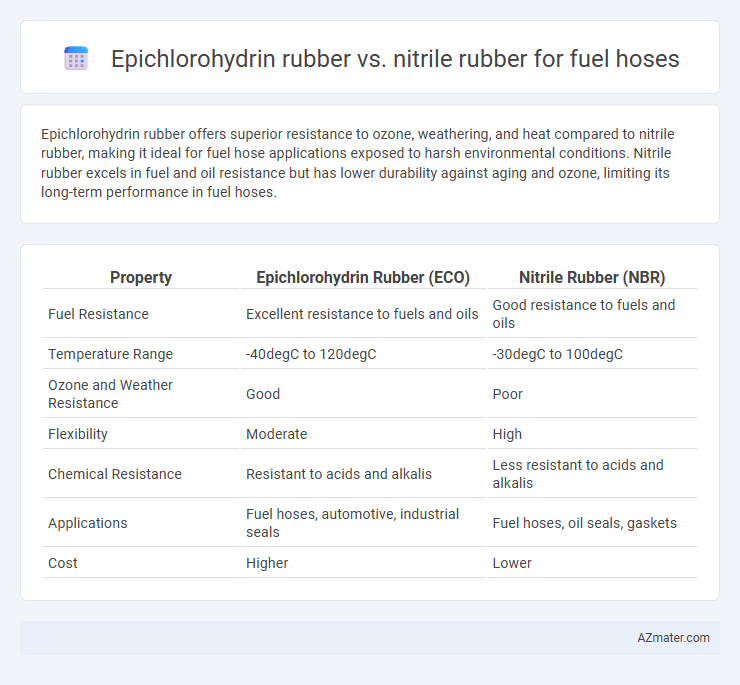
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior resistance to ozone, weathering, and heat compared to nitrile rubber, making it ideal for fuel hose applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Nitrile rubber excels in fuel and oil resistance but has lower durability against aging and ozone, limiting its long-term performance in fuel hoses.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Resistance | Excellent resistance to fuels and oils | Good resistance to fuels and oils |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -30degC to 100degC |
| Ozone and Weather Resistance | Good | Poor |
| Flexibility | Moderate | High |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to acids and alkalis | Less resistant to acids and alkalis |
| Applications | Fuel hoses, automotive, industrial seals | Fuel hoses, oil seals, gaskets |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Epichlorohydrin and Nitrile Rubber
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) exhibits excellent resistance to ozone, heat, and oil, making it highly suitable for fuel hose applications where durability and chemical resistance are critical. Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers superior resistance to petroleum-based fuels and oils but has limited ozone and weather resistance compared to epichlorohydrin. Both elastomers serve as primary materials for fuel hoses, with epichlorohydrin favored for harsh environmental exposure and nitrile preferred for cost-effective fuel compatibility.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) features a polymer backbone derived from epichlorohydrin monomers, characterized by molecular chains containing chlorine atoms that provide excellent resistance to oil, fuels, and ozone. Nitrile rubber (NBR) consists of copolymers of acrylonitrile and butadiene, with polar nitrile groups responsible for its strong resistance to hydrocarbons and fuel absorption. The chlorine content in Epichlorohydrin imparts superior ozone and weather resistance, while the nitrile groups in NBR enhance compatibility with a wider range of fuel types, influencing their respective performance in fuel hose applications.
Fuel Resistance Properties
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior resistance to a wide range of fuels and oils, especially in environments containing alcohol-blended fuels, making it highly suitable for fuel hose applications requiring enhanced fuel resistance. Nitrile rubber offers excellent resistance to hydrocarbons, including gasoline and diesel, but tends to degrade more rapidly when exposed to oxygenated fuels such as ethanol blends. Selecting Epichlorohydrin rubber for fuel hoses ensures longer service life and reduced permeability in modern fuel systems with diverse fuel compositions.
Temperature Performance in Fuel Hose Applications
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior resistance to low temperatures, maintaining flexibility down to -40degC, which is critical for fuel hose applications in cold climates. Nitrile rubber typically performs well at moderate temperatures but becomes brittle below -25degC, limiting its use in extreme cold environments. For high-temperature fuel hose applications, nitrile rubber withstands continuous heat up to 120degC, whereas epichlorohydrin rubber operates effectively up to around 135degC, providing enhanced thermal stability.
Ozone and Weathering Resistance
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior ozone and weathering resistance compared to nitrile rubber, making it more suitable for fuel hoses exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Its molecular structure provides enhanced protection against degradation caused by ozone, UV light, and ozone-induced cracking. Nitrile rubber, while excellent in oil and fuel resistance, tends to degrade faster when subjected to prolonged outdoor exposure and ozone, limiting its durability in fuel hose applications requiring extended weathering performance.
Flexibility and Mechanical Strength
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior flexibility and excellent resistance to heat and oils, making it ideal for fuel hoses requiring moderate mechanical strength in automotive applications. Nitrile rubber (NBR) excels in mechanical strength and abrasion resistance, providing enhanced durability under high-pressure fuel system conditions. While Epichlorohydrin delivers better flexibility for dynamic movement, Nitrile is preferred for applications demanding robust tensile strength and puncture resistance.
Cost and Availability
Epichlorohydrin rubber typically offers a lower cost compared to nitrile rubber while maintaining excellent resistance to heat, oils, and fuels, making it a cost-effective option for fuel hoses. Nitrile rubber is widely available and preferred for its superior resistance to petroleum-based fluids but usually comes at a higher price point. The availability of epichlorohydrin rubber can be more limited globally due to production constraints, whereas nitrile rubber benefits from broader manufacturing and supply chain infrastructure.
Compatibility with Automotive Fuels
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits excellent resistance to ethanol-blended fuels, biodiesel, and aromatic hydrocarbons, making it highly compatible with modern automotive fuels. Nitrile rubber offers strong resistance to gasoline and diesel but degrades more quickly when exposed to oxygenated fuels like ethanol. For fuel hoses in vehicles using ethanol-blended or biodiesel fuels, epichlorohydrin rubber provides superior fuel compatibility and durability.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent resistance to heat, oil, and ozone, making it suitable for fuel hose applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions, while also exhibiting low permeability to fuel vapors, reducing environmental emissions. Nitrile rubber provides superior resistance to petroleum-based fuels and oils but tends to degrade faster under ozone and UV exposure, increasing maintenance and replacement intervals, which can affect safety. Safety considerations highlight epichlorohydrin's better performance in extreme temperatures and oxidative environments, whereas nitrile's compatibility with various fuel types demands careful selection to minimize environmental impact and ensure long-term durability.
Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Rubber for Fuel Hoses
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent resistance to ozone, weathering, and fuel oils, making it ideal for fuel hoses exposed to harsh environmental conditions and a broad range of hydrocarbons. Nitrile rubber excels in fuel resistance, particularly to petroleum-based fuels and oils, providing superior durability against swelling and degradation in standard automotive applications. Selecting the optimal rubber depends on specific fuel types and operational environments, with epichlorohydrin preferred for synthetic and alcohol fuel blends, while nitrile remains the best choice for conventional gasoline and diesel fuels.
Infographic: Epichlorohydrin rubber vs Nitrile rubber for Fuel hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com