Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and low cost, making it suitable for inner tubes in passenger vehicles. Butyl rubber provides superior air retention and chemical resistance, ideal for high-performance inner tubes requiring long-lasting inflation stability.
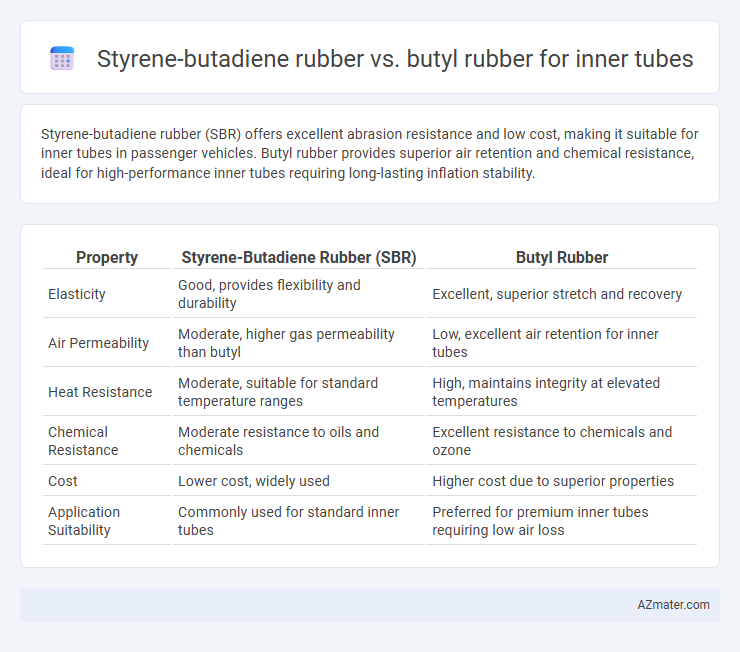
Table of Comparison
| Property | Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) | Butyl Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Elasticity | Good, provides flexibility and durability | Excellent, superior stretch and recovery |
| Air Permeability | Moderate, higher gas permeability than butyl | Low, excellent air retention for inner tubes |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate, suitable for standard temperature ranges | High, maintains integrity at elevated temperatures |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance to oils and chemicals | Excellent resistance to chemicals and ozone |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely used | Higher cost due to superior properties |
| Application Suitability | Commonly used for standard inner tubes | Preferred for premium inner tubes requiring low air loss |
Introduction to Inner Tube Materials
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it a common choice for inner tubes in consumer vehicles. Butyl rubber provides superior air impermeability and chemical stability, enhancing the durability and air retention of inner tubes used in high-performance and heavy-duty applications. The choice between SBR and Butyl rubber depends on factors like cost, lifespan, and performance requirements in pneumatic tire inner tubes.
Overview of Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is a synthetic rubber known for its excellent abrasion resistance, good aging stability, and cost-effectiveness, making it a popular choice for inner tubes in tires. Compared to butyl rubber, SBR offers superior traction and flexibility but has lower air permeability and chemical resistance, which affects inner tube durability. Its balanced combination of mechanical properties and affordability makes SBR suitable for inner tubes in standard passenger vehicles, where performance and cost are critical factors.
Overview of Butyl Rubber (IIR)
Butyl rubber (IIR) is a synthetic elastomer primarily composed of isobutylene with a small amount of isoprene, known for its excellent impermeability to gases and superior air retention properties compared to styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR). This unique molecular structure provides outstanding resistance to heat, chemicals, and ozone, making it ideal for inner tubes where durability and long-lasting inflation are crucial. Butyl rubber's low permeability significantly reduces air leakage, enhancing tire performance and safety in automotive and bicycle inner tubes.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) exhibits higher tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to butyl rubber, making it more durable under mechanical stress in inner tube applications. Butyl rubber, however, provides superior elasticity and air impermeability, which enhances the airtightness and flexibility of inner tubes. The choice between SBR and butyl rubber hinges on prioritizing either mechanical toughness or exceptional gas retention and flexibility.
Air Retention and Permeability
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) exhibits higher air permeability compared to Butyl rubber, resulting in faster air loss in inner tubes made from SBR. Butyl rubber, known for its excellent air retention properties, significantly reduces gas permeation due to its dense molecular structure, making it ideal for maintaining tire pressure over extended periods. The superior impermeability of Butyl rubber enhances inner tube durability and performance, especially in high-pressure applications.
Resistance to Heat and Aging
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) exhibits moderate resistance to heat and aging, making it suitable for inner tubes operating under typical conditions but less effective in prolonged high-temperature environments. Butyl rubber demonstrates superior heat resistance and exceptional aging stability due to its impermeability and chemical inertness, which extends the durability of inner tubes in harsh environments. The choice between SBR and butyl rubber for inner tubes depends largely on the required thermal performance and lifespan expectations.
Puncture and Chemical Resistance
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers moderate puncture resistance but excels in abrasion resistance, making it suitable for everyday inner tube applications with moderate risk of punctures. Butyl rubber provides superior puncture resistance due to its impermeability and elasticity, significantly reducing air loss and enhancing inner tube durability in harsh conditions. Chemically, butyl rubber exhibits excellent resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering compared to SBR, which is more susceptible to degradation from oils and solvents.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers a more cost-effective option for inner tubes due to its lower production expenses and widespread availability in global markets. Butyl rubber, while typically more durable and airtight, commands higher prices and suffers from limited supply primarily concentrated in specialized rubber-producing regions. The cost-efficiency and accessibility of SBR make it a preferred choice for mass-produced inner tubes, whereas butyl rubber is favored in premium applications demanding superior performance.
Common Applications in Inner Tubes
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is widely used in inner tubes due to its excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for bicycle and motorcycle tires. Butyl rubber excels in maintaining air retention and impermeability, which is critical for automotive and heavy-duty inner tubes requiring long-lasting inflation stability. The choice between SBR and Butyl rubber hinges on application-specific needs such as durability versus air retention performance in inner tube manufacturing.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Inner Tubes
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for inner tubes used in standard vehicles and bicycles. Butyl rubber provides superior air retention and resistance to gases, ideal for inner tubes that require longer inflation intervals and enhanced durability in harsh conditions. Selecting the right rubber depends on the application priorities: SBR for affordability and wear resistance, butyl rubber for airtightness and longevity.
Infographic: Styrene-butadiene rubber vs Butyl rubber for Inner tube
 azmater.com
azmater.com