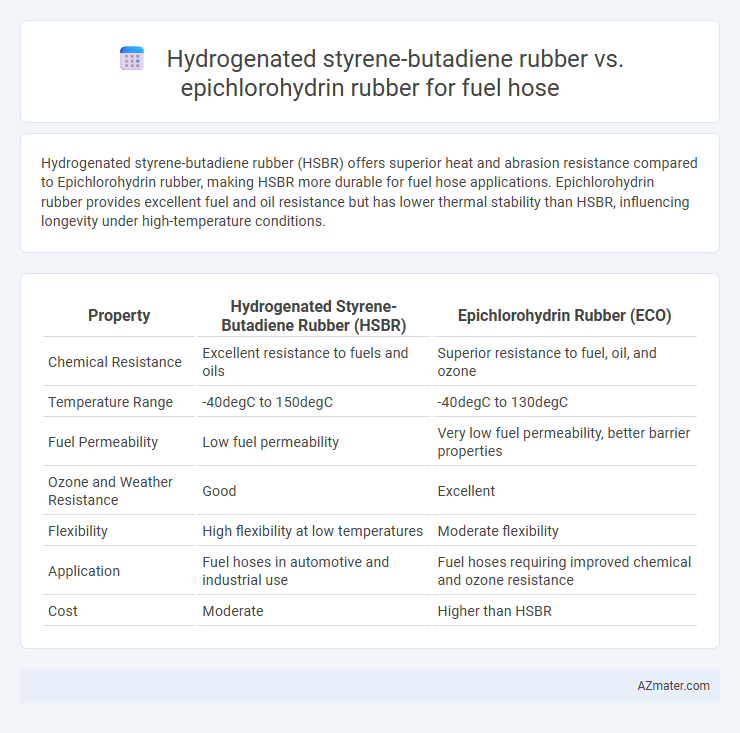
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior heat and abrasion resistance compared to Epichlorohydrin rubber, making HSBR more durable for fuel hose applications. Epichlorohydrin rubber provides excellent fuel and oil resistance but has lower thermal stability than HSBR, influencing longevity under high-temperature conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) | Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to fuels and oils | Superior resistance to fuel, oil, and ozone |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC | -40degC to 130degC |
| Fuel Permeability | Low fuel permeability | Very low fuel permeability, better barrier properties |
| Ozone and Weather Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Flexibility | High flexibility at low temperatures | Moderate flexibility |
| Application | Fuel hoses in automotive and industrial use | Fuel hoses requiring improved chemical and ozone resistance |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher than HSBR |
Introduction to Fuel Hose Materials
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers excellent oil and fuel resistance with enhanced heat aging properties, making it suitable for fuel hose applications exposed to high temperatures and aggressive fuels. Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) provides superior resistance to ozone, weather, and a broad range of chemicals, ensuring durability in harsh environmental conditions and prolonged fuel exposure. Both materials are preferred in fuel hose manufacturing for their balance of flexibility, chemical stability, and resistance to degradation from modern fuel blends.
Overview of Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR)
Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) offers superior resistance to heat, ozone, and oxidative degradation, making it highly suitable for demanding applications such as fuel hoses. Its hydrogenation process enhances saturation of polymer chains, significantly improving chemical stability and compatibility with hydrocarbons compared to conventional SBR. HSBR's excellent mechanical strength, flexibility, and durability extend fuel hose lifespan under high-temperature and fuel exposure conditions, outperforming Epichlorohydrin rubber in resistance to swelling and cracking from fuels and additives.
Overview of Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO)
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) offers superior resistance to fuels, oils, and chemicals, making it ideal for fuel hose applications requiring durability under harsh environments. Its low permeability to fuels and excellent flexibility at low temperatures provide a reliable performance advantage over hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR). ECO's balance of chemical resistance and mechanical strength ensures long service life in automotive and industrial fuel systems.
Chemical Resistance Properties: HSBR vs ECO
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior resistance to aromatic hydrocarbons, oxidizing agents, and ozone, making it highly suitable for fuel hoses exposed to harsh chemical environments. Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) excels in resistance against oils, fuels, and moderate acids, with outstanding resistance to heat and ozone but limited performance against aromatic solvents. For fuel hose applications demanding robustness against aggressive fuel formulations and oxidative degradation, HSBR delivers enhanced chemical stability compared to ECO.
Fuel Permeability: Comparative Analysis
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) exhibits significantly lower fuel permeability compared to epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO), making it more suitable for fuel hose applications requiring enhanced fuel resistance. HSBR's saturated polymer backbone resists hydrocarbon swelling and permeation, while epichlorohydrin rubber, although resistant to oil and fuel, has higher permeability rates due to its polar ether groups. This difference results in HSBR fuel hoses offering superior durability and reduced volatile organic compound emissions in fuel system environments.
Temperature Performance of HSBR and ECO
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) exhibits exceptional temperature resistance, typically maintaining performance in environments ranging from -40degC to 150degC, making it highly suitable for fuel hoses exposed to fluctuating and high-temperature conditions. Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) offers good thermal stability but generally operates effectively within a narrower temperature range of approximately -30degC to 120degC, limiting its application in extreme temperature scenarios. HSBR's superior heat resistance and oxidative stability provide enhanced durability and safety for fuel hose applications in demanding thermal environments compared to ECO.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) exhibits superior mechanical strength with enhanced abrasion resistance and tensile properties, making it ideal for fuel hoses exposed to high pressure and mechanical stress. Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) offers excellent flexibility and oil resistance, maintaining elasticity over a wide temperature range, which is crucial for dynamic fuel hose applications requiring bending and movement. HSBR provides better durability under mechanical strain, while ECO excels in flexibility and chemical resistance, allowing optimal selection based on specific fuel hose performance requirements.
Aging and Durability in Fuel Hose Applications
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) exhibits superior resistance to fuel-induced aging due to its saturated polymer backbone, which reduces oxidative degradation and maintains mechanical properties over prolonged exposure to fuels. Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) offers excellent resistance to fuels and oils, with high polarity improving compatibility with polar fuels, but its durability may decline under high-temperature aging conditions compared to HSBR. For fuel hose applications, HSBR provides enhanced long-term durability and resistance to swelling and cracking, while ECO is favored for moderate aging scenarios requiring strong fuel and oil resistance.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior fuel resistance and thermal stability, but its manufacturing process involves higher costs due to complex hydrogenation steps and catalyst usage. Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) provides cost-effective fuel hose solutions with good resistance to oil and fuel, benefiting from simpler polymerization and curing methods that reduce production expenses. Choosing between HSBR and ECO balances higher raw material and processing costs of HSBR against ECO's affordability and adequate performance in fuel hose applications.
Summary: Choosing the Right Rubber for Fuel Hoses
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior resistance to heat, ozone, and fuel permeability, making it ideal for high-temperature fuel hose applications requiring durability. Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) provides excellent fuel, oil, and chemical resistance, along with good low-temperature flexibility, suitable for hoses exposed to diverse harsh chemical environments. Selecting the right rubber depends on specific fuel compatibility, temperature range, and environmental exposure to ensure optimal hose performance and longevity.
Infographic: Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber vs Epichlorohydrin rubber for Fuel hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com