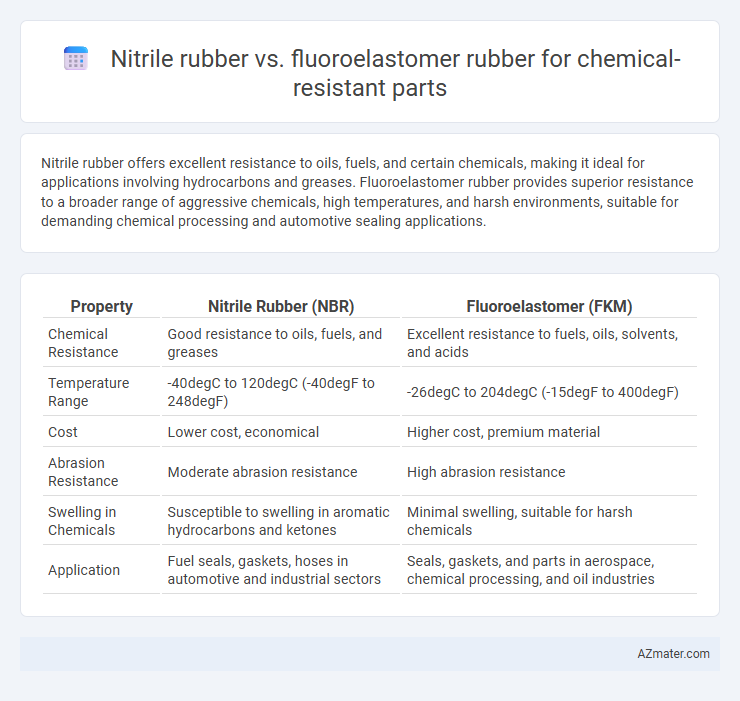
Nitrile rubber offers excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and certain chemicals, making it ideal for applications involving hydrocarbons and greases. Fluoroelastomer rubber provides superior resistance to a broader range of aggressive chemicals, high temperatures, and harsh environments, suitable for demanding chemical processing and automotive sealing applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) | Fluoroelastomer (FKM) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils, fuels, and greases | Excellent resistance to fuels, oils, solvents, and acids |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC (-40degF to 248degF) | -26degC to 204degC (-15degF to 400degF) |
| Cost | Lower cost, economical | Higher cost, premium material |
| Abrasion Resistance | Moderate abrasion resistance | High abrasion resistance |
| Swelling in Chemicals | Susceptible to swelling in aromatic hydrocarbons and ketones | Minimal swelling, suitable for harsh chemicals |
| Application | Fuel seals, gaskets, hoses in automotive and industrial sectors | Seals, gaskets, and parts in aerospace, chemical processing, and oil industries |
Introduction to Chemical Resistant Rubbers
Chemical resistant rubbers like Nitrile (NBR) and Fluoroelastomer (FKM) are engineered to withstand exposure to aggressive chemicals in industrial applications. Nitrile rubber provides excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and certain chemicals, making it suitable for oil handling and automotive seals, while Fluoroelastomer offers superior resistance to a broader range of chemicals, including acids, solvents, and high temperatures, ideal for aerospace and chemical processing equipment. The choice between these elastomers depends on the chemical environment, temperature range, and mechanical requirements of the application.
Overview of Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
Nitrile Rubber (NBR) is a synthetic rubber renowned for its excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and other chemicals, making it ideal for chemical-resistant parts. Its molecular structure offers high tensile strength and abrasion resistance, ensuring durability in demanding industrial applications. NBR performs well in temperatures ranging from -40degC to 108degC, balancing cost-effectiveness with chemical resistance compared to alternatives like Fluoroelastomer rubber.
Overview of Fluoroelastomer Rubber (FKM/FPM/Viton)
Fluoroelastomer rubber (FKM/FPM/Viton) offers superior chemical resistance compared to nitrile rubber, excelling in high-temperature environments and aggressive chemical exposure such as oils, fuels, and solvents. Its fluorine content provides excellent resistance to oxidation, fuels, and acids, making it ideal for seals and gaskets in automotive, aerospace, and chemical processing industries. Despite higher costs, fluorocarbon elastomers deliver enhanced longevity and performance in demanding applications where nitrile compounds may degrade quickly.
