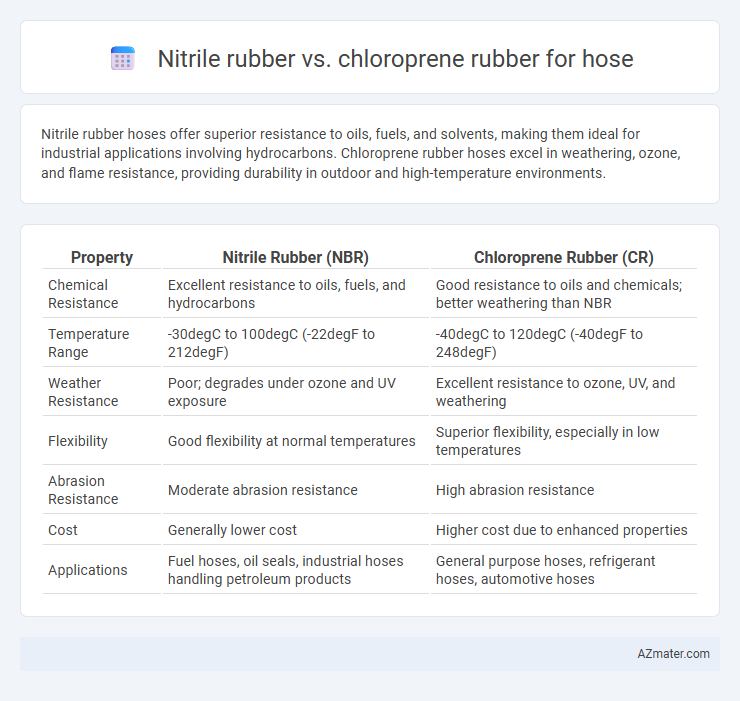
Nitrile rubber hoses offer superior resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents, making them ideal for industrial applications involving hydrocarbons. Chloroprene rubber hoses excel in weathering, ozone, and flame resistance, providing durability in outdoor and high-temperature environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) | Chloroprene Rubber (CR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and hydrocarbons | Good resistance to oils and chemicals; better weathering than NBR |
| Temperature Range | -30degC to 100degC (-22degF to 212degF) | -40degC to 120degC (-40degF to 248degF) |
| Weather Resistance | Poor; degrades under ozone and UV exposure | Excellent resistance to ozone, UV, and weathering |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility at normal temperatures | Superior flexibility, especially in low temperatures |
| Abrasion Resistance | Moderate abrasion resistance | High abrasion resistance |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to enhanced properties |
| Applications | Fuel hoses, oil seals, industrial hoses handling petroleum products | General purpose hoses, refrigerant hoses, automotive hoses |
Introduction to Nitrile and Chloroprene Rubber
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, making it ideal for industrial hose applications requiring durability in harsh environments. Chloroprene rubber (CR), commonly known as neoprene, offers superior weather resistance, ozone resistance, and moderate chemical resistance, which suits hoses exposed to outdoor conditions and varying temperatures. Both materials serve distinct purposes in hose manufacturing, with nitrile excelling in oil resistance and chloroprene providing enhanced longevity against environmental factors.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is a copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene, characterized by its polar nitrile groups that provide excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, making it ideal for hose applications exposed to hydrocarbon fluids. Chloroprene rubber (CR), or polychloroprene, contains chlorinated polymer chains providing superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and moderate oils, with a balanced elasticity due to its unique molecular structure featuring chlorine atoms along the backbone. The chemical composition of NBR offers enhanced oil resistance through strong dipole interactions, whereas CR's chlorine content imparts stability against environmental degradation, influencing their selection based on specific chemical exposure requirements in hose design.
Key Mechanical Properties Comparison
Nitrile rubber (NBR) hoses offer superior resistance to oil, fuel, and chemicals, with tensile strength typically ranging from 15 to 25 MPa and elongation at break between 300-500%, making them ideal for abrasive environments. Chloroprene rubber (CR) hoses exhibit excellent weather, ozone, and flame resistance, with tensile strength around 12 to 22 MPa and elongation at break of 300-450%, providing robust performance in outdoor applications. Both materials provide good flexibility and abrasion resistance, but NBR excels in oil resistance while CR is preferred for its durability under harsh environmental conditions.
Resistance to Oil and Chemicals
Nitrile rubber (NBR) exhibits superior resistance to oils, fuels, and many chemicals, making it an ideal choice for hose applications in automotive and industrial settings where exposure to petroleum-based fluids is common. Chloroprene rubber (CR), while offering good resistance to weathering and ozone, shows moderate resistance to oils but excels in chemical resistance against acids and alkalis, suitable for hoses carrying diverse chemical fluids. Selecting between nitrile and chloroprene rubber for hoses requires considering the specific oil or chemical exposure to ensure optimal durability and performance.
Temperature Tolerance and Stability
Nitrile rubber (NBR) exhibits excellent resistance to temperatures ranging from -40degC to 120degC, making it suitable for hydraulic hoses and applications involving petroleum-based fluids. Chloroprene rubber (CR), also known as Neoprene, maintains stability across a broader temperature range of -40degC to 130degC and offers superior resistance to ozone, weathering, and aging compared to NBR. The enhanced thermal stability of chloroprene rubber makes it preferable for hoses exposed to harsh environmental conditions and fluctuating temperatures.
Flexibility and Abrasion Resistance
Nitrile rubber offers superior abrasion resistance compared to chloroprene rubber, making it ideal for hoses exposed to rough surfaces and hydraulic fluids. Chloroprene rubber provides enhanced flexibility at low temperatures, ensuring better bend radius and resilience in cold environments. For applications demanding high durability and moderate flexibility, nitrile rubber excels, while chloroprene rubber is preferred when flexibility and weather resistance are critical.
Cost and Availability Factors
Nitrile rubber hoses generally offer a more cost-effective solution due to lower raw material prices and widespread production, enhancing their availability in global markets. Chloroprene rubber hoses tend to be pricier because of higher manufacturing costs and more specialized applications, which limits their availability compared to nitrile options. The consistent demand for nitrile rubber in fuel and oil handling sectors drives high production volumes, ensuring better accessibility and competitive pricing.
Typical Applications in Hose Manufacturing
Nitrile rubber is extensively used in hose manufacturing for applications involving oil, fuel, and petroleum-based fluids due to its excellent resistance to hydrocarbons and abrasion. Chloroprene rubber, also known as neoprene, is preferred for hoses exposed to weathering, ozone, and moderate chemicals, making it ideal for industrial and refrigeration hoses. Both materials offer flexibility and durability, but nitrile excels in fuel handling hoses while chloroprene is favored in general-purpose and outdoor hose applications.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers excellent resistance to oils and fuels, making it ideal for applications requiring chemical stability and reduced environmental contamination risks. Chloroprene rubber (CR) provides superior weather, ozone, and flame resistance, enhancing safety in outdoor or high-temperature hose use. Both materials contribute to safety compliance, but NBR's lower volatility reduces harmful emissions, while CR's inherent flame retardancy minimizes fire hazards.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Hose Applications
Nitrile rubber offers superior resistance to oils, fuels, and abrasion, making it ideal for hoses in automotive, petroleum, and industrial applications requiring durability against hydrocarbons. Chloroprene rubber provides excellent weather, ozone, and chemical resistance, suited for hoses exposed to outdoor elements, acids, and alkalis. Selecting the right rubber depends on the specific environment and substances the hose will encounter, with nitrile favored for petrochemical fluids and chloroprene preferred for chemical and environmental resilience.
Infographic: Nitrile rubber vs Chloroprene rubber for Hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com