Biobased rubber, derived from renewable natural sources like guayule or dandelion, offers superior biodegradability and a lower carbon footprint compared to synthetic rubber, which is petroleum-based and less eco-friendly. Shoe soles made from biobased rubber provide enhanced sustainability while maintaining comparable durability and flexibility to synthetic alternatives.
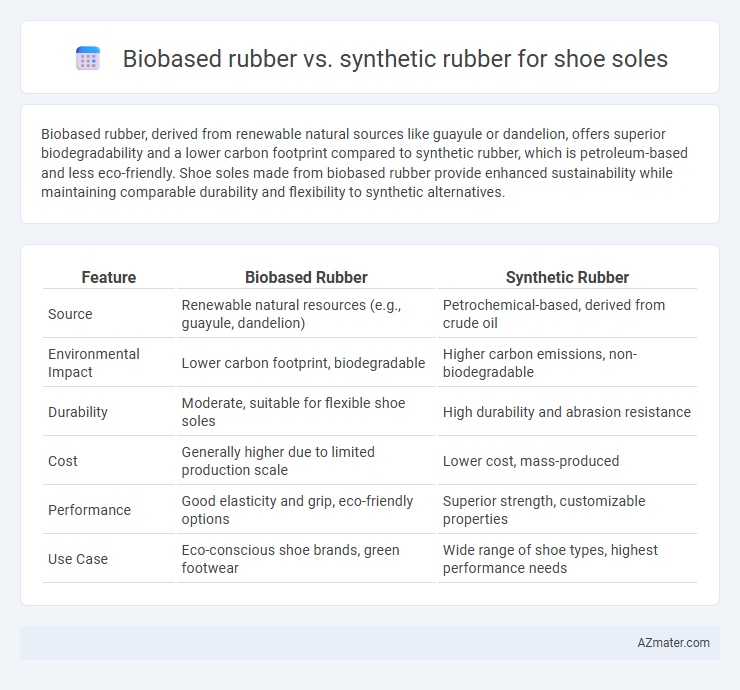
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biobased Rubber | Synthetic Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Renewable natural resources (e.g., guayule, dandelion) | Petrochemical-based, derived from crude oil |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, biodegradable | Higher carbon emissions, non-biodegradable |
| Durability | Moderate, suitable for flexible shoe soles | High durability and abrasion resistance |
| Cost | Generally higher due to limited production scale | Lower cost, mass-produced |
| Performance | Good elasticity and grip, eco-friendly options | Superior strength, customizable properties |
| Use Case | Eco-conscious shoe brands, green footwear | Wide range of shoe types, highest performance needs |
Introduction to Biobased and Synthetic Rubber
Biobased rubber, derived from natural sources such as rubber trees and plants, offers renewable and sustainable alternatives for shoe sole manufacturing, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Synthetic rubber, produced through chemical polymerization of petroleum-based monomers like styrene and butadiene, provides consistent quality and enhanced durability for diverse footwear applications. Understanding the material properties and environmental impact of both biobased and synthetic rubber is essential for optimizing performance and sustainability in shoe sole production.
Material Sources and Sustainability
Biobased rubber for shoe soles is derived from renewable plant sources like natural rubber trees (Hevea brasiliensis), making it a sustainable alternative to synthetic rubber, which is produced from petroleum-based polymers. The renewable nature of biobased rubber reduces carbon footprint and dependence on fossil fuels, contributing to environmental conservation and circular economy principles. Synthetic rubber offers consistent performance but poses sustainability challenges due to resource depletion and limited biodegradability.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Biobased rubber for shoe soles significantly reduces carbon footprint by utilizing renewable natural resources like guayule or dandelion-derived latex, lowering greenhouse gas emissions compared to synthetic rubber derived from petroleum. Biobased rubber enhances biodegradability and reduces microplastic pollution in footwear waste, addressing end-of-life environmental concerns more effectively than non-biodegradable synthetic alternatives. Life cycle assessments demonstrate that biobased rubber production consumes less non-renewable energy and generates fewer toxic byproducts, making it a more sustainable choice for environmentally conscious shoe manufacturing.
Physical Properties and Performance
Biobased rubber used in shoe soles offers high tensile strength and excellent elasticity, making it comparable to synthetic rubber in flexibility and durability. Synthetic rubber typically exhibits superior abrasion resistance and better performance under extreme temperature variations, ensuring longer-lasting shoe soles. Both materials provide effective cushioning, but biobased rubber excels in environmental sustainability without significantly compromising physical performance.
Durability and Longevity in Shoe Soles
Biobased rubber, derived from natural sources like guayule or dandelion, offers eco-friendly properties but generally exhibits lower durability and accelerated wear compared to synthetic rubber when used in shoe soles. Synthetic rubber, composed of petrochemical polymers like styrene-butadiene, provides superior abrasion resistance and longer lifespan, making it more suitable for high-performance footwear. Advances in blending biobased and synthetic materials aim to enhance the longevity of sustainable shoe soles without compromising durability.
Comfort and Wearability
Biobased rubber for shoe soles offers enhanced breathability and flexibility, contributing to superior comfort during extended wear. Synthetic rubber provides greater durability and resistance to abrasion, ensuring longer-lasting performance under various conditions. The balance between biobased rubber's natural cushioning and synthetic rubber's strength optimizes wearability and support for diverse footwear applications.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Biobased rubber for shoe soles offers a sustainable alternative but often comes with higher raw material costs due to limited production scale and specialized extraction processes. Synthetic rubber benefits from established large-scale manufacturing techniques, resulting in lower per-unit costs and more consistent quality. Manufacturing synthetic soles allows for greater design flexibility and faster production cycles, while biobased rubber requires adaptation of existing machinery to handle its unique physical properties.
Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
The global market reveals a growing preference for biobased rubber in shoe soles due to sustainability concerns and increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly products, driving innovation and investment in renewable materials. Synthetic rubber remains dominant for its durability and cost-effectiveness, but shifting regulations and consumer awareness are expanding the biobased segment at a CAGR of over 8%. Brands leveraging biobased rubber emphasize biodegradability and reduced carbon footprints, aligning with evolving market trends towards environmental responsibility and ethical manufacturing.
Challenges in Adoption of Biobased Rubber
Biobased rubber for shoe soles faces significant challenges including higher production costs and variability in material properties compared to synthetic rubber, which is consistently engineered for performance and durability. Supply chain limitations and scalability issues hinder widespread adoption, as biobased rubber relies on agricultural feedstocks subject to seasonal and geographic constraints. Furthermore, compatibility with existing manufacturing processes and long-term wear resistance remain critical obstacles that manufacturers must overcome to replace synthetic rubber in footwear applications effectively.
Future Outlook for Sustainable Shoe Soles
Biobased rubber, derived from natural sources such as guayule and dandelion plants, offers a renewable and biodegradable alternative to traditional synthetic rubber made from petroleum-based polymers. Advances in biopolymer technology and eco-friendly processing methods are expected to enhance the durability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness of biobased rubber shoe soles, making them more competitive in the global footwear market. Increasing consumer demand for sustainable products and stricter environmental regulations are driving brands to invest in biobased rubber innovations, positioning it as a key component in the future of eco-conscious shoe sole manufacturing.
Infographic: Biobased rubber vs Synthetic rubber for Shoe sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com