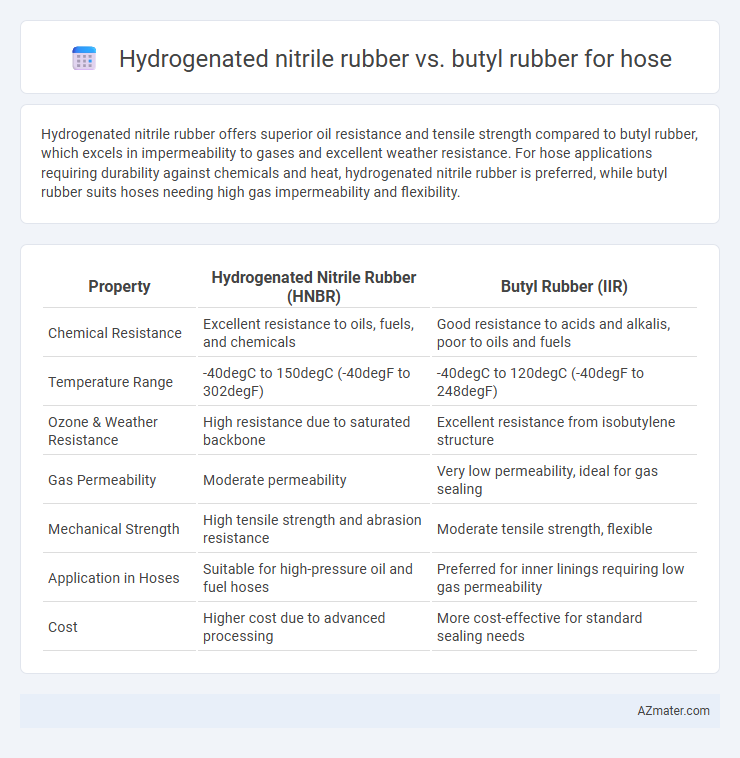
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber offers superior oil resistance and tensile strength compared to butyl rubber, which excels in impermeability to gases and excellent weather resistance. For hose applications requiring durability against chemicals and heat, hydrogenated nitrile rubber is preferred, while butyl rubber suits hoses needing high gas impermeability and flexibility.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) | Butyl Rubber (IIR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Good resistance to acids and alkalis, poor to oils and fuels |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC (-40degF to 302degF) | -40degC to 120degC (-40degF to 248degF) |
| Ozone & Weather Resistance | High resistance due to saturated backbone | Excellent resistance from isobutylene structure |
| Gas Permeability | Moderate permeability | Very low permeability, ideal for gas sealing |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and abrasion resistance | Moderate tensile strength, flexible |
| Application in Hoses | Suitable for high-pressure oil and fuel hoses | Preferred for inner linings requiring low gas permeability |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced processing | More cost-effective for standard sealing needs |
Introduction to Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber and Butyl Rubber
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its exceptional resistance to heat, oil, and chemical degradation, making it ideal for high-performance hose applications in automotive and industrial settings. Butyl rubber, composed of isobutylene with small amounts of isoprene, excels in impermeability to gases and outstanding flexibility at low temperatures, widely used in inner linings of hoses for air and gas transport. Both materials offer unique benefits: HNBR provides superior durability and chemical resistance, while butyl rubber delivers excellent air retention and flexibility under harsh conditions.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) features a saturated polymer backbone with nitrile groups providing exceptional resistance to oils, heat, and chemicals, while butyl rubber (IIR) consists of an isobutylene backbone with isoprene units, offering superior impermeability and flexibility. The hydrogenation process in HNBR reduces double bonds, enhancing stability and aging resistance compared to the more unsaturated butyl rubber structure prone to ozone and weathering degradation. HNBR's polar nitrile groups improve adhesion and chemical resistance, whereas butyl rubber's saturated hydrocarbon chains excel in gas retention and resilience under various mechanical stresses.
