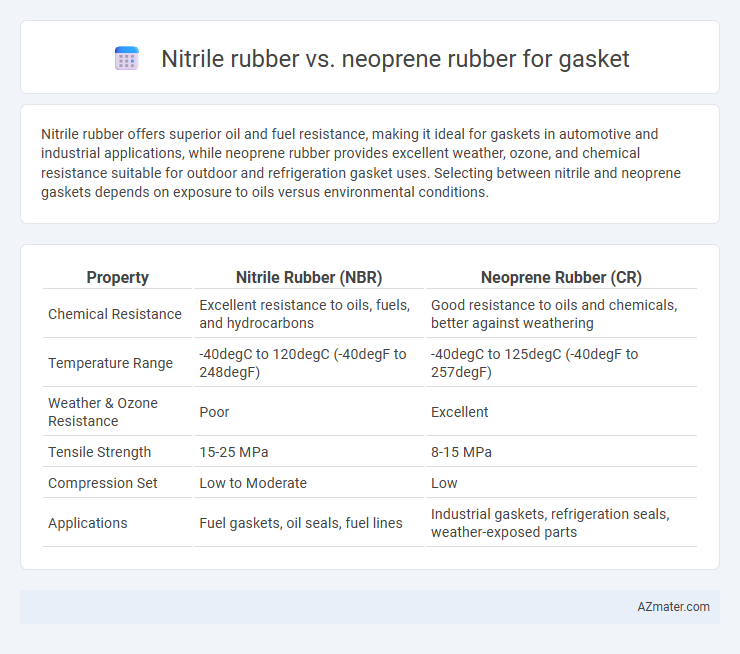
Nitrile rubber offers superior oil and fuel resistance, making it ideal for gaskets in automotive and industrial applications, while neoprene rubber provides excellent weather, ozone, and chemical resistance suitable for outdoor and refrigeration gasket uses. Selecting between nitrile and neoprene gaskets depends on exposure to oils versus environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) | Neoprene Rubber (CR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and hydrocarbons | Good resistance to oils and chemicals, better against weathering |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC (-40degF to 248degF) | -40degC to 125degC (-40degF to 257degF) |
| Weather & Ozone Resistance | Poor | Excellent |
| Tensile Strength | 15-25 MPa | 8-15 MPa |
| Compression Set | Low to Moderate | Low |
| Applications | Fuel gaskets, oil seals, fuel lines | Industrial gaskets, refrigeration seals, weather-exposed parts |
Introduction to Gasket Materials
Nitrile rubber, known for its excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, is commonly used in gasket applications requiring durability against petroleum-based fluids. Neoprene rubber offers superior weathering, ozone, and aging resistance, making it ideal for outdoor or exposed gasket environments. Selecting between nitrile and neoprene depends on the specific chemical exposure and environmental conditions of the gasket's operational setting.
What is Nitrile Rubber?
Nitrile rubber, also known as NBR or Buna-N, is a synthetic elastomer widely used in gasket manufacturing due to its excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and chemicals. It offers high tensile strength and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for sealing applications in automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery. Compared to neoprene rubber, nitrile provides superior oil and fuel resistance, enhancing gasket performance in harsh, oil-exposed environments.
What is Neoprene Rubber?
Neoprene rubber, a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent chemical stability and flexibility, is widely used in gasket applications requiring resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering. Unlike nitrile rubber, which excels in oil resistance and mechanical strength, neoprene offers superior performance against ozone, UV rays, and aging, making it suitable for outdoor and harsh environmental conditions. Its balanced durability and resilience ensure effective sealing in applications exposed to moderate heat and varying environmental factors.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers superior oil resistance and tensile strength, making it ideal for gaskets exposed to petroleum-based fluids and high mechanical stress. Neoprene rubber (CR) demonstrates excellent weathering, ozone resistance, and moderate chemical stability, suited for outdoor applications and exposure to refrigerants or mild acids. Both materials provide good compression set resistance, but nitrile typically outperforms neoprene in temperature range (-40degC to 108degC vs. -40degC to 121degC) and abrasion resistance for gasket sealing performance.
Chemical Resistance: Nitrile vs Neoprene
Nitrile rubber exhibits superior resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and many chemicals, making it ideal for applications involving hydrocarbons. Neoprene rubber offers enhanced resistance to weathering, ozone, and a broader range of chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and some solvents. Choosing between nitrile and neoprene gaskets depends on the specific chemical exposure and environmental conditions of the application.
Temperature Resistance Differences
Nitrile rubber gaskets typically withstand temperatures ranging from -40degC to 120degC, making them suitable for applications involving oils and fuels but limited in high-temperature environments. Neoprene rubber gaskets offer a broader temperature resistance, ranging from -40degC to 150degC, providing enhanced durability in moderate heat and outdoor conditions. The superior heat resistance of neoprene makes it preferable for applications requiring extended exposure to elevated temperatures.
Oil and Fuel Compatibility
Nitrile rubber exhibits superior oil and fuel resistance, making it the preferred choice for gaskets in automotive and industrial applications involving petroleum-based fluids. Neoprene rubber offers moderate chemical resistance but is less effective against hydrocarbons compared to nitrile, limiting its use where prolonged contact with oils and fuels occurs. Selecting nitrile ensures enhanced durability and sealing performance in environments exposed to oils, fuels, and hydraulic fluids.
Applications in Gasket Manufacturing
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is widely used in gasket manufacturing for oil, fuel, and chemical-resistant applications due to its superior resistance to petroleum-based fluids and excellent tensile strength. Neoprene rubber (CR) gaskets are preferred in environments requiring good weather, ozone, and moderate chemical resistance, making them ideal for refrigeration, automotive, and HVAC systems. Both materials offer distinct advantages in gasket production, with nitrile excelling in fuel and oil sealing and neoprene providing durability in outdoor and industrial applications.
Cost and Durability Considerations
Nitrile rubber offers a cost-effective solution for gaskets with excellent resistance to oils and fuels, making it suitable for automotive and industrial applications where budget constraints are critical. Neoprene rubber, while generally more expensive, provides superior weather, ozone, and chemical resistance, enhancing gasket durability in outdoor and harsh environmental conditions. Choosing between nitrile and neoprene depends on balancing initial budget and long-term durability requirements specific to the gasket's operating environment.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Gasket Needs
Nitrile rubber offers excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, making it ideal for gaskets in automotive and industrial applications where exposure to petroleum-based fluids is common. Neoprene rubber provides superior weather resistance, ozone stability, and flexibility, suited for outdoor gaskets or those exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Selecting the right rubber involves evaluating the chemical compatibility, temperature range, and environmental factors specific to the gasket's application to ensure optimal performance and durability.
Infographic: Nitrile rubber vs Neoprene rubber for Gasket
 azmater.com
azmater.com