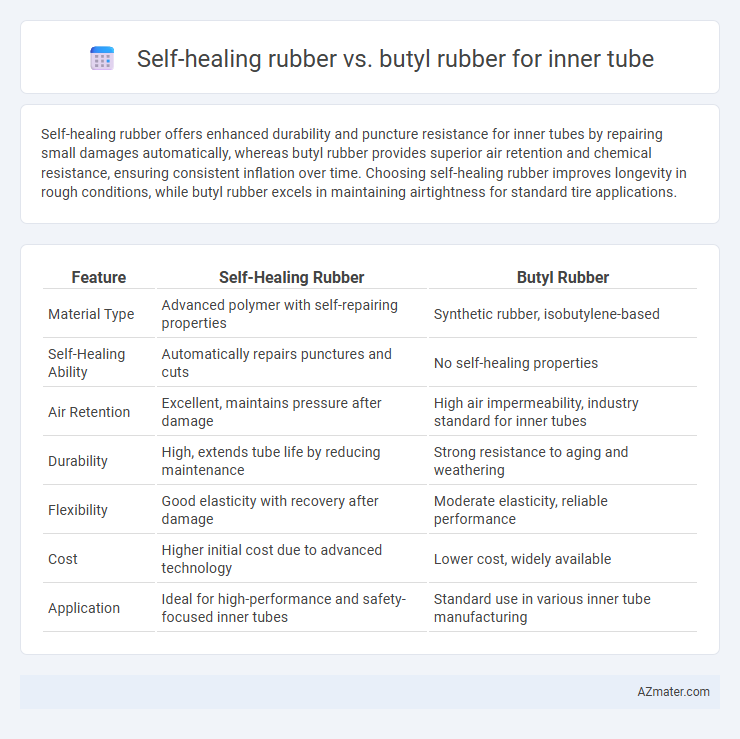
Self-healing rubber offers enhanced durability and puncture resistance for inner tubes by repairing small damages automatically, whereas butyl rubber provides superior air retention and chemical resistance, ensuring consistent inflation over time. Choosing self-healing rubber improves longevity in rough conditions, while butyl rubber excels in maintaining airtightness for standard tire applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Self-Healing Rubber | Butyl Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Advanced polymer with self-repairing properties | Synthetic rubber, isobutylene-based |
| Self-Healing Ability | Automatically repairs punctures and cuts | No self-healing properties |
| Air Retention | Excellent, maintains pressure after damage | High air impermeability, industry standard for inner tubes |
| Durability | High, extends tube life by reducing maintenance | Strong resistance to aging and weathering |
| Flexibility | Good elasticity with recovery after damage | Moderate elasticity, reliable performance |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to advanced technology | Lower cost, widely available |
| Application | Ideal for high-performance and safety-focused inner tubes | Standard use in various inner tube manufacturing |
Introduction to Inner Tube Materials
Inner tubes commonly use butyl rubber due to its excellent air retention and durability under pressure, making it the industry standard for bicycles and automotive tires. Self-healing rubber, embedded with microcapsules containing healing agents, offers innovative repair capabilities by autonomously sealing punctures without losing structural integrity. This advancement in inner tube materials enhances longevity and reduces maintenance, potentially surpassing the conventional performance of butyl rubber in resilience and usability.
What is Self-Healing Rubber?
Self-healing rubber is an advanced material designed to automatically repair small punctures or cuts, enhancing durability and extending the lifespan of inner tubes. Unlike traditional butyl rubber, which relies on airtight properties but cannot self-repair, self-healing rubber incorporates microcapsules or reversible chemical bonds that activate upon damage. This innovation significantly reduces maintenance needs and improves performance in applications such as bicycle and motorcycle inner tubes.
Overview of Butyl Rubber Properties
Butyl rubber, a synthetic elastomer composed mainly of isobutylene with a small amount of isoprene, is known for its exceptional air impermeability and excellent resistance to ozone, weathering, and heat, making it an ideal material for inner tubes. Its low gas permeability ensures prolonged air retention, which enhances tire performance and durability compared to self-healing rubber alternatives that have intrinsic puncture repair capabilities but typically higher permeability. The superior chemical resistance and flexibility of butyl rubber contribute to its widespread use in automotive inner tubes, balancing longevity and reliability under diverse driving conditions.
Air Retention: Self-Healing vs Butyl Rubber
Self-healing rubber demonstrates superior air retention in inner tubes due to its ability to automatically seal punctures, reducing the likelihood of prolonged air loss. Butyl rubber, while traditionally favored for its excellent impermeability to gases, lacks the inherent puncture-sealing properties, leading to slower but consistent air leakage over time. Advances in self-healing polymers enable inner tubes to maintain optimal pressure longer, enhancing performance and reducing maintenance compared to standard butyl alternatives.
Puncture Resistance and Repair Capabilities
Self-healing rubber inner tubes offer superior puncture resistance by autonomously sealing small holes through embedded microcapsules containing healing agents, significantly reducing the need for manual repairs. Butyl rubber inner tubes, known for their excellent airtightness and chemical stability, provide robust puncture resistance but require external patching or replacement after damage. The self-healing capability enhances durability and longevity, making self-healing rubber a more efficient choice for minimizing downtime caused by punctures compared to traditional butyl rubber inner tubes.
Durability and Longevity Comparisons
Self-healing rubber exhibits enhanced durability by automatically repairing punctures, significantly extending the lifespan of inner tubes compared to traditional butyl rubber. Butyl rubber offers excellent air retention and resistance to environmental degradation but lacks the autonomous repair capacity, leading to potential failures over time. The integration of self-healing polymers substantially improves inner tube longevity by minimizing maintenance and reducing the frequency of replacements.
Weight and Performance Impacts
Self-healing rubber offers notable advantages in weight reduction compared to traditional butyl rubber, improving overall bicycle inner tube efficiency by decreasing rotational mass. Performance-wise, self-healing compounds enhance puncture resistance and durability through their inherent ability to automatically seal small punctures, resulting in fewer flats and longer tube lifespan. Butyl rubber remains favored for its excellent air retention and lower material cost, although it is generally heavier and less adaptive to damage recovery than emerging self-healing technologies.
Cost Considerations and Market Availability
Self-healing rubber offers advanced longevity and reduced maintenance costs for inner tubes, but its higher production expenses limit widespread market availability compared to butyl rubber. Butyl rubber remains the industry standard due to its low manufacturing costs and extensive distribution network, making it more accessible for mass-market applications. Cost-effective scalability and established supply chains give butyl rubber a dominant position despite the innovative benefits of self-healing alternatives.
Environmental Sustainability and Recycling
Self-healing rubber incorporates microcapsules that repair punctures autonomously, reducing waste and extending inner tube lifespan, thereby enhancing environmental sustainability. Butyl rubber, known for its excellent impermeability and durability, is traditionally favored but poses challenges in recycling due to complex vulcanization processes. Advances in self-healing rubber technology offer promising improvements in recyclability and reduced environmental impact compared to conventional butyl rubber inner tubes.
Choosing the Best Inner Tube for Your Needs
Self-healing rubber offers advanced puncture resistance by automatically sealing small holes, making it ideal for riders seeking minimal maintenance and enhanced durability in inner tubes. Butyl rubber, known for its excellent air retention and affordability, provides reliable performance and is widely preferred for traditional inner tubes. Selecting between self-healing and butyl rubber depends on whether puncture prevention or cost-effectiveness and airtightness are your primary concerns.
Infographic: Self-healing rubber vs Butyl rubber for Inner tube
 azmater.com
azmater.com