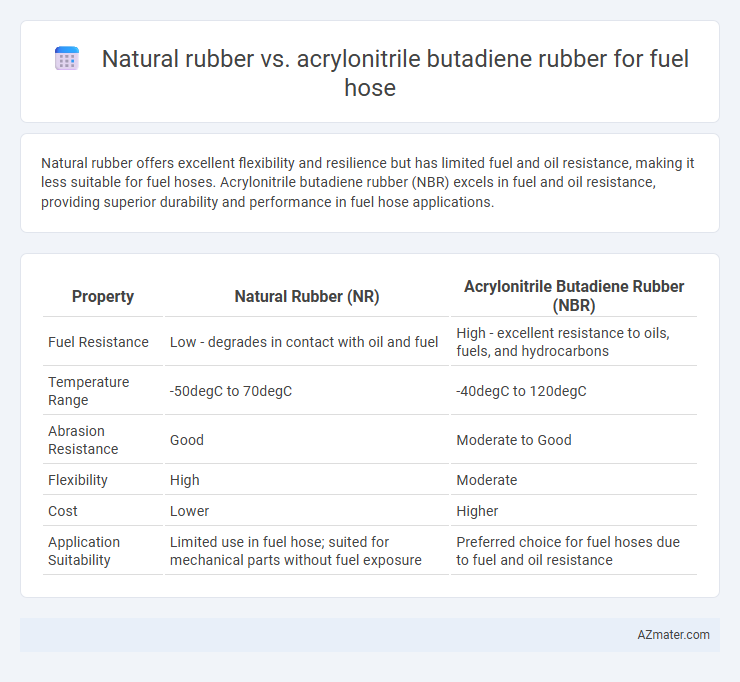
Natural rubber offers excellent flexibility and resilience but has limited fuel and oil resistance, making it less suitable for fuel hoses. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) excels in fuel and oil resistance, providing superior durability and performance in fuel hose applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Natural Rubber (NR) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Resistance | Low - degrades in contact with oil and fuel | High - excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and hydrocarbons |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 70degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good | Moderate to Good |
| Flexibility | High | Moderate |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Application Suitability | Limited use in fuel hose; suited for mechanical parts without fuel exposure | Preferred choice for fuel hoses due to fuel and oil resistance |
Introduction to Fuel Hose Materials
Natural rubber offers excellent flexibility and abrasion resistance for fuel hose applications, but its poor resistance to oil and hydrocarbons limits its use in fuel systems. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) provides superior resistance to petroleum-based fuels, oils, and chemicals, making it the preferred material for fuel hoses in automotive and industrial sectors. The choice between natural rubber and NBR depends on the specific fuel compatibility, temperature range, and durability requirements of the fuel hose application.
Overview of Natural Rubber
Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity, tensile strength, and resistance to wear, making it a preferred material for fuel hose applications requiring flexibility and durability. Its natural resistance to heat, abrasion, and certain chemicals provides reliable performance in moderate fuel exposure environments. However, natural rubber is less resistant to oils, fuels, and ozone compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), which limits its use in aggressive fuel formulations or prolonged exposure.
Overview of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) is a synthetic rubber known for excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and chemicals, making it ideal for fuel hose applications. Compared to natural rubber, NBR offers superior durability in harsh environments, including higher resistance to swelling and degradation from hydrocarbons. Its composition of acrylonitrile and butadiene allows for customizable acrylonitrile content, enhancing fuel resistance and mechanical properties for specialized fuel hose performance.
Chemical Resistance: Natural Rubber vs NBR
Natural rubber exhibits poor resistance to fuels and oils, making it unsuitable for fuel hose applications exposed to aggressive hydrocarbons. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), with its high acrylonitrile content, offers excellent chemical resistance against petroleum-based fuels and oils, ensuring superior performance and durability. This resistance difference is critical when selecting fuel hoses, as NBR prevents swelling, softening, and degradation that commonly occur in natural rubber under fuel exposure.
Temperature Tolerance Comparison
Natural rubber fuel hoses exhibit excellent flexibility but typically withstand continuous temperatures up to around 70degC, making them less suitable for high-heat engine environments. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) fuel hoses offer superior temperature tolerance, with resistance to temperatures ranging from -40degC to 100degC or higher, enhancing durability in hotter conditions. The higher thermal stability of NBR makes it a preferred choice for fuel systems exposed to elevated temperatures and aggressive chemical exposure.
Flexibility and Mechanical Properties
Natural rubber offers superior flexibility and excellent tensile strength, making it ideal for fuel hoses requiring elasticity under varying temperature conditions. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) provides enhanced resistance to oils, fuels, and abrasion while maintaining good mechanical strength, but it tends to be less flexible than natural rubber. The choice between these materials depends on the specific mechanical demands and chemical exposure of the fuel hose environment.
Durability and Lifespan in Fuel Applications
Natural rubber exhibits excellent flexibility and resistance to wear, making it suitable for fuel hose applications with moderate exposure to hydrocarbons, but its durability may decline in prolonged contact with aggressive fuels. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) offers superior resistance to oil, fuel, and chemical degradation, resulting in enhanced durability and an extended lifespan of fuel hoses subjected to harsh fuel environments. In fuel applications demanding high chemical resistance and long-term performance, NBR is generally preferred due to its robustness against swelling, cracking, and hardening.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Natural rubber offers a cost-effective option for fuel hoses due to its abundant availability and lower raw material prices compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR). Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber, while generally more expensive, provides superior resistance to fuels and oils, which can reduce maintenance costs over time. Supply chain stability for natural rubber is influenced by agricultural production cycles, whereas NBR relies on petrochemical feedstocks, impacting availability and pricing fluctuations.
Environmental and Health Impacts
Natural rubber fuel hoses offer biodegradability and lower toxicity, reducing environmental pollution and health risks during production and disposal compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR). NBR fuel hoses, while highly resistant to fuel and oil, involve synthetic chemicals that can release hazardous volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and potential carcinogens during manufacturing and degradation. Choosing natural rubber supports sustainable practices by minimizing microplastic pollution and toxic chemical exposure, enhancing overall environmental safety in automotive applications.
Best Applications: Choosing the Right Material for Fuel Hoses
Natural rubber offers excellent flexibility, abrasion resistance, and resilience, making it ideal for fuel hoses in low-temperature environments and petroleum-based fuels. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) excels in fuel resistance, particularly against oils, gasoline, and synthetic fuels, with superior chemical stability and heat resistance. For fuel hoses exposed to harsh chemicals, higher temperatures, and prolonged fuel contact, NBR is the preferred choice, while natural rubber suits applications requiring superior elasticity and durability in moderate conditions.
Infographic: Natural rubber vs Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber for Fuel hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com