Key Physical Properties: HNBR vs Butyl Rubber
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior abrasion resistance, tensile strength, and heat resistance compared to butyl rubber, which excels in impermeability and flexibility at low temperatures. HNBR typically withstands temperatures up to 150degC, while butyl rubber performs well in extreme cold, maintaining elasticity below -40degC. Both materials provide excellent resistance to chemicals and ozone, but HNBR's enhanced durability makes it preferable for high-performance hose applications requiring longevity and thermal stability.
Resistance to Heat, Oils, and Chemicals
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, oils, and chemicals compared to butyl rubber, making it ideal for hoses exposed to high temperatures and aggressive petroleum-based fluids. HNBR maintains flexibility and durability in temperatures ranging from -40degC to 150degC, while butyl rubber typically withstands lower heat levels up to about 120degC. Chemically, HNBR exhibits excellent resistance to mineral oils, synthetic oils, and a wide range of chemicals, whereas butyl rubber performs better against oxygen, ozone, and weathering but has limited oil resistance.
Mechanical Performance in Hose Applications
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to butyl rubber, making it ideal for high-pressure hose applications requiring durability under mechanical stress. Butyl rubber exhibits excellent flexibility and impermeability, enhancing resistance to gas permeation and weathering but with lower mechanical strength than HNBR. In demanding hose environments like automotive and industrial sectors, HNBR's enhanced mechanical performance supports extended service life and resistance to heat and oil exposure.
Environmental and Weathering Resistance
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior environmental resistance, with exceptional resistance to ozone, weathering, and a wide range of chemicals, making it ideal for demanding hose applications in harsh climates. Butyl rubber offers excellent impermeability to gases and outstanding resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, but it typically falls short of HNBR's chemical resistance and mechanical strength under prolonged exposure. For hoses exposed to extreme weather and diverse chemical environments, HNBR provides enhanced durability and longer service life compared to butyl rubber.
Cost Efficiency and Manufacturing Considerations
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior oil resistance and high-temperature durability compared to butyl rubber, making it cost-efficient in applications requiring long service life despite its higher initial material cost. Butyl rubber excels in impermeability and flexibility, leading to lower manufacturing complexity and reduced processing time, which can decrease overall production expenses. Manufacturers must balance HNBR's enhanced performance benefits with butyl's ease of processing to optimize hose cost-efficiency for specific industrial uses.
Common Hose Applications for HNBR and Butyl Rubber
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) excels in automotive fuel and oil hoses due to its superior heat, oil, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for demanding environments. Butyl rubber is commonly used in air and water hoses, offering excellent impermeability and flexibility, especially for applications requiring resistance to gases and weathering. Both materials serve specialized roles in industrial and automotive industries, with HNBR favored for high-temperature durability and butyl for airtightness and weather resistance.
Limitations and Drawbacks: HNBR vs Butyl Rubber
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior heat and oil resistance but suffers from reduced flexibility at low temperatures and higher cost compared to butyl rubber. Butyl rubber offers excellent impermeability to gases and superior resistance to weathering and ozone, yet it performs poorly in oil and hydrocarbon environments and has lower tensile strength than HNBR. The selection between HNBR and butyl rubber for hose applications depends heavily on the operating temperature range and chemical exposure, with HNBR limited by cost and low-temperature brittleness, whereas butyl rubber's drawbacks include swelling and degradation in petroleum-based fluids.
Choosing the Right Material for Hose Durability
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, abrasion, and chemicals, making it ideal for high-performance hose applications exposed to harsh environments. Butyl rubber excels in impermeability and flexibility, providing excellent resistance to gas permeability and ozone, suitable for hoses requiring airtight seals and elasticity. Selecting the right hose material depends on operating temperature, chemical exposure, and pressure conditions to ensure optimal durability and service life.
Infographic: Hydrogenated nitrile rubber vs Butyl rubber for Hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com