Chemical Resistance Comparison: Nitrile vs Fluoroelastomer
Fluoroelastomer rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to nitrile rubber, especially against fuels, oils, acids, and high-temperature solvents. Nitrile rubber performs well with hydrocarbons and aliphatic oils but degrades quickly when exposed to aromatic hydrocarbons, ketones, and chlorinated solvents. Fluoroelastomers maintain integrity in aggressive chemical environments up to 200degC, making them ideal for demanding chemical-resistant applications, whereas nitrile rubber is typically limited to temperatures below 120degC.
Temperature Performance and Stability
Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels with temperature performance ranging from -40degC to 120degC, but its chemical stability diminishes at higher temperatures and in aggressive chemicals. Fluoroelastomer (FKM) excels in high-temperature stability, maintaining integrity between -26degC and 204degC, and demonstrates superior resistance to a wide range of chemicals including acids, fuels, and solvents. For chemical-resistant parts requiring extended exposure to elevated temperatures and aggressive media, fluoroelastomer provides better thermal performance and long-term stability than nitrile rubber.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers excellent mechanical properties such as high tensile strength and abrasion resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring flexibility and durability under pressure. Fluoroelastomer rubber (FKM), on the other hand, provides superior chemical resistance, especially against fuels, oils, and aggressive solvents, while maintaining good mechanical stability at elevated temperatures. For chemical-resistant parts requiring long-term durability, fluoroelastomers typically outperform nitrile due to their enhanced thermal stability and resistance to harsh chemicals, despite nitrile's advantage in cost and mechanical toughness.
Cost Analysis: Nitrile vs Fluoroelastomer
Nitrile rubber offers a cost-effective solution for chemical-resistant parts, with material prices typically ranging from $1 to $3 per pound, making it suitable for applications with moderate chemical exposure. Fluoroelastomer rubber, though significantly more expensive at approximately $10 to $20 per pound, provides superior resistance to harsh chemicals, high temperatures, and oxidative environments, prolonging part lifespan and reducing replacement frequency. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals that nitrile may minimize upfront expenses, while fluoroelastomer's durability justifies higher initial costs in demanding chemical resistance applications.
Typical Applications in Chemical Environments
Nitrile rubber excels in fuel system components, oil seals, and gaskets due to its strong resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and hydraulic fluids. Fluoroelastomer rubber is preferred for high-temperature chemical processing seals, fuel system hoses, and automotive engine parts because of its superior resistance to aggressive chemicals, solvents, and high heat. Both materials serve critical roles in chemical environments, with nitrile rubber favored for economical oil and fuel contact applications, while fluoroelastomers handle demanding acidic and solvent exposures.
Selection Criteria for Chemical Resistant Parts
Nitrile rubber offers excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and alkalis, making it suitable for applications involving hydrocarbons and mineral oils but shows limited performance against ketones, esters, and chlorinated solvents. Fluoroelastomer rubber provides superior chemical resistance across a broader spectrum, including strong acids, aromatic and chlorinated hydrocarbons, and high-temperature environments, which makes it ideal for harsh chemical conditions requiring durability and long service life. Selection criteria for chemical resistant parts prioritize the specific chemical exposure, temperature range, mechanical properties, and cost-effectiveness, where nitrile is preferred for cost-sensitive hydrocarbon applications, and fluoroelastomer is chosen for aggressive media and extreme conditions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Needs
Nitrile rubber offers excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels, making it a cost-effective choice for applications involving hydrocarbons and general chemical exposure. Fluoroelastomer rubber provides superior resistance to a broader range of chemicals, high temperatures, and aggressive solvents, ideal for demanding environments like automotive, aerospace, and chemical processing industries. Selecting the right rubber depends on the specific chemical exposure, temperature range, and budget constraints of your application to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Nitrile rubber vs Fluoroelastomer rubber for Chemical resistant part
 azmater.com
azmater.com