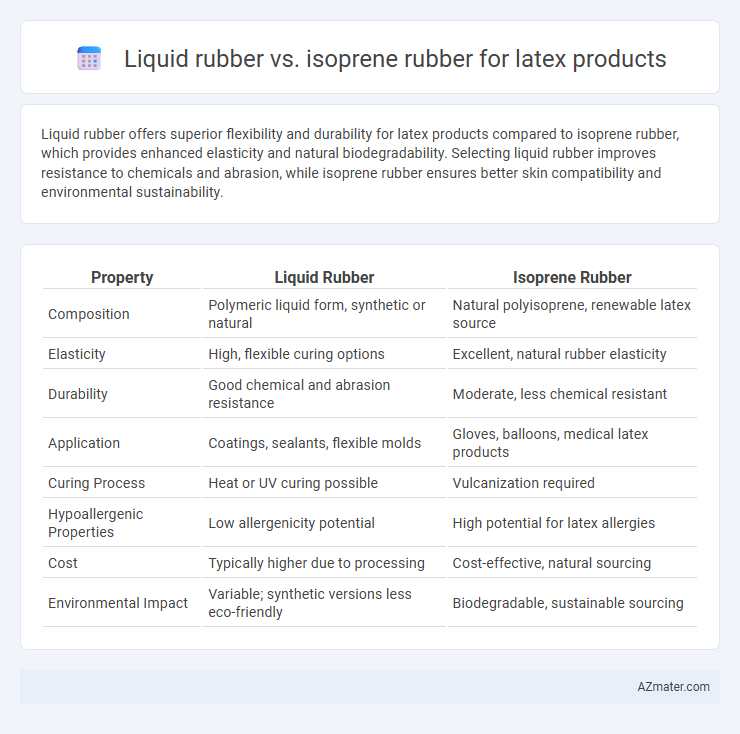
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility and durability for latex products compared to isoprene rubber, which provides enhanced elasticity and natural biodegradability. Selecting liquid rubber improves resistance to chemicals and abrasion, while isoprene rubber ensures better skin compatibility and environmental sustainability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Liquid Rubber | Isoprene Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Polymeric liquid form, synthetic or natural | Natural polyisoprene, renewable latex source |
| Elasticity | High, flexible curing options | Excellent, natural rubber elasticity |
| Durability | Good chemical and abrasion resistance | Moderate, less chemical resistant |
| Application | Coatings, sealants, flexible molds | Gloves, balloons, medical latex products |
| Curing Process | Heat or UV curing possible | Vulcanization required |
| Hypoallergenic Properties | Low allergenicity potential | High potential for latex allergies |
| Cost | Typically higher due to processing | Cost-effective, natural sourcing |
| Environmental Impact | Variable; synthetic versions less eco-friendly | Biodegradable, sustainable sourcing |
Introduction to Liquid Rubber and Isoprene Rubