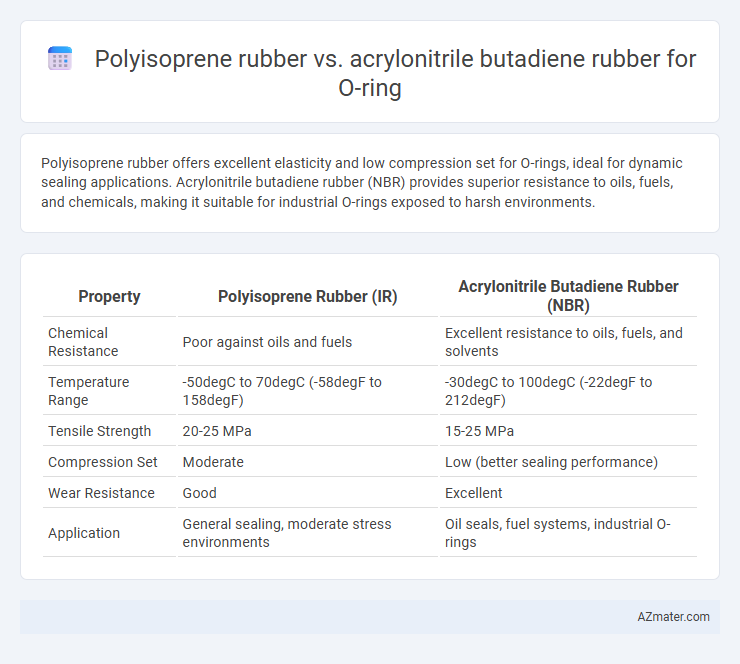
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent elasticity and low compression set for O-rings, ideal for dynamic sealing applications. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) provides superior resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, making it suitable for industrial O-rings exposed to harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyisoprene Rubber (IR) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Poor against oils and fuels | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 70degC (-58degF to 158degF) | -30degC to 100degC (-22degF to 212degF) |
| Tensile Strength | 20-25 MPa | 15-25 MPa |
| Compression Set | Moderate | Low (better sealing performance) |
| Wear Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Application | General sealing, moderate stress environments | Oil seals, fuel systems, industrial O-rings |
Introduction to O-Ring Materials
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent elasticity and resilience, closely mimicking natural rubber, making it suitable for O-rings requiring high flexibility and compression set resistance. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (Nitrile or NBR) excels in oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, providing superior durability in automotive and industrial sealing applications. Selecting between polyisoprene and NBR depends on the O-ring's operating environment, temperature range, and exposure to chemicals or oils.
Overview of Polyisoprene Rubber (IR)
Polyisoprene rubber (IR), a synthetic version of natural rubber, offers excellent elasticity, tensile strength, and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for dynamic O-ring applications. IR exhibits superior flexibility and low compression set, enhancing seal longevity in low to moderate temperature environments ranging from -50degC to 70degC. While its chemical resistance is limited, especially against oils and fuels compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), IR remains preferred for O-rings requiring outstanding resilience and mechanical performance.
Overview of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) is a synthetic elastomer widely used for O-rings due to its excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, making it ideal for automotive and industrial applications. NBR offers superior mechanical strength and abrasion resistance compared to Polyisoprene rubber, with a typical acrylonitrile content of 18-50%, which enhances its oil resistance but may reduce flexibility at low temperatures. The material's versatility in temperature ranges from -40degC to 108degC ensures durability in dynamic sealing environments where hydrocarbon exposure is frequent.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Polyisoprene rubber offers good resistance to water, alcohols, and mild acids but shows poor resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents, limiting its use in harsh chemical environments. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) excels in resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and alkalis, making it highly suitable for O-rings in automotive and industrial applications requiring fuel and oil exposure. The chemical resistance of NBR surpasses polyisoprene in hydrocarbon applications, while polyisoprene provides better performance in non-petroleum environments.
Temperature Performance Analysis
Polyisoprene rubber exhibits excellent flexibility and resilience at lower temperatures, maintaining performance typically down to -50degC, making it suitable for applications requiring elasticity in cold environments. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) offers superior temperature resistance, functioning effectively in a wider range from -40degC to 120degC, and demonstrates strong resistance to heat aging and oil exposure. Comparing thermal stability, NBR is preferred for high-temperature O-ring applications, while polyisoprene is favored for low-temperature flexibility and resilience.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Polyisoprene rubber exhibits excellent tensile strength and flexibility with a high resistance to abrasion, making it suitable for O-rings requiring elasticity and comfort under cyclic loading. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) offers superior oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, combined with good mechanical strength, which enhances durability in harsh industrial environments. While polyisoprene has moderate chemical resistance, NBR's superior resistance to hydrocarbons ensures longer service life in applications involving petroleum-based fluids.
Sealing Performance in Various Applications
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent resilience, low compression set, and superior sealing performance in low-temperature and general-purpose O-ring applications, making it ideal for dynamic seals in automotive and medical industries. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (Nitrile or NBR) provides outstanding resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, ensuring reliable sealing performance under harsh chemical exposure and high-temperature conditions commonly encountered in fuel systems and hydraulic equipment. Selecting between Polyisoprene and NBR for O-ring applications depends on the operational environment's temperature range, chemical compatibility, and mechanical stress requirements.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Polyisoprene rubber typically offers lower cost and higher availability compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber (Nitrile) for O-ring manufacturing, making it a budget-friendly choice for general sealing applications. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber, while more expensive, provides enhanced resistance to oils and chemicals which justifies its higher price in specialized uses. Availability of polyisoprene is widespread due to its natural rubber origins, whereas acrylonitrile butadiene rubber may have variable supply depending on synthetic polymer production facilities.
Industry-Specific Recommendations
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent elasticity and tear resistance, making it ideal for O-rings in automotive fuel systems and medical devices where flexibility and biocompatibility are critical. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) excels in oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, recommended for industrial machinery, aerospace, and hydraulic equipment exposed to aggressive fluids. Industry experts prefer polyisoprene for applications demanding natural rubber's resilience, while NBR is favored in environments requiring superior chemical durability and temperature resistance.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Rubber for O-Rings
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent elasticity and low compression set, making it ideal for dynamic O-ring applications in low to moderate temperature ranges. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) excels in oil and chemical resistance, with superior performance in environments exposed to fuels, lubricants, and hydraulic fluids. Selecting the right rubber depends on the specific operational conditions: choose Polyisoprene for flexibility and resilience, and NBR for enhanced chemical and oil resistance in O-ring seals.
Infographic: Polyisoprene rubber vs Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber for O-ring
 azmater.com
azmater.com