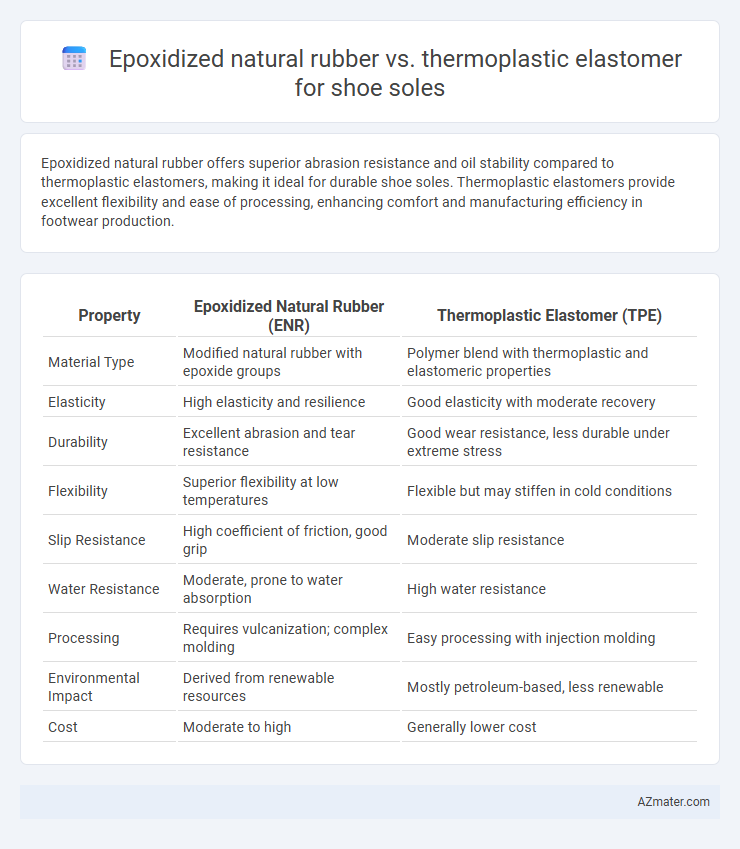
Epoxidized natural rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and oil stability compared to thermoplastic elastomers, making it ideal for durable shoe soles. Thermoplastic elastomers provide excellent flexibility and ease of processing, enhancing comfort and manufacturing efficiency in footwear production.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) | Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Modified natural rubber with epoxide groups | Polymer blend with thermoplastic and elastomeric properties |
| Elasticity | High elasticity and resilience | Good elasticity with moderate recovery |
| Durability | Excellent abrasion and tear resistance | Good wear resistance, less durable under extreme stress |
| Flexibility | Superior flexibility at low temperatures | Flexible but may stiffen in cold conditions |
| Slip Resistance | High coefficient of friction, good grip | Moderate slip resistance |
| Water Resistance | Moderate, prone to water absorption | High water resistance |
| Processing | Requires vulcanization; complex molding | Easy processing with injection molding |
| Environmental Impact | Derived from renewable resources | Mostly petroleum-based, less renewable |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Generally lower cost |
Introduction to Shoe Sole Materials
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced abrasion resistance, flexibility, and oil resistance, making it suitable for shoe soles requiring durability and comfort. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) provide excellent elasticity, lightweight properties, and easy processability, ideal for mass production and customizable designs. Both materials balance performance factors like wear resistance and flexibility but differ in biodegradability and recycling potential, influencing shoe sole choice based on application needs.
Overview of Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR)
Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) is a chemically modified form of natural rubber with improved oil resistance, abrasion resistance, and enhanced mechanical properties due to the introduction of epoxy groups along the polymer chain. ENR exhibits superior elasticity and resilience, making it suitable for durable and flexible shoe sole applications, especially where chemical resistance is required. Compared to Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPEs), ENR offers better performance in dynamic environments, although TPEs provide easier processability and recyclability.
Overview of Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE)
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) for shoe soles combine the elastic properties of rubber with the processing advantages of plastics, offering superior flexibility, durability, and abrasion resistance. Compared to epoxidized natural rubber, TPEs provide enhanced chemical resistance, easier recyclability, and faster production cycles due to their thermoplastic nature. These materials enable lightweight, weather-resistant shoe soles with tailored hardness and improved performance in various environmental conditions.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior abrasion resistance and tensile strength compared to thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs), making ENR highly durable for shoe soles under high-stress conditions. Thermoplastic elastomers exhibit better flexibility and processability, enabling enhanced comfort and easier manufacturing of complex sole designs. While ENR maintains excellent resilience and aging stability, TPEs provide improved compression set and elasticity recovery, optimizing shock absorption in footwear applications.
Flexibility and Comfort Analysis
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced flexibility due to its chemically modified polymer chains, providing superior resilience and cushioning in shoe soles compared to many thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs). Thermoplastic elastomers deliver consistent comfort with their ability to combine the elastic properties of rubber with the processing advantages of plastics, often resulting in lightweight and durable soles. Flexibility in ENR is higher at varied temperatures, while TPEs provide better compression set resistance, making both materials advantageous depending on specific comfort and performance requirements.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior durability and wear resistance for shoe soles due to its enhanced chemical stability and increased polarity, which improves abrasion resistance compared to conventional rubbers. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) provide good flexibility and ease of processing but generally exhibit lower wear resistance and durability under prolonged mechanical stress. ENR's crosslinked structure imparts higher toughness, making it more suitable for high-performance footwear requiring long-lasting sole materials.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced biodegradability and renewable sourcing, reducing reliance on fossil fuels compared to thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs), which are petroleum-based and less eco-friendly. ENR's improved resistance to oils and abrasion extends shoe sole lifespan, decreasing waste generation, while TPE soles may contribute more to microplastic pollution due to slower degradation. Choosing ENR supports circular economy principles and lowers carbon footprint, making it a more sustainable material for environmentally conscious footwear manufacturing.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior abrasion resistance and elasticity but incurs higher raw material costs and more complex vulcanization processes compared to thermoplastic elastomers (TPE). Thermoplastic elastomers provide simplified manufacturing through injection molding and faster cycle times, reducing labor and energy expenses, making them cost-effective for large-scale shoe sole production. The choice between ENR and TPE depends on balancing durability requirements against production efficiency and budget constraints in footwear manufacturing.
Application Suitability in Footwear Industry
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior abrasion resistance, elasticity, and chemical stability, making it highly suitable for durable, high-performance shoe soles in the footwear industry. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) provide excellent processability and recyclability with good flexibility, ideal for lightweight, cost-effective shoe sole manufacturing. ENR is preferred for applications requiring long-lasting wear and enhanced grip, while TPEs are optimal for mass production of comfortable, flexible footwear with streamlined manufacturing processes.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Material
Epoxidized natural rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and excellent flexibility, making it ideal for high-performance shoe soles requiring durability and comfort. Thermoplastic elastomers provide easier recyclability and better processability, with balanced mechanical properties suitable for mass production and cost efficiency. Selecting the optimal material depends on prioritizing durability and elasticity with epoxidized rubber or manufacturing scalability and environmental sustainability with thermoplastic elastomers.
Infographic: Epoxidized natural rubber vs Thermoplastic elastomer for Shoe sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com