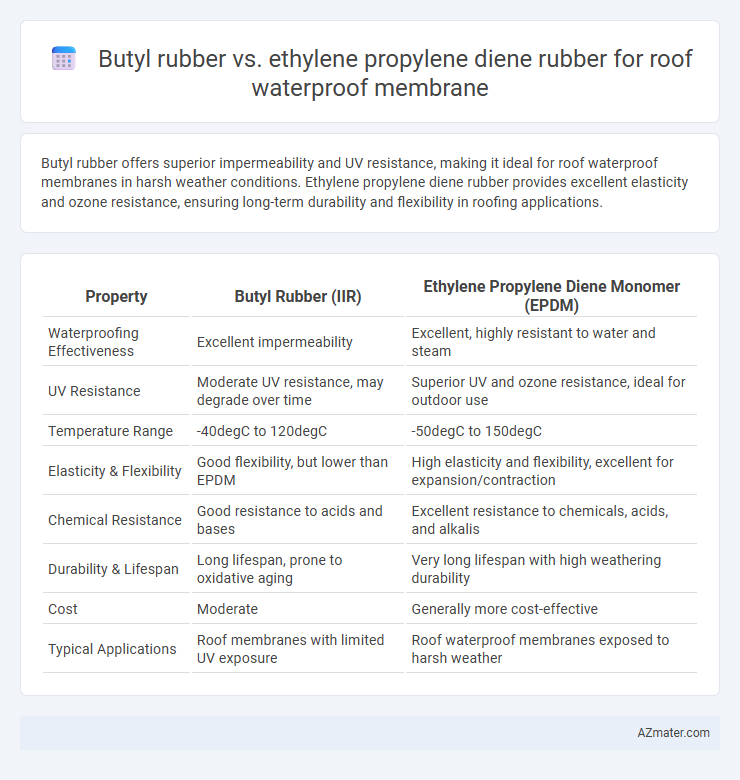
Butyl rubber offers superior impermeability and UV resistance, making it ideal for roof waterproof membranes in harsh weather conditions. Ethylene propylene diene rubber provides excellent elasticity and ozone resistance, ensuring long-term durability and flexibility in roofing applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Butyl Rubber (IIR) | Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Waterproofing Effectiveness | Excellent impermeability | Excellent, highly resistant to water and steam |
| UV Resistance | Moderate UV resistance, may degrade over time | Superior UV and ozone resistance, ideal for outdoor use |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -50degC to 150degC |
| Elasticity & Flexibility | Good flexibility, but lower than EPDM | High elasticity and flexibility, excellent for expansion/contraction |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and bases | Excellent resistance to chemicals, acids, and alkalis |
| Durability & Lifespan | Long lifespan, prone to oxidative aging | Very long lifespan with high weathering durability |
| Cost | Moderate | Generally more cost-effective |
| Typical Applications | Roof membranes with limited UV exposure | Roof waterproof membranes exposed to harsh weather |
Introduction to Roof Waterproof Membranes
Roof waterproof membranes rely heavily on the choice of materials like Butyl rubber and Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) due to their durability and waterproofing capabilities. Butyl rubber offers excellent impermeability and flexibility, making it ideal for resisting water infiltration and thermal expansion in roofing applications. EPDM provides superior UV resistance, weather durability, and elasticity, ensuring long-term protection against environmental elements in flat and low-slope roofing systems.
Overview of Butyl Rubber in Roofing
Butyl rubber, known for its excellent impermeability and resistance to weathering, is widely used in roofing membranes to provide superior waterproofing. Its unique molecular structure offers outstanding durability against ozone, UV radiation, and temperature fluctuations, making it ideal for long-lasting roof protection. Compared to ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM), butyl rubber exhibits lower permeability to water vapor, enhancing the roof's overall resistance to moisture intrusion.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM)
Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) is a synthetic rubber widely used in roof waterproof membranes due to its exceptional resistance to UV radiation, ozone, and weathering, ensuring long-lasting durability. Its chemical structure provides excellent elasticity and flexibility across a broad temperature range, making it ideal for environments with frequent temperature fluctuations. Compared to Butyl rubber, EPDM offers superior environmental resistance and easier installation, which enhances its popularity in commercial and residential roofing applications.
Material Composition and Properties Comparison
Butyl rubber, composed primarily of isobutylene with a small amount of isoprene, offers excellent impermeability and chemical resistance, making it highly effective for roof waterproof membranes. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber consists of ethylene, propylene, and diene comonomers, providing superior weather resistance, flexibility, and UV stability ideal for long-term roofing applications. While butyl rubber excels in airtightness and chemical inertness, EPDM outperforms in durability and resistance to environmental aging factors.
Durability and Longevity: Butyl vs EPDM
Butyl rubber offers exceptional impermeability and resistance to weathering, making it highly durable for roof waterproof membranes with a lifespan typically ranging from 20 to 30 years. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber boasts superior UV, ozone, and temperature resistance, contributing to an average longevity of 25 to 30 years or more in roofing applications. While Butyl provides excellent flexibility and chemical resistance, EPDM's resilience against environmental stressors often results in enhanced durability in diverse climates.
Weather Resistance and UV Stability
Butyl rubber exhibits excellent weather resistance and superior UV stability, making it highly suitable for roof waterproof membranes exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) also offers good weather resistance and UV stability but tends to degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure compared to butyl rubber. The molecular structure of butyl rubber contributes to its enhanced impermeability and durability, ensuring long-lasting performance in outdoor applications.
Installation Process and Flexibility
Butyl rubber offers superior adhesion and ease of installation for roof waterproof membranes due to its self-adhesive properties and compatibility with a variety of substrates. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber, known for exceptional flexibility and resistance to UV radiation and weathering, requires mechanical fasteners or adhesives during installation, which can extend application time. The high elongation capacity of EPDM enables it to accommodate structural movements and thermal expansions better than butyl rubber, making it a preferred choice for roofs with frequent temperature fluctuations.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
Butyl rubber offers excellent impermeability and durability for roof waterproof membranes but tends to have higher material costs compared to ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber, which provides a more cost-effective solution with competitive weather resistance. EPDM's lower price per square foot and easier installation can significantly reduce overall project expenses, making it a preferred choice for budget-conscious roofing projects. While butyl rubber may require less frequent maintenance and replacement, the initial investment for EPDM membranes aligns better with tight budget constraints without substantial compromise on performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Butyl rubber offers excellent impermeability and chemical resistance, making it highly durable for roof waterproof membranes with a relatively low environmental footprint due to its energy-efficient manufacturing process and recyclability. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber is also environmentally favorable, characterized by its long lifespan, resistance to UV radiation and ozone, and compatibility with cold-application methods that reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. Both materials contribute to sustainable roofing solutions, but EPDM's broader acceptance in green building certifications and potential for post-use recycling slightly enhances its sustainability profile compared to butyl rubber.
Choosing the Right Rubber Membrane for Your Roof
Butyl rubber offers superior impermeability to gases and exceptional UV resistance, making it ideal for roof waterproof membranes exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber provides excellent flexibility, weather resistance, and durability, often preferred for flat or low-slope roofs requiring long-lasting waterproofing. Selecting the right rubber membrane depends on specific roof requirements such as climate exposure, membrane thickness, installation ease, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Butyl rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene rubber for Roof waterproof membrane
 azmater.com
azmater.com