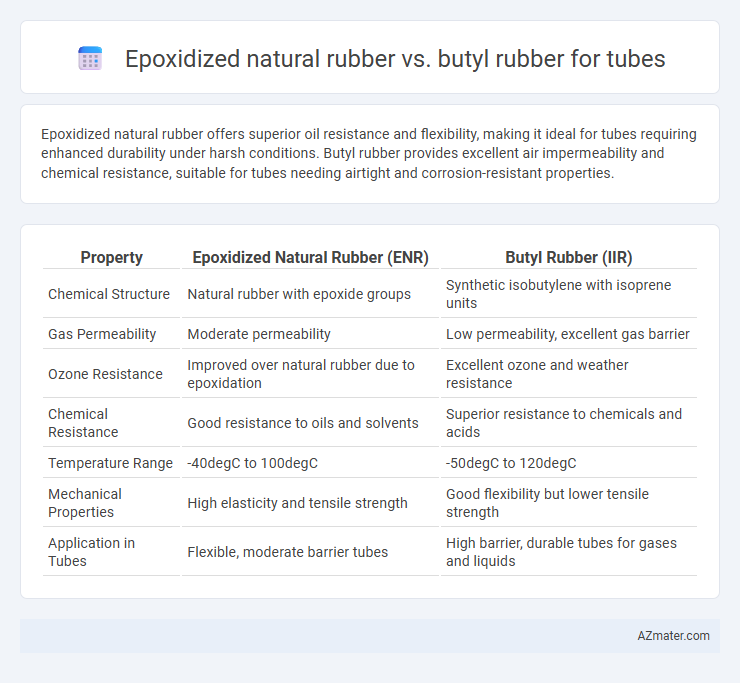
Epoxidized natural rubber offers superior oil resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for tubes requiring enhanced durability under harsh conditions. Butyl rubber provides excellent air impermeability and chemical resistance, suitable for tubes needing airtight and corrosion-resistant properties.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) | Butyl Rubber (IIR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Natural rubber with epoxide groups | Synthetic isobutylene with isoprene units |
| Gas Permeability | Moderate permeability | Low permeability, excellent gas barrier |
| Ozone Resistance | Improved over natural rubber due to epoxidation | Excellent ozone and weather resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and solvents | Superior resistance to chemicals and acids |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 100degC | -50degC to 120degC |
| Mechanical Properties | High elasticity and tensile strength | Good flexibility but lower tensile strength |
| Application in Tubes | Flexible, moderate barrier tubes | High barrier, durable tubes for gases and liquids |
Introduction to Tube Materials: Epoxidized Natural Rubber vs Butyl Rubber
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced oil resistance, improved tensile strength, and greater elasticity compared to traditional natural rubber, making it suitable for flexible tubing applications requiring durability and chemical stability. Butyl rubber, known for its excellent air impermeability, resistance to heat, and outstanding chemical inertness, is ideal for tubes used in harsh environments or requiring superior gas retention. Selection between ENR and butyl rubber for tubing depends on application-specific demands such as flexibility, chemical exposure, and environmental resistance.
Chemical Structure and Composition Differences
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) contains epoxide groups incorporated into the polyisoprene backbone, enhancing polarity and improving oil and gas resistance compared to natural rubber. Butyl rubber, a copolymer of isobutylene with a small amount of isoprene, features a saturated hydrocarbon backbone with minimal unsaturation, providing exceptional impermeability and chemical inertness. The chemical structure of ENR offers increased reactivity and compatibility with polar solvents, whereas butyl rubber's composition delivers superior airtightness and resistance to weathering and chemicals in tube applications.
Air Retention Properties in Tubes
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits superior air retention properties compared to butyl rubber in tube applications due to its enhanced gas barrier characteristics derived from the epoxide groups, which reduce permeability to oxygen and nitrogen. Butyl rubber, while traditionally known for excellent air impermeability, often shows higher gas permeability under prolonged stress and temperature variations than ENR. The improved air retention of ENR tubes results in longer inflation periods and reduced maintenance needs in pneumatic systems.
Resistance to Heat and Oxidation
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits superior resistance to heat and oxidative degradation compared to butyl rubber due to the presence of epoxy groups that enhance its thermal stability and inhibit free radical formation. Butyl rubber, while highly impermeable and resistant to air and chemicals, tends to have lower heat resistance and degrades faster under prolonged exposure to high temperatures and oxidative environments. This makes ENR a preferred material for applications requiring enhanced durability against thermal and oxidative stress in tube manufacturing.
Flexibility and Elasticity Comparison
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior flexibility and elasticity compared to butyl rubber in tube applications, making it ideal for scenarios requiring high resilience and dynamic deformation. The presence of epoxy groups in ENR enhances its tensile strength and elongation at break, contributing to better elastic recovery and durability under cyclic loading. Butyl rubber, while providing excellent air impermeability and chemical resistance, exhibits limited flexibility and lower elasticity, which can restrict its performance in highly flexible tubing needs.
Durability and Aging Performance
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits superior aging resistance due to its enhanced oxidative stability and resistance to ozone cracking, making it highly durable for tube applications. Butyl rubber offers excellent impermeability and chemical resistance, contributing to its long-lasting performance, especially in harsh environments. However, ENR's improved thermal stability and elasticity provide better durability under cyclic stress compared to butyl rubber, which tends to stiffen over time.
Compatibility with Various Tyre Types
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits excellent compatibility with various tire types, enhancing adhesion and wet grip performance, particularly in passenger car and truck tires. Butyl rubber offers superior air retention and chemical resistance, making it ideal for inner tubes in tires requiring long-lasting inflation, such as bicycle and motorcycle tires. Choosing between ENR and butyl rubber depends on the specific tire application, balancing the need for elasticity and wet traction against air impermeability and durability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) demonstrates superior environmental benefits compared to butyl rubber due to its renewable origin from natural latex and enhanced biodegradability, which reduce long-term environmental impact. Butyl rubber, predominantly derived from petrochemical sources, exhibits lower sustainability because of non-renewable feedstocks and longer degradation periods in landfills. Lifecycle assessments highlight ENR's reduced carbon footprint and potential for eco-friendly applications in tubing, promoting sustainable manufacturing practices.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Epoxidized natural rubber offers a balance of enhanced chemical resistance and flexibility but generally incurs higher costs due to complex processing and lower large-scale production volumes. Butyl rubber, widely available and produced in bulk, is more cost-effective for tube manufacturing, benefiting from established supply chains and stable raw material pricing. Cost considerations favor butyl rubber for budget-sensitive applications, while epoxidized natural rubber commands premiums in specialized, performance-driven uses.
Choosing the Right Tube Material: Application Guidelines
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers excellent flexibility, chemical resistance, and enhanced gas barrier properties, making it ideal for fluid transport and medical tubing applications. Butyl rubber excels in impermeability to gases and superior resistance to ozone and weathering, suited for air or gas tubes requiring long-term durability. Selecting between ENR and butyl rubber depends on specific application needs, such as chemical exposure, gas permeability, and environmental conditions to optimize tube performance and lifespan.
Infographic: Epoxidized natural rubber vs Butyl rubber for Tube
 azmater.com
azmater.com