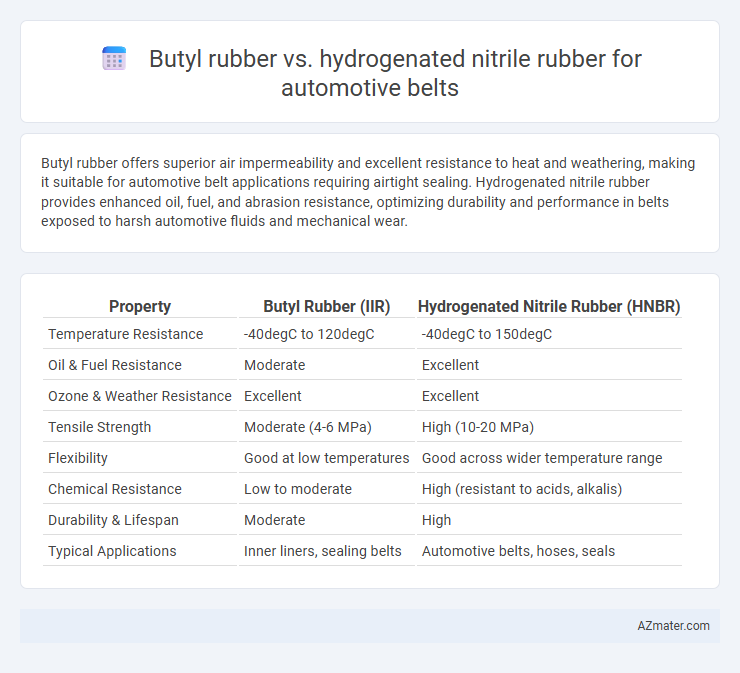
Butyl rubber offers superior air impermeability and excellent resistance to heat and weathering, making it suitable for automotive belt applications requiring airtight sealing. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber provides enhanced oil, fuel, and abrasion resistance, optimizing durability and performance in belts exposed to harsh automotive fluids and mechanical wear.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Butyl Rubber (IIR) | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | -40degC to 120degC | -40degC to 150degC |
| Oil & Fuel Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Ozone & Weather Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Tensile Strength | Moderate (4-6 MPa) | High (10-20 MPa) |
| Flexibility | Good at low temperatures | Good across wider temperature range |
| Chemical Resistance | Low to moderate | High (resistant to acids, alkalis) |
| Durability & Lifespan | Moderate | High |
| Typical Applications | Inner liners, sealing belts | Automotive belts, hoses, seals |
Introduction to Automotive Belt Materials
Butyl rubber offers excellent impermeability and flexibility, making it suitable for automotive belts requiring resistance to air and moisture. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior heat, oil, and abrasion resistance, enhancing belt durability in high-temperature engine environments. Automotive belt materials must balance elasticity, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength to ensure long-term performance under dynamic and harsh operating conditions.
Overview of Butyl Rubber (IIR)
Butyl Rubber (IIR) offers exceptional air impermeability and resistance to heat, making it ideal for automotive belt applications that require durability and flexibility. This synthetic rubber exhibits excellent resistance to aging, ozone, and weathering, ensuring long-term performance in demanding engine environments. Its low gas permeability and strong chemical resistance contribute to enhanced reliability and lifespan compared to other elastomers used in automotive belts.
Overview of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) is a high-performance elastomer known for its excellent resistance to heat, oil, and abrasion, making it ideal for automotive belt applications. Compared to butyl rubber, HNBR offers superior mechanical properties and enhanced durability under extreme temperatures and aggressive chemical exposure. Its hydrogenation process reduces unsaturation, resulting in improved aging resistance and long-term reliability in demanding automotive environments.
Key Properties Comparison: Butyl vs HNBR
Butyl rubber offers excellent impermeability to gases and superior resistance to heat aging, making it ideal for long-lasting automotive belts exposed to high temperatures. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides enhanced tensile strength, oil resistance, and resistance to abrasion, which is crucial for belts operating in harsh engine environments. The choice between butyl and HNBR hinges on specific requirements: butyl excels in sealing and chemical resistance, while HNBR delivers higher mechanical durability and resistance to hydrocarbons.
Resistance to Heat and Oxidation
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat and oxidation compared to butyl rubber, making it ideal for automotive belt applications exposed to high temperatures and aggressive environmental conditions. HNBR maintains mechanical strength and elasticity at continuous temperatures up to 150degC, while butyl rubber typically degrades faster under similar thermal stress. Enhanced oxidative stability in HNBR ensures longer service life and reduces maintenance frequency in demanding engine environments.
Chemical and Oil Resistance Performance
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical and oil resistance compared to butyl rubber, making it more suitable for automotive belt applications exposed to aggressive fluids and harsh operating conditions. HNBR's enhanced saturation level provides exceptional resistance to hydrocarbons, oils, and heat, maintaining elasticity and durability over prolonged use. Butyl rubber, while resistant to weathering and ozone, generally exhibits lower resistance to petroleum-based oils and higher temperatures, limiting its effectiveness in demanding automotive environments.
Durability and Longevity in Automotive Applications
Butyl rubber offers excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it durable for automotive belt applications exposed to harsh conditions. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, enhancing longevity under high stress and oil exposure typical in engine environments. HNBR's enhanced abrasion resistance and resilience to dynamic flexing result in longer service life compared to butyl rubber in demanding automotive belt conditions.
Cost-Efficiency and Manufacturing Considerations
Butyl rubber offers excellent air impermeability and heat resistance but typically incurs higher raw material and processing costs compared to hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR). HNBR provides superior abrasion resistance, chemical stability, and durability, leading to longer belt life, which can reduce replacement frequency and overall lifecycle costs in automotive applications. Manufacturing considerations favor HNBR for high-performance requirements despite its higher initial investment, while butyl rubber remains cost-efficient for standard, less demanding belt functions.
Typical Automotive Belt Applications for Each Material
Butyl rubber is commonly used in automotive belts requiring excellent impermeability and resistance to heat and chemicals, making it ideal for timing belts and auxiliary drive belts exposed to harsh engine environments. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior abrasion resistance, high tensile strength, and excellent performance in oil and fuel exposure, which suits it well for serpentine belts and other high-stress automotive applications. Both materials are selected based on specific operational demands, with Butyl rubber favored for durability in sealed systems and HNBR for dynamic mechanical performance under high thermal and chemical stress.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Automotive Belts
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, oil, and abrasion, making it ideal for automotive belts exposed to harsh engine environments. Butyl rubber, while excellent for air impermeability and flexibility at low temperatures, lacks the durability and chemical resistance required for long-term automotive belt performance. Selecting HNBR ensures enhanced longevity and reliability in automotive belts subjected to high temperatures and mechanical stress.
Infographic: Butyl rubber vs Hydrogenated nitrile rubber for Automotive belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com