Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior resistance to oils, fuels, and ozone, making it ideal for gasket applications in automotive and industrial environments. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) provides excellent weather, heat, and steam resistance, suitable for gaskets exposed to outdoor and high-temperature conditions.
Table of Comparison
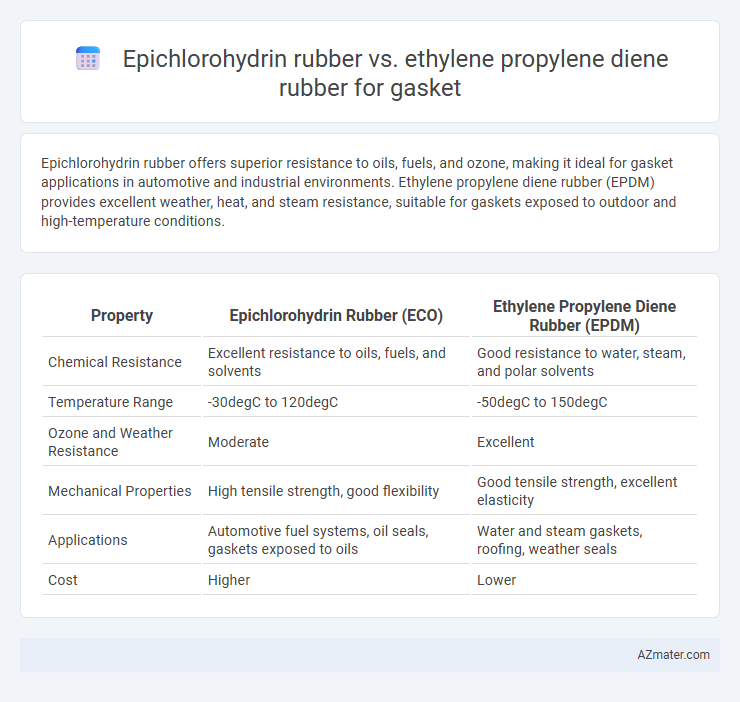
| Property | Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) | Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents | Good resistance to water, steam, and polar solvents |
| Temperature Range | -30degC to 120degC | -50degC to 150degC |
| Ozone and Weather Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Mechanical Properties | High tensile strength, good flexibility | Good tensile strength, excellent elasticity |
| Applications | Automotive fuel systems, oil seals, gaskets exposed to oils | Water and steam gaskets, roofing, weather seals |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Gasket Materials
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and weathering, making it suitable for gasket applications in automotive and industrial environments. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in high-temperature stability, ozone resistance, and flexibility, ideal for sealing systems exposed to steam, water, and weather conditions. Both materials provide specific advantages depending on the chemical and thermal requirements of the gasket application.
Overview of Epichlorohydrin Rubber
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) is a synthetic elastomer renowned for its excellent oil, ozone, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for gaskets in automotive and industrial applications exposed to fuel and lubricants. Its superior resistance to ozone and weather aging outperforms ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM), especially in environments requiring strong hydrocarbon resistance. ECO's low gas permeability and strong compression set resistance contribute to its reliability in sealing applications where durability and flexibility under harsh conditions are critical.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM)
Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) is a synthetic elastomer known for its exceptional resistance to weathering, ozone, and UV exposure, making it ideal for gasket applications in outdoor and automotive environments. EPDM offers excellent heat resistance up to 150degC and outstanding flexibility across a wide temperature range, ensuring reliable sealing performance. Compared to Epichlorohydrin rubber, EPDM provides superior resistance to water and steam, while also demonstrating strong chemical stability against acids and alkalis.
Chemical Resistance: Epichlorohydrin vs EPDM
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior chemical resistance against oils, fuels, and solvents, making it ideal for gaskets exposed to hydraulic fluids and petroleum-based products. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber provides excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and water-based chemicals but has limited compatibility with hydrocarbons and petroleum fluids. For gasket applications requiring durable performance in aggressive chemical environments, epichlorohydrin rubber is generally preferred over EPDM.
Temperature Performance Comparison
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) maintains excellent flexibility and chemical resistance in temperature ranges from -40degC to 125degC, making it ideal for environments exposed to oils and weathering. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) offers superior heat resistance, performing effectively between -50degC and 150degC, with outstanding resistance to steam, ozone, and aging. For gasket applications requiring higher maximum temperature tolerance and weather resistance, EPDM generally outperforms Epichlorohydrin rubber.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) exhibits superior resistance to oils, fuels, and ozone, making it highly durable in harsh chemical environments, with tensile strength typically ranging from 10 to 20 MPa. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) offers excellent weather, heat, and ozone resistance, with tensile strength often between 6 and 15 MPa, providing good elasticity and flexibility for gasket applications in automotive and industrial settings. ECO generally outperforms EPDM in mechanical strength and chemical resistance, while EPDM excels in outdoor durability and temperature variation tolerance, influencing gasket selection based on service conditions.
Environmental and Weather Resistance
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) offers superior resistance to ozone, oxygen, and various weathering conditions, making it highly effective for gaskets exposed to harsh environmental factors. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in UV radiation, heat, and moisture resistance, providing excellent durability in outdoor and automotive gasket applications. Both materials exhibit strong resistance profiles, but EPDM is preferred in extreme weather environments while Epichlorohydrin rubber offers enhanced chemical and oil resistance.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) offers superior oil and chemical resistance, making it cost-effective in high-demand industrial gasket applications despite its higher raw material price compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber. EPDM rubber, widely available and generally less expensive, provides excellent weather, ozone, and heat resistance but lacks the chemical resilience needed for harsh environments, influencing its lower cost in gasket manufacturing. Availability of EPDM is higher globally due to extensive production and usage, whereas epichlorohydrin's specialized applications result in more limited but stable supply chains, impacting overall cost and procurement strategies.
Typical Applications in Gasket Manufacturing
Epichlorohydrin rubber is preferred for gaskets in automotive and industrial applications requiring excellent oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, particularly in fuel system seals and HVAC units. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in sealing applications exposed to weather, ozone, steam, and water, making it ideal for outdoor, refrigeration, and water system gaskets. Both materials provide durability, but epichlorohydrin offers superior resistance to hydrocarbons, while EPDM is favored for environmental resistance in gasket manufacturing.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Gasket Applications
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior chemical resistance and excellent oil and fuel stability, making it ideal for gasket applications exposed to harsh chemicals and fuels. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in weather, ozone, and heat resistance, providing long-lasting performance in outdoor and high-temperature environments. Selecting the right rubber depends on the specific operational conditions, with epichlorohydrin best suited for chemical exposure and EPDM preferred for environmental durability in gasket manufacturing.
Infographic: Epichlorohydrin rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene rubber for Gasket
 azmater.com
azmater.com