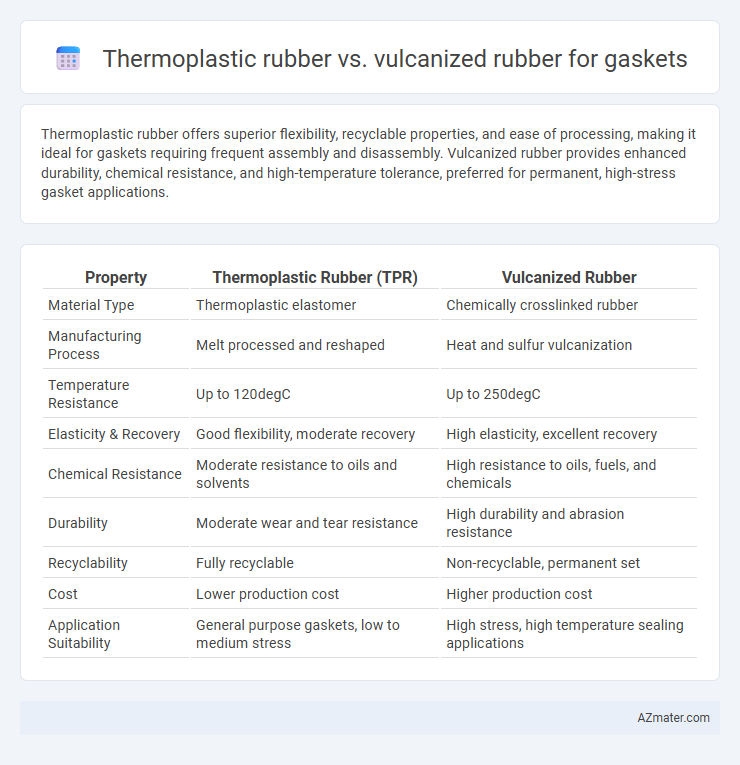
Thermoplastic rubber offers superior flexibility, recyclable properties, and ease of processing, making it ideal for gaskets requiring frequent assembly and disassembly. Vulcanized rubber provides enhanced durability, chemical resistance, and high-temperature tolerance, preferred for permanent, high-stress gasket applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Thermoplastic Rubber (TPR) | Vulcanized Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic elastomer | Chemically crosslinked rubber |
| Manufacturing Process | Melt processed and reshaped | Heat and sulfur vulcanization |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 120degC | Up to 250degC |
| Elasticity & Recovery | Good flexibility, moderate recovery | High elasticity, excellent recovery |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance to oils and solvents | High resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals |
| Durability | Moderate wear and tear resistance | High durability and abrasion resistance |
| Recyclability | Fully recyclable | Non-recyclable, permanent set |
| Cost | Lower production cost | Higher production cost |
| Application Suitability | General purpose gaskets, low to medium stress | High stress, high temperature sealing applications |
Introduction to Gasket Materials
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) and vulcanized rubber are two primary materials used in gasket manufacturing, each offering unique properties for sealing applications. Thermoplastic rubber combines elasticity and processability, enabling easy molding and recycling, while vulcanized rubber provides superior durability and resistance to heat and chemicals due to its cross-linked molecular structure. Selecting the right gasket material involves balancing factors like temperature resistance, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress to ensure optimal sealing performance.
What is Thermoplastic Rubber?
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) is a versatile elastomer combining the elastic properties of rubber with the recyclability and processability of thermoplastics, making it ideal for gasket applications requiring flexibility and durability. Unlike vulcanized rubber, which undergoes a permanent chemical cross-linking process, TPR can be repeatedly melted and reshaped without losing its elastic characteristics. This recyclability and ease of manufacturing reduce costs and environmental impact while maintaining excellent resistance to abrasion, chemical exposure, and temperature variations in sealing components.
What is Vulcanized Rubber?
Vulcanized rubber is a chemically treated material created by heating natural rubber with sulfur, enhancing its elasticity, strength, and resistance to temperature and chemicals, making it ideal for gasket applications. Unlike thermoplastic rubber, which softens when heated and can be reshaped, vulcanized rubber maintains its shape and durability under high stress and varying environmental conditions. This makes vulcanized rubber particularly effective in sealing applications requiring long-term reliability and resilience against harsh industrial environments.
Material Properties Comparison
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers excellent flexibility, chemical resistance, and the ability to be reshaped with heat, making it ideal for gaskets requiring frequent assembly or disassembly. Vulcanized rubber, formed through a vulcanization process, provides superior durability, heat resistance, and mechanical strength, ensuring long-term performance in high-pressure and high-temperature sealing applications. The choice between TPR and vulcanized rubber depends on the gasket's operational environment, with TPR favored for moderate conditions and vulcanized rubber preferred for harsh, demanding conditions.
Chemical Resistance Differences
Thermoplastic rubber exhibits moderate chemical resistance but can degrade when exposed to strong acids, solvents, and oils over time. Vulcanized rubber offers superior chemical resistance, with enhanced durability against harsh chemicals, including oils, fuels, and various solvents, due to its cross-linked polymer structure. These differences make vulcanized rubber more suitable for gaskets requiring prolonged exposure to aggressive chemical environments.
Temperature Performance
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers moderate temperature resistance, typically withstanding continuous use up to 120degC, making it suitable for applications with fluctuating thermal conditions. Vulcanized rubber, due to its cross-linked molecular structure, provides superior temperature performance, enduring extreme heat up to 250degC or higher without losing elasticity or sealing integrity. For gasket applications where high thermal stability and long-term durability are critical, vulcanized rubber is the preferred choice over thermoplastic rubber.
Durability and Longevity
Thermoplastic rubber offers excellent durability with resistance to abrasion, weathering, and chemicals, making it suitable for gasket applications requiring flexibility and repeated use. Vulcanized rubber, created through a chemical curing process, provides superior longevity by enhancing tensile strength, elasticity, and heat resistance, resulting in gaskets that maintain performance under high pressure and temperature over extended periods. For gasket durability, vulcanized rubber generally outperforms thermoplastic rubber in harsh environments, while thermoplastic rubber excels in applications needing easy molding and recyclability.
Ease of Fabrication and Installation
Thermoplastic rubber offers superior ease of fabrication and installation for gaskets due to its ability to be melted and reshaped multiple times, enabling faster and more flexible manufacturing processes. Vulcanized rubber requires a curing process that limits reprocessing, making fabrication more time-consuming and less adaptable to design changes. The thermoplastic's lower processing temperatures and improved moldability reduce installation time, enhancing overall efficiency in gasket applications.
Cost Analysis
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers a lower initial production cost due to its easier molding process and recyclability, reducing waste and material expenses. Vulcanized rubber requires more energy-intensive processing and longer curing times, increasing manufacturing costs despite providing superior durability. When considering gasket applications, TPR is more cost-effective for short to medium production runs, while vulcanized rubber is financially viable for high-performance or long-term use where material longevity justifies the higher cost.
Best Applications for Each Rubber Type
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers excellent flexibility and is ideal for gaskets requiring frequent compression and decompression, such as sealing automotive fluid systems and consumer appliances. Vulcanized rubber provides superior heat resistance and chemical stability, making it best suited for high-temperature industrial applications and heavy-duty sealing in oil and gas pipelines. Selecting the appropriate rubber depends on operational temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress specific to each gasket application.
Infographic: Thermoplastic rubber vs Vulcanized rubber for Gasket
 azmater.com
azmater.com