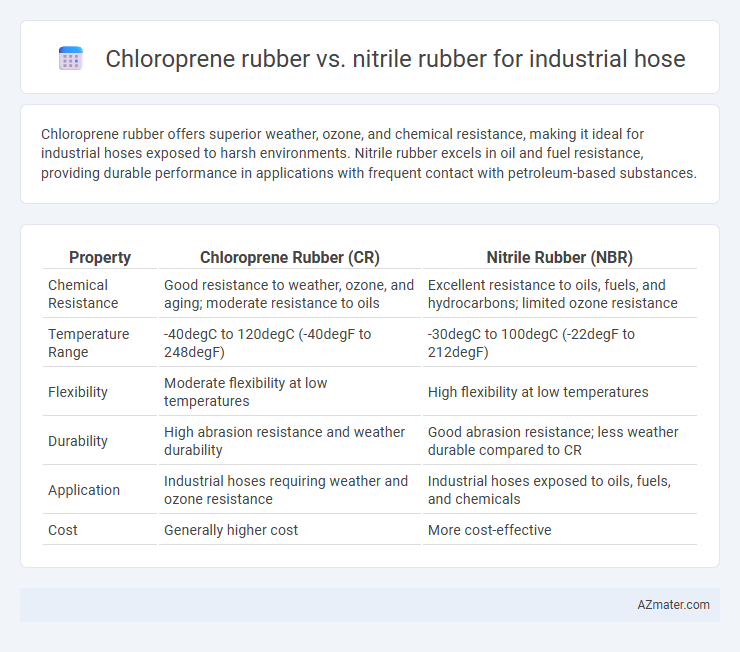
Chloroprene rubber offers superior weather, ozone, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for industrial hoses exposed to harsh environments. Nitrile rubber excels in oil and fuel resistance, providing durable performance in applications with frequent contact with petroleum-based substances.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chloroprene Rubber (CR) | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to weather, ozone, and aging; moderate resistance to oils | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and hydrocarbons; limited ozone resistance |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC (-40degF to 248degF) | -30degC to 100degC (-22degF to 212degF) |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility at low temperatures | High flexibility at low temperatures |
| Durability | High abrasion resistance and weather durability | Good abrasion resistance; less weather durable compared to CR |
| Application | Industrial hoses requiring weather and ozone resistance | Industrial hoses exposed to oils, fuels, and chemicals |
| Cost | Generally higher cost | More cost-effective |
Introduction to Chloroprene and Nitrile Rubber
Chloroprene rubber (CR), known for its excellent chemical stability, ozone resistance, and moderate oil resistance, is widely used in industrial hoses exposed to weather and diverse chemicals. Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers superior resistance to petroleum oils, fuels, and various hydraulic fluids, making it ideal for hoses in demanding oil and fuel transfer applications. Both materials provide distinct advantages based on environmental and fluid compatibility requirements in industrial hose manufacturing.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Chloroprene rubber (CR) features a polymer backbone of polychloroprene, distinguished by chlorine atoms along its chain that provide enhanced chemical and weather resistance, making it highly suitable for industrial hoses exposed to ozone and sunlight. Nitrile rubber (NBR) consists of copolymerized acrylonitrile and butadiene units, offering superior resistance to oils, fuels, and aliphatic hydrocarbons due to the polar nitrile groups in its molecular structure. The chemical composition of CR imparts balanced flexibility and durability in harsh environments, while NBR's molecular structure emphasizes solvent resistance and mechanical strength for industrial hose applications.
Key Physical Properties: Strength, Flexibility, & Durability
Chloroprene rubber exhibits excellent strength with high tensile values around 20 MPa and superior flexibility due to its balanced polymer structure, making it highly resistant to weathering and ozone degradation. Nitrile rubber offers exceptional durability in oil and fuel resistance, maintaining flexibility at low temperatures with tensile strength typically between 15-25 MPa. Both materials provide robust performance for industrial hoses, but chloroprene excels in environmental resistance while nitrile is preferred for hydrocarbon exposure.
Resistance to Chemicals, Oils, and Fuels
Chloroprene rubber offers excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals, oils, and fuels, making it highly suitable for industrial hoses exposed to harsh environments and moderate fuels. Nitrile rubber excels in resisting oils, fuels, and hydrocarbons, providing superior protection against petroleum-based fluids and commonly used industrial chemicals. The choice between chloroprene and nitrile rubber depends on specific chemical exposure, with nitrile preferred for high oil and fuel resistance, while chloroprene provides balanced durability against diverse chemical agents.
Temperature Tolerance in Industrial Environments
Chloroprene rubber exhibits a temperature tolerance range from -40degC to 120degC, making it suitable for moderate heat applications in industrial hoses. Nitrile rubber offers a broader temperature resistance, typically from -40degC to 135degC, providing enhanced performance in higher temperature industrial environments. The superior heat endurance of nitrile rubber makes it the preferred choice for hoses exposed to more extreme thermal conditions and petroleum-based fluids.
Weather, Ozone, and UV Resistance Factors
Chloroprene rubber exhibits superior weather, ozone, and UV resistance compared to nitrile rubber, making it ideal for industrial hoses exposed to harsh outdoor conditions. Its molecular structure provides enhanced protection against ozone cracking and UV degradation, resulting in longer service life and reduced maintenance costs. Nitrile rubber, while excellent for oil and fuel resistance, tends to degrade faster under prolonged sunlight and ozone exposure, limiting its suitability for outdoor applications.
Cost Analysis: Material and Maintenance Considerations
Chloroprene rubber typically has a higher initial material cost compared to nitrile rubber due to its superior chemical and weather resistance properties, making it durable in harsh industrial environments. Maintenance expenses for chloroprene hoses tend to be lower as their resistance to ozone, oil, and heat reduces the frequency of replacements and repairs. Nitrile rubber hoses offer a more cost-effective upfront option but may incur higher long-term maintenance costs in applications involving exposure to oils and extreme conditions.
Typical Industrial Hose Applications
Chloroprene rubber excels in industrial hose applications requiring excellent weather, ozone, and oil resistance, making it ideal for chemical, petroleum, and refrigeration industries. Nitrile rubber offers superior resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels, often used in fuel delivery, automotive, and hydraulic hose systems. Both materials provide flexibility and durability, but chloroprene is preferred for broader environmental exposure, while nitrile is favored for strong oil and fuel resistance.
Environmental and Safety Impacts
Chloroprene rubber offers superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and flame, making it safer for industrial hoses used in harsh outdoor or high-temperature environments, with lower emissions of hazardous compounds during degradation. Nitrile rubber excels in chemical and oil resistance, reducing the risk of hazardous leaks and spills, but its production and disposal pose more significant environmental challenges due to higher volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. Choosing chloroprene rubber minimizes long-term environmental impact and enhances workplace safety by reducing toxic exposure compared to nitrile rubber in industrial hose applications.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Industrial Hose Needs
Chloroprene rubber offers excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and moderate chemicals, making it ideal for industrial hoses exposed to outdoor conditions and mild chemical environments. Nitrile rubber excels in oil and fuel resistance, providing superior durability in applications involving hydrocarbons and petroleum-based fluids. Selecting the right rubber depends on the specific industrial hose application, chemical exposure, and environmental factors to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Chloroprene rubber vs Nitrile rubber for Industrial hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com