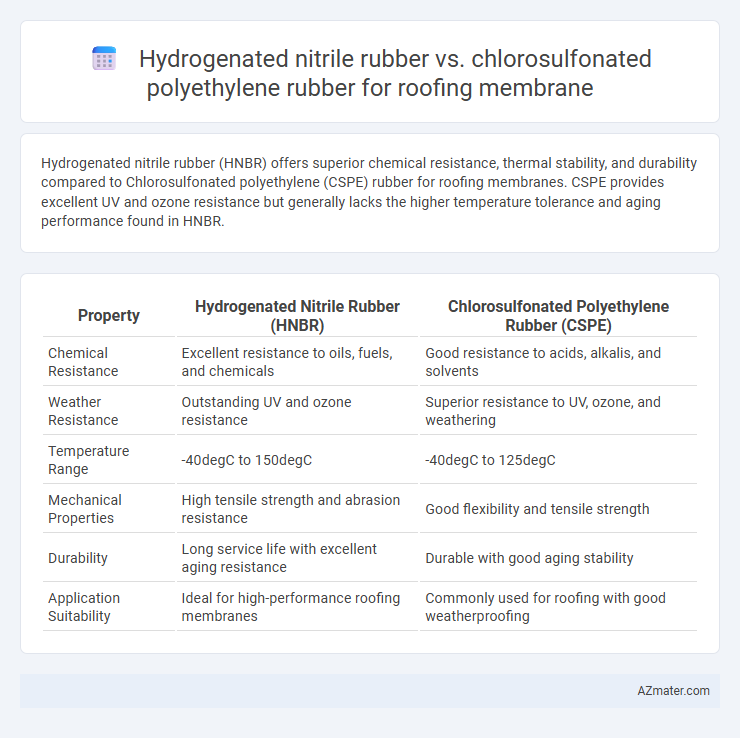
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance, thermal stability, and durability compared to Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber for roofing membranes. CSPE provides excellent UV and ozone resistance but generally lacks the higher temperature tolerance and aging performance found in HNBR.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) | Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene Rubber (CSPE) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Good resistance to acids, alkalis, and solvents |
| Weather Resistance | Outstanding UV and ozone resistance | Superior resistance to UV, ozone, and weathering |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC | -40degC to 125degC |
| Mechanical Properties | High tensile strength and abrasion resistance | Good flexibility and tensile strength |
| Durability | Long service life with excellent aging resistance | Durable with good aging stability |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for high-performance roofing membranes | Commonly used for roofing with good weatherproofing |
Introduction to Roofing Membranes
Roofing membranes made from hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offer exceptional resistance to heat, oils, and chemicals, making them durable choices for industrial environments. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber membranes excel in UV and weather resistance, providing long-lasting protection against environmental degradation. Selecting between HNBR and CSPE depends on specific application needs, including exposure to chemical agents and climatic conditions.
Overview of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) is a highly durable synthetic elastomer known for excellent resistance to heat, oil, ozone, and weathering, making it suitable for demanding roofing membrane applications. Its molecular structure, enhanced by hydrogenation, improves thermal stability and aging resistance compared to traditional nitrile rubber, ensuring long-term performance in harsh environments. HNBR membranes provide superior tensile strength and elasticity, offering enhanced protection against UV radiation, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress in roofing systems.
Overview of Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene Rubber (CSM)
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) offers exceptional weather resistance, chemical stability, and UV protection, making it highly suitable for roofing membranes exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Its molecular structure provides superior resistance to ozone, oxidation, and various chemicals compared to hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR), enhancing durability in outdoor applications. CSM membranes exhibit excellent tensile strength and flexibility, ensuring long-term performance and leak prevention in diverse climates.
Chemical Structure Comparison: HNBR vs CSM
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) features a saturated hydrocarbon backbone with hydrogenated nitrile groups, providing enhanced chemical resistance, thermal stability, and ozone resistance compared to regular nitrile rubber. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber consists of a polyethylene backbone functionalized with chlorosulfonyl groups, which impart superior weather resistance, chemical resistance, and flame retardancy. The saturated structure of HNBR offers better resistance to heat and oils, whereas CSM's chlorosulfonyl groups provide excellent UV and chemical durability, making each polymer suitable for different roofing membrane performance requirements.
Weather and UV Resistance Properties
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior weather and UV resistance due to its saturated polymer backbone, providing excellent durability against ozone, sunlight, and extreme temperatures, making it ideal for roofing membranes in harsh environments. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) also offers strong weathering and UV resistance with outstanding chemical and abrasion resilience, though it can exhibit some degradation under prolonged UV exposure compared to HNBR. Both materials provide reliable roofing membrane performance, but HNBR's enhanced oxidative stability offers longer-lasting protection in severe climatic conditions.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility Differences
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior mechanical strength with enhanced tensile strength and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for high-stress roofing membrane applications. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSPE) provides excellent flexibility and elongation at break, ensuring better performance under dynamic weather conditions and thermal expansion. While HNBR excels in durability and resistance to mechanical wear, CSPE outperforms in maintaining elasticity and flexibility over a broad temperature range.
Chemical and Ozone Resistance in Roof Applications
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance against oils, fuels, and solvents compared to chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSPE), making it highly suitable for roofing membranes exposed to industrial pollutants. HNBR also demonstrates excellent ozone resistance due to its saturated polymer backbone, which prevents cracking and degradation under prolonged UV and ozone exposure. While CSPE provides good weatherability and flexibility, HNBR's enhanced durability in harsh chemical and ozone environments leads to longer service life in demanding roof applications.
Temperature Tolerance: HNBR vs CSM
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior temperature tolerance for roofing membranes, withstanding continuous exposure from -40degC to 150degC, which ensures durability in extreme climates. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber exhibits reliable performance in temperatures ranging from -30degC to 120degC but may degrade faster under prolonged heat stress. The enhanced thermal stability of HNBR makes it a preferred choice for high-temperature roofing applications requiring long-term resilience.
Cost and Installation Considerations
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) roofing membranes generally offer higher resistance to heat, chemicals, and weathering but come at a higher material cost compared to chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber. CSPE membranes tend to be more cost-effective initially and provide ease of installation due to their flexibility and compatibility with common adhesives. Installation of HNBR requires specialized handling and techniques to ensure proper curing and adhesion, which can increase labor costs and extend project timelines compared to the more straightforward installation process of CSPE membranes.
Conclusion: Best Choice for Roofing Membranes
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance, durability, and thermal stability, making it highly effective for roofing membranes exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber provides excellent UV resistance and weatherability but may lack the enhanced mechanical strength and temperature tolerance of HNBR. For roofing membranes requiring long-term performance and resilience against chemical and thermal stress, HNBR is generally the best choice.
Infographic: Hydrogenated nitrile rubber vs Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber for Roofing membrane
 azmater.com
azmater.com