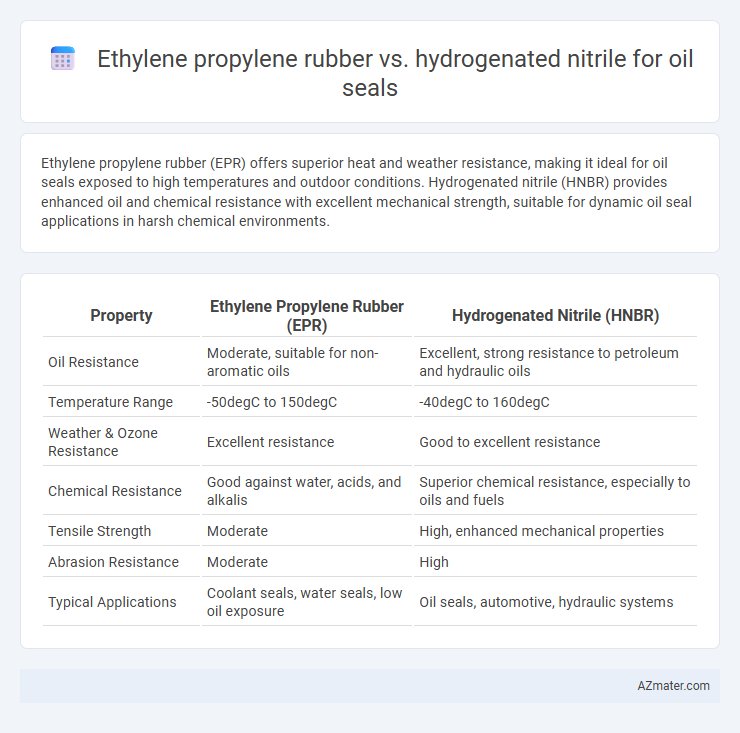
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior heat and weather resistance, making it ideal for oil seals exposed to high temperatures and outdoor conditions. Hydrogenated nitrile (HNBR) provides enhanced oil and chemical resistance with excellent mechanical strength, suitable for dynamic oil seal applications in harsh chemical environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR) | Hydrogenated Nitrile (HNBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Resistance | Moderate, suitable for non-aromatic oils | Excellent, strong resistance to petroleum and hydraulic oils |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 150degC | -40degC to 160degC |
| Weather & Ozone Resistance | Excellent resistance | Good to excellent resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against water, acids, and alkalis | Superior chemical resistance, especially to oils and fuels |
| Tensile Strength | Moderate | High, enhanced mechanical properties |
| Abrasion Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Typical Applications | Coolant seals, water seals, low oil exposure | Oil seals, automotive, hydraulic systems |
Introduction to Oil Seal Materials
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it suitable for oil seals exposed to moderate temperatures and non-polar fluids. Hydrogenated nitrile (HNBR) provides superior oil, fuel, and chemical resistance combined with high mechanical strength and thermal stability, ideal for demanding oil seal applications in automotive and industrial environments. Selecting the proper material depends on specific operational conditions, including temperature range, fluid compatibility, and exposure to wear.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPDM)
Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPDM) is a synthetic elastomer widely used in oil seal applications due to its excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering. EPDM offers superior flexibility and resilience, maintaining performance in temperatures ranging from -40degC to 150degC, which makes it ideal for dynamic sealing environments. Its chemical resistance, however, is limited against petroleum-based oils and fuels, where Hydrogenated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (HNBR) typically performs better due to enhanced oil and chemical resistance.
Overview of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) offers exceptional resistance to heat, oil, and chemical exposure, making it highly suitable for demanding oil seal applications. Compared to Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR), HNBR exhibits superior mechanical strength, durability, and resistance to hydrocarbon-based fluids. Its enhanced thermal stability up to 150degC ensures prolonged sealing performance in automotive and industrial environments.
Chemical Resistance: EPDM vs HNBR
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPDM) shows excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including brake fluids, ketones, and hot water, but its performance significantly declines when exposed to petroleum oils and hydrocarbons. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance against oils, fuels, and most aliphatic hydrocarbons, making it highly suitable for oil seal applications in harsh environments. While EPDM is preferred for non-oil applications due to its weather and ozone resistance, HNBR's robust resistance to oils and high temperatures ensures longer durability in oil seals exposed to aggressive chemical conditions.
Temperature Range Performance Comparison
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPDM) typically performs well within a temperature range of -40degC to 150degC, making it suitable for moderate temperature oil seal applications but less effective in high-heat environments. Hydrogenated nitrile (HNBR) offers a broader temperature resistance, functioning efficiently between -40degC and 165degC, providing superior thermal stability and durability under more extreme conditions. The enhanced heat resistance of HNBR allows oil seals to maintain integrity and prevent leakage in automotive and industrial applications involving higher temperature fluctuations.
Compatibility with Lubricating Oils
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) exhibits excellent compatibility with a wide range of lubricating oils, including mineral and synthetic oils, making it suitable for oil seal applications in various automotive and industrial environments. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to aromatic and aliphatic oils, as well as improved mechanical properties under high temperature and oxidative conditions, ensuring prolonged seal life in aggressive oil environments. While EPR provides good swelling resistance and flexibility, HNBR is often preferred for high-performance oil seals due to its enhanced oil resistance and durability.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) exhibits excellent flexibility and resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it highly durable for oil seal applications in moderate temperature ranges. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior mechanical properties including higher tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and exceptional resistance to oil, fuels, and chemicals, enhancing the longevity of oil seals under harsh conditions. The choice between EPR and HNBR depends on the specific operating temperature and chemical exposure, with HNBR generally providing better performance in demanding oil seal environments.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers a cost-effective solution for oil seals with moderate chemical resistance and broad availability due to its widespread production and use. Hydrogenated nitrile (HNBR) provides superior resistance to heat, oil, and chemicals, resulting in higher performance oil seals but at a significantly increased material cost and limited availability compared to EPR. Manufacturers often weigh the balance between EPR's affordability and accessibility against HNBR's enhanced durability for high-stress sealing applications.
Typical Applications in Industry
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) is widely used in automotive and electrical industries for oil seals due to its excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and water, making it ideal for outdoor and high-temperature engine seals. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) excels in oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, making it suitable for heavy-duty industrial applications such as oil field equipment, hydraulic systems, and automotive fuel systems. Both materials are essential in manufacturing oil seals, with EPR favored for its flexibility and low-temperature performance, while HNBR is chosen for aggressive chemical environments and high abrasion resistance.
Selecting the Right Material for Oil Seals
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for oil seals exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Hydrogenated nitrile (HNBR) provides superior resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, along with enhanced mechanical properties suitable for high-temperature applications up to 150degC. Selecting the right material requires evaluating operating temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress to ensure optimal oil seal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Ethylene propylene rubber vs Hydrogenated nitrile for Oil seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com