is moderate. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR), while more expensive, delivers superior chemical, heat, and abrasion resistance, which can reduce lifecycle costs in demanding environments despite higher initial investment. Availability of EPR O-rings is widespread across various industrial suppliers, whereas HNBR O-rings may have more limited stock but are readily obtainable from specialized manufacturers targeting high-performance sealing solutions.
Choosing the Right O-Ring Material
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for outdoor and automotive O-ring applications requiring flexibility and durability. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior chemical resistance, especially against oils, fuels, and hydrocarbons, along with enhanced mechanical strength for high-pressure sealing. Selecting the right O-ring material depends on environmental exposure, temperature range, and chemical compatibility, with EPR suited for weather-resistant seals and HNBR preferred for oil and fuel system seals.
Infographic: Ethylene propylene rubber vs Hydrogenated nitrile rubber for O-ring
 azmater.com
azmater.com