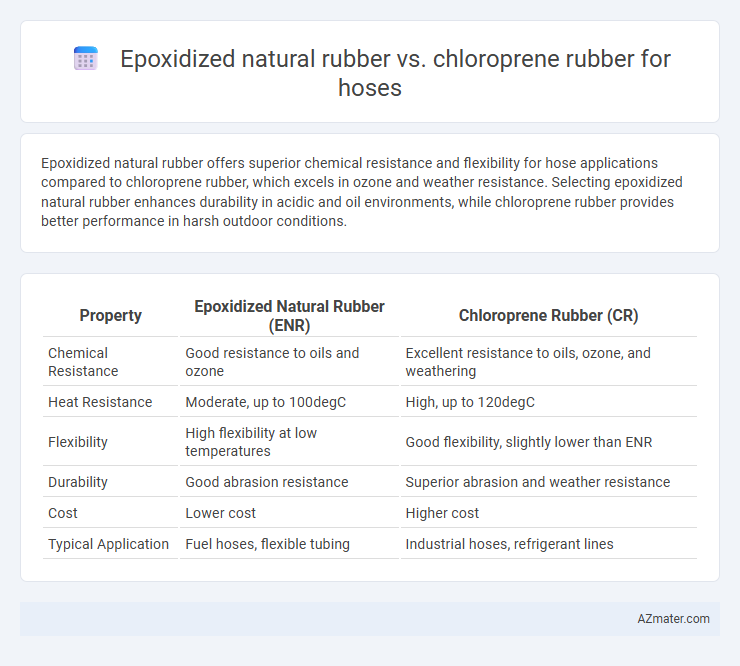
Epoxidized natural rubber offers superior chemical resistance and flexibility for hose applications compared to chloroprene rubber, which excels in ozone and weather resistance. Selecting epoxidized natural rubber enhances durability in acidic and oil environments, while chloroprene rubber provides better performance in harsh outdoor conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) | Chloroprene Rubber (CR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and ozone | Excellent resistance to oils, ozone, and weathering |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate, up to 100degC | High, up to 120degC |
| Flexibility | High flexibility at low temperatures | Good flexibility, slightly lower than ENR |
| Durability | Good abrasion resistance | Superior abrasion and weather resistance |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Typical Application | Fuel hoses, flexible tubing | Industrial hoses, refrigerant lines |
Overview of Epoxidized Natural Rubber and Chloroprene Rubber
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) is a chemically modified variant of natural rubber with enhanced oil, heat, and ozone resistance, making it ideal for hose applications requiring flexibility and durability in harsh environments. Chloroprene rubber (CR), commonly known as neoprene, offers excellent resistance to weather, chemicals, and moderate heat, providing robust performance for hoses exposed to aggressive conditions and varying temperatures. Both materials serve critical roles in industrial hose manufacturing, with ENR excelling in elasticity and environmental resistance, while CR is preferred for its balanced chemical and mechanical properties.
Key Chemical Structures and Properties
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) contains oxirane groups introduced into the polyisoprene backbone, enhancing polarity and improving oil resistance and adhesion compared to natural rubber. Chloroprene rubber (CR) features chlorine atoms in its polychloroprene polymer chain, providing excellent chemical stability, ozone resistance, and flame retardancy. ENR excels in flexibility and resilience under dynamic stress, while CR offers superior weathering resistance and durability, making the choice dependent on specific hose application requirements.
Mechanical Performance Comparison
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to chloroprene rubber, making it more suitable for high-stress hose applications. Chloroprene rubber provides excellent weathering and ozone resistance but has comparatively lower elasticity and mechanical durability under repeated flexing. ENR's enhanced mechanical performance arises from its modified molecular structure, improving elasticity, tear resistance, and resilience essential for durable hose manufacturing.
Resistance to Oils and Chemicals
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior resistance to oils and chemicals compared to chloroprene rubber, making it ideal for hoses exposed to petroleum-based fluids and aggressive chemicals. ENR's enhanced polarity improves its compatibility with a wide range of oils, acids, and alkalis, reducing swelling and degradation during prolonged chemical exposure. Chloroprene rubber provides moderate chemical resistance but can deteriorate faster in harsh oil environments, limiting its performance in demanding industrial hose applications.
Aging and Weatherability Assessment
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits superior aging resistance and enhanced weatherability compared to chloroprene rubber, thanks to its improved oxidation stability and reduced susceptibility to ozone cracking. In hose applications, ENR maintains mechanical integrity and flexibility over prolonged exposure to heat, UV radiation, and environmental pollutants, while chloroprene rubber tends to harden and crack under similar conditions. The enhanced durability of ENR-rich compounds results in longer service life and reduced maintenance requirements for hoses used in outdoor and harsh environments.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers improved oil and heat resistance compared to chloroprene rubber (CR), but typically comes at a higher raw material cost, influencing overall hose production expenses. Chloroprene rubber provides a more cost-effective solution with balanced performance and durability, often making it the preferred choice for large-scale manufacturing where budget constraints are critical. Considering lifecycle costs, ENR hoses may yield longer service life in specialized applications, potentially offsetting initial cost differences in economic evaluations.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior biodegradability and reduced reliance on petrochemicals compared to chloroprene rubber, making it a more sustainable option for hoses. ENR's production involves renewable resources and generates fewer toxic emissions, contributing to lower environmental impact. In contrast, chloroprene rubber's synthesis relies heavily on non-renewable fossil fuels and releases hazardous chemicals, posing greater challenges for waste management and environmental safety.
Processability in Hose Manufacturing
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior processability in hose manufacturing due to its enhanced compatibility with various fillers and improved curing characteristics, leading to better dispersion and uniform vulcanization. Chloroprene rubber (CR) provides excellent chemical resistance and weathering stability but often requires more complex compounding and slower curing times, which can hinder efficient hose production. ENR's ability to blend well with other polymers and fillers facilitates faster extrusion and molding processes, optimizing manufacturing speed and product consistency.
Common Applications in Hose Industry
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) is widely used in hoses requiring enhanced oil resistance, flexibility, and heat tolerance, making it ideal for fuel and hydraulic hoses in automotive and industrial applications. Chloroprene rubber (CR) excels in chemical resistance, weather resistance, and abrasion resistance, commonly utilized in industrial hoses exposed to harsh environments, such as chemical transfer, air and water hoses, and refrigeration systems. Both materials offer unique benefits, with ENR favored for improved mechanical properties and CR preferred for its all-weather durability and chemical stability.
Final Selection Guidelines for Hose Material
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior oil resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for hoses in fuel transfer and chemical applications, while chloroprene rubber (CR) excels in ozone, weather, and heat resistance, suited for outdoor and industrial environments. Selection guidelines emphasize ENR when hydrocarbon resistance and elasticity are prioritized and CR when durability against harsh weather, aging, and moderate chemical exposure is essential. Evaluating operating temperature range, chemical compatibility, abrasion resistance, and environmental exposure ensures optimal hose material choice between ENR and CR.
Infographic: Epoxidized natural rubber vs Chloroprene rubber for Hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com