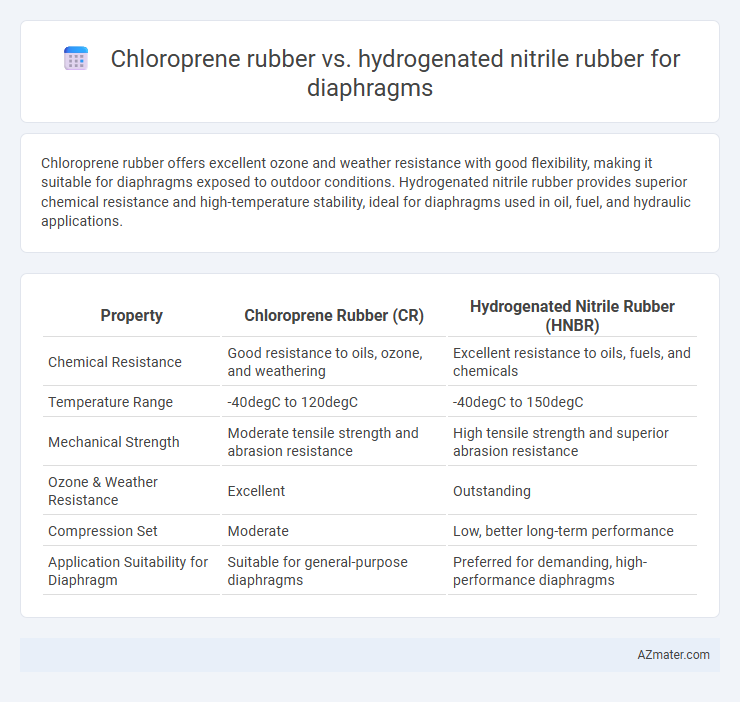
Chloroprene rubber offers excellent ozone and weather resistance with good flexibility, making it suitable for diaphragms exposed to outdoor conditions. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber provides superior chemical resistance and high-temperature stability, ideal for diaphragms used in oil, fuel, and hydraulic applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chloroprene Rubber (CR) | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils, ozone, and weathering | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -40degC to 150degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate tensile strength and abrasion resistance | High tensile strength and superior abrasion resistance |
| Ozone & Weather Resistance | Excellent | Outstanding |
| Compression Set | Moderate | Low, better long-term performance |
| Application Suitability for Diaphragm | Suitable for general-purpose diaphragms | Preferred for demanding, high-performance diaphragms |
Introduction to Diaphragm Materials
Chloroprene rubber (CR) and hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) are prominent materials used in diaphragm manufacturing due to their excellent mechanical properties and chemical resistance. CR offers superior weather, ozone, and aging resistance, making it suitable for applications exposed to outdoor environments. HNBR provides enhanced oil, heat, and abrasion resistance, ideal for demanding industrial applications requiring high durability and performance.
Overview of Chloroprene Rubber (CR)
Chloroprene rubber (CR), also known as neoprene, is widely used in diaphragm applications due to its excellent chemical stability and resistance to oils, solvents, and weathering. Its balanced properties include good mechanical strength, moderate resistance to heat up to 120degC, and inherent flame retardancy, making it suitable for dynamic sealing environments. CR offers superior resistance to ozone, oxidation, and aging compared to many other elastomers, supporting durability in harsh operating conditions.
Overview of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) is a high-performance elastomer known for its excellent resistance to heat, ozone, chemicals, and oil, making it ideal for diaphragm applications in demanding environments. It offers superior mechanical properties and enhancedNai ozone and oxidative degradation compared to Chloroprene Rubber (CR), resulting in longer service life and reliability. HNBR's hydrogenation process enhances its saturated backbone, contributing to improved thermal stability and compatibility with aggressive fluids commonly encountered in automotive and industrial sealing components.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Chloroprene rubber offers superior resistance to ozone, weathering, and moderate chemicals but shows vulnerability to strong acids and solvents, making it suitable for general industrial diaphragms. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) excels in chemical resistance against a wide range of oils, fuels, and hydrogenated hydrocarbons, providing enhanced durability in aggressive chemical environments. When comparing chemical resistance for diaphragms, HNBR outperforms chloroprene in hydrocarbon and solvent exposure, while chloroprene is preferable for environments with ozone and moderate chemical exposure.
Temperature Resistance and Operating Range
Chloroprene rubber (CR) offers excellent temperature resistance, typically operating effectively between -40degC and 120degC, making it suitable for diaphragms exposed to moderate heat. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior high-temperature stability, with an operating range extending from -40degC up to 150degC, enhancing durability in more demanding thermal environments. The choice between CR and HNBR for diaphragms depends on the specific temperature exposure, where HNBR is preferred for applications requiring higher heat resistance and extended operating life.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Chloroprene rubber (CR) offers excellent mechanical strength, high tensile and tear resistance, and good flexibility, making it suitable for diaphragms requiring durability under dynamic stress. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior abrasion resistance, enhanced chemical stability, and excellent compression set resistance, which extends diaphragm lifespan in harsh environments. Both materials exhibit high durability, but HNBR outperforms CR in heat resistance and resistance to oils, essential for demanding mechanical applications.
Aging and Ozone Resistance
Chloroprene rubber (CR) exhibits excellent aging resistance due to its inherent polymer stability and effective resistance to oxidation, making it highly durable in diaphragm applications exposed to environmental stress. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior ozone resistance compared to chloroprene rubber, attributed to its saturated polymer backbone that resists ozone cracking and surface degradation over time. Both materials provide robust performance for diaphragms, but HNBR is preferable in environments with high ozone exposure, while CR excels in general aging stability under varied atmospheric conditions.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Chloroprene rubber offers moderate cost with wide availability due to its extensive industrial production, making it a cost-effective choice for diaphragms in various applications. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) generally incurs higher costs because of its specialized production processes, though it provides superior chemical and temperature resistance. Availability of HNBR can be more limited compared to chloroprene, impacting lead times and procurement for large-scale diaphragm manufacturing.
Typical Applications in Diaphragms
Chloroprene rubber (CR) is commonly used in diaphragms for automotive, industrial, and chemical processing applications due to its excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and moderate oil exposure. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance, high temperature tolerance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for diaphragms in extreme conditions such as oilfield equipment, hydraulic systems, and high-performance pumps. HNBR diaphragms provide enhanced durability in harsh chemical environments compared to chloroprene, which excels in general-purpose sealing and resistance to aging factors.
Selecting the Right Material for Diaphragm Performance
Chloroprene rubber offers excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and moderate chemical exposure, making it suitable for diaphragms in general-purpose applications requiring durability and flexibility. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) excels in high-temperature environments and aggressive chemical resistance, ideal for diaphragms exposed to hydrocarbons, oils, and fuels. Selecting the right diaphragm material depends on environmental conditions, chemical compatibility, temperature range, and mechanical stress tolerance to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Chloroprene rubber vs Hydrogenated nitrile rubber for Diaphragm
 azmater.com
azmater.com