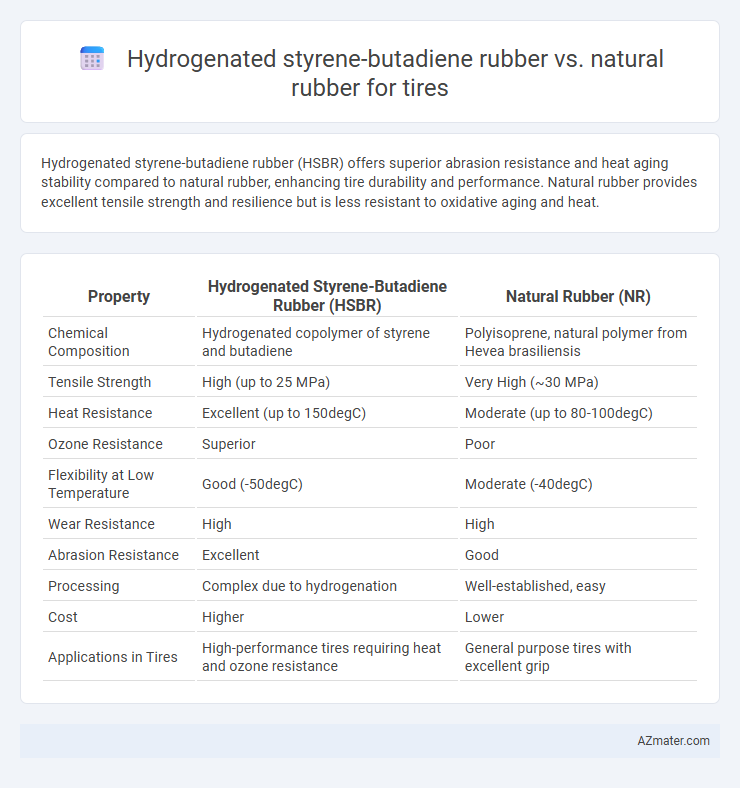
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and heat aging stability compared to natural rubber, enhancing tire durability and performance. Natural rubber provides excellent tensile strength and resilience but is less resistant to oxidative aging and heat.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) | Natural Rubber (NR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Hydrogenated copolymer of styrene and butadiene | Polyisoprene, natural polymer from Hevea brasiliensis |
| Tensile Strength | High (up to 25 MPa) | Very High (~30 MPa) |
| Heat Resistance | Excellent (up to 150degC) | Moderate (up to 80-100degC) |
| Ozone Resistance | Superior | Poor |
| Flexibility at Low Temperature | Good (-50degC) | Moderate (-40degC) |
| Wear Resistance | High | High |
| Abrasion Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Processing | Complex due to hydrogenation | Well-established, easy |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Applications in Tires | High-performance tires requiring heat and ozone resistance | General purpose tires with excellent grip |
Introduction to Tire Rubber Materials
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior abrasion resistance, thermal stability, and aging properties compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for high-performance tire treads. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity, resilience, and tear strength, contributing to enhanced grip and ride comfort in tires but is more susceptible to oxidation and heat degradation. The combination of HSBR and natural rubber in tire compounds balances durability and flexibility, optimizing tire performance across various driving conditions.
Overview of Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR)
Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) is a synthetic rubber known for its enhanced resistance to heat, ozone, and aging compared to Natural Rubber, making it ideal for tire applications requiring durability and performance. HSBR's molecular structure modification through hydrogenation improves its thermal stability and chemical resistance, enabling better fuel efficiency and wear resistance in tires. This synthetic alternative offers superior low rolling resistance and wet traction, crucial factors in modern tire technology and safety standards.
Characteristics of Natural Rubber in Tire Manufacturing
Natural rubber exhibits exceptional elasticity and tensile strength, making it ideal for tire manufacturing where high durability and flexibility are essential. Its superior resilience to wear and fatigue enhances tire lifespan and performance under varying road conditions. Despite its sensitivity to temperature and ozone, natural rubber's excellent grip and tear resistance contribute to safer and more reliable tires.
Performance Comparison: HSBR vs Natural Rubber
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior heat resistance, enhanced abrasion durability, and improved aging stability compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for high-performance tire treads. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity, tensile strength, and resilience, contributing to better wet traction and ride comfort in tires. The combination of HSBR's chemical stability with natural rubber's mechanical properties often results in optimized tire performance, balancing durability and flexibility.
Durability and Longevity in Tire Applications
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior resistance to heat, ozone, and oxidative degradation compared to natural rubber, enhancing tire durability under high-stress conditions. HSBR's improved abrasion resistance and lower rolling resistance contribute significantly to extended tire longevity and fuel efficiency. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and tensile strength, but it typically undergoes faster degradation in harsh environments, limiting its lifespan relative to HSBR in tire applications.
Wet and Dry Traction Differences
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers enhanced wet traction compared to natural rubber due to its superior abrasion resistance and optimized polymer structure, which improves tire grip on slippery surfaces. Natural rubber, however, excels in dry traction with its high elasticity and resilience, providing better road contact and handling performance under dry conditions. The molecular stability of HSBR under wet conditions ensures longer-lasting tread performance, while natural rubber's natural tackiness contributes to superior friction on dry pavements.
Fuel Efficiency and Rolling Resistance
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) exhibits lower rolling resistance compared to natural rubber, significantly enhancing tire fuel efficiency by reducing energy loss during tire deformation. HSBR's superior thermal stability and resistance to oxidative aging allow for better performance under high temperatures, maintaining consistent rolling resistance over long distances. In contrast, natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and grip but generally results in higher rolling resistance, negatively impacting overall fuel economy.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers enhanced resistance to heat and aging compared to natural rubber, leading to longer tire life and reduced replacement frequency, which can lower overall environmental impact. Natural rubber, derived from renewable rubber tree plantations, supports biodegradability and a carbon-neutral lifecycle but involves challenges such as land use and deforestation. The sustainability of HSBR depends on petrochemical sources, whereas natural rubber benefits from renewable sourcing but faces ecological concerns related to large-scale cultivation.
Cost and Availability Factors
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers enhanced durability and heat resistance compared to natural rubber but comes at a higher production cost due to its complex synthesis process. Natural rubber remains more cost-effective and widely available, primarily sourced from rubber trees in Southeast Asia, making it the preferred choice for large-scale tire manufacturing. The supply chain stability and lower raw material expenses of natural rubber contribute significantly to its sustained dominance in the tire industry despite HSBR's performance advantages.
Future Trends in Tire Rubber Technology
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior heat resistance and durability compared to natural rubber, making it a key material in the development of high-performance tires for electric and autonomous vehicles. Future trends in tire rubber technology emphasize eco-friendly formulations with enhanced wear resistance and reduced rolling resistance, where HSBR blends are increasingly favored for their customizable properties and improved fuel efficiency. Innovations in sustainable synthetic rubber production and advanced polymer modification techniques are driving the shift from traditional natural rubber toward specialized hydrogenated synthetic alternatives.
Infographic: Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber vs Natural rubber for Tire
 azmater.com
azmater.com