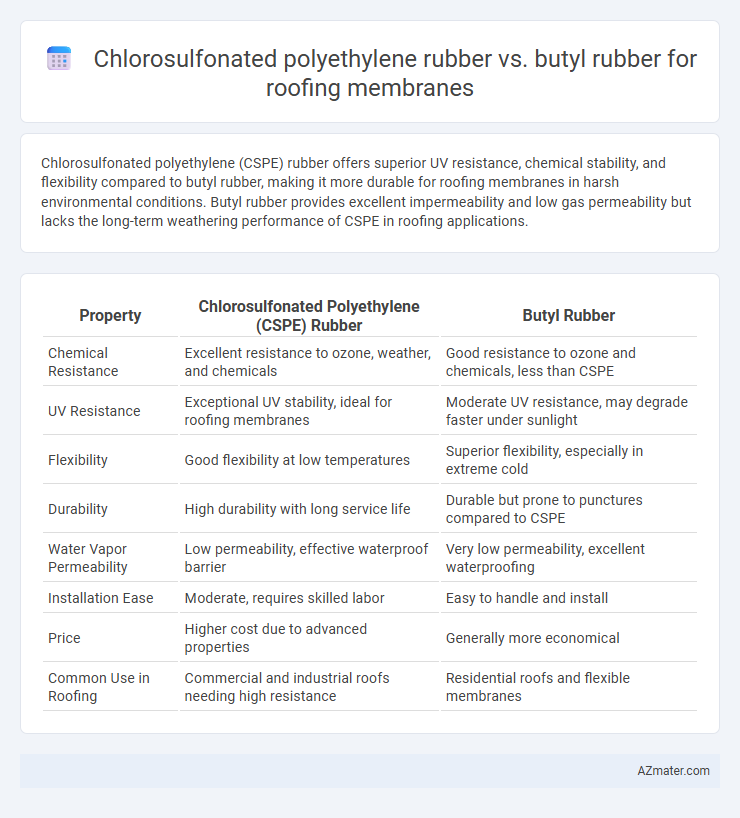
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber offers superior UV resistance, chemical stability, and flexibility compared to butyl rubber, making it more durable for roofing membranes in harsh environmental conditions. Butyl rubber provides excellent impermeability and low gas permeability but lacks the long-term weathering performance of CSPE in roofing applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene (CSPE) Rubber | Butyl Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to ozone, weather, and chemicals | Good resistance to ozone and chemicals, less than CSPE |
| UV Resistance | Exceptional UV stability, ideal for roofing membranes | Moderate UV resistance, may degrade faster under sunlight |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility at low temperatures | Superior flexibility, especially in extreme cold |
| Durability | High durability with long service life | Durable but prone to punctures compared to CSPE |
| Water Vapor Permeability | Low permeability, effective waterproof barrier | Very low permeability, excellent waterproofing |
| Installation Ease | Moderate, requires skilled labor | Easy to handle and install |
| Price | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Generally more economical |
| Common Use in Roofing | Commercial and industrial roofs needing high resistance | Residential roofs and flexible membranes |
Introduction to Roofing Membranes
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSPE) offers excellent weather resistance, UV stability, and chemical durability, making it a preferred choice for roofing membranes in harsh climates. Butyl rubber excels in impermeability and flexibility, providing superior resistance to water vapor and gas, which is critical for waterproof roofing applications. Both materials serve as robust roofing membranes, but CSPE is often selected for environments requiring enhanced weather and chemical performance, while butyl rubber is favored for superior moisture and gas barrier properties.
Overview of Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene (CSPE) Rubber
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber exhibits excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and UV radiation, making it highly suitable for roofing membranes in harsh environmental conditions. Its chemical structure provides superior elasticity and durability compared to butyl rubber, which often exhibits lower resistance to chemicals and UV exposure. CSPE membranes also offer enhanced tear strength and long service life, ensuring reliable performance in roofing applications.
Properties of Butyl Rubber Membranes
Butyl rubber membranes exhibit exceptional impermeability to gases and excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and chemical degradation, making them highly durable for roofing applications. Their superior flexibility and tensile strength enable them to accommodate building movements without cracking or losing waterproofing integrity. These membranes also provide strong adhesion to various substrates, enhancing long-term waterproof performance compared to chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber options.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber offers excellent weather resistance, UV stability, and chemical durability, resulting in a roofing membrane lifespan that typically exceeds 30 years. Butyl rubber membranes provide superior impermeability to gases and exceptional resilience to ozone and weathering, yet their longevity is generally shorter, averaging around 20 to 25 years under similar environmental conditions. The enhanced UV and chemical resistance of CSPE makes it more durable for long-term roofing applications in harsh climates compared to butyl rubber.
Weather and UV Resistance Analysis
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber exhibits superior weather and UV resistance compared to butyl rubber, maintaining flexibility and tensile strength under prolonged sun exposure and harsh environmental conditions. CSPE's molecular structure provides excellent impermeability to ozone, UV radiation, and chemical degradation, making it ideal for roofing membranes exposed to extreme weather. In contrast, butyl rubber is more susceptible to UV-induced cracking and degradation, reducing its lifespan and performance in outdoor roofing applications.
Flexibility and Ease of Installation
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber offers superior flexibility at both low and high temperatures, enhancing its adaptability to roof movements without cracking or tearing. Butyl rubber, while possessing excellent air and moisture impermeability, tends to be less flexible, especially in colder climates, which can complicate installation around complex roof contours. CSPE membranes generally allow for easier handling and faster installation due to their pliability, reducing labor time and costs compared to the stiffer butyl rubber options.
Chemical and Puncture Resistance
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber offers superior chemical resistance due to its resistance to oils, solvents, and ozone, making it highly durable for roofing membranes exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Butyl rubber exhibits excellent puncture resistance owing to its dense molecular structure, which provides high impermeability and flexibility, enhancing its durability under mechanical stress. Both materials provide strong chemical resistance, but CSPE's enhanced resistance to a broader range of chemicals and ultraviolet degradation makes it preferable in chemically aggressive environments.
Cost Effectiveness and Budget Considerations
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber offers superior weather resistance and durability for roofing membranes but typically comes at a higher initial cost compared to Butyl rubber. Butyl rubber provides a more budget-friendly option with excellent impermeability and flexibility, making it cost-effective for projects with tight budget constraints. Long-term maintenance expenses should be weighed, as CSPE's extended lifespan can result in lower overall lifecycle costs despite its premium upfront price.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber roofing membranes exhibit high resistance to UV radiation, ozone, and chemicals, contributing to longer service life and reduced material replacement frequency, which enhances their environmental sustainability. Butyl rubber membranes offer excellent air impermeability and weather resistance but generally have a shorter lifespan and higher volatility organic compound (VOC) emissions during manufacture. Lifecycle assessments indicate that CSPE roofing membranes tend to have a lower overall environmental impact due to durability and lower VOC content compared to butyl rubber alternatives.
Best Applications: CSPE vs Butyl Rubber in Roofing
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber excels in roofing applications requiring superior chemical resistance, UV stability, and weatherproofing, making it ideal for flat and low-slope roofing membranes exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Butyl rubber offers exceptional impermeability and flexibility, providing excellent performance in waterproofing and sealing for roofing systems subject to movement and temperature fluctuations. CSPE is preferred for industrial and commercial roofs demanding long-term durability, while butyl rubber suits residential and specialty roofing requiring elasticity and resistance to water vapor transmission.
Infographic: Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber vs Butyl rubber for Roofing membrane
 azmater.com
azmater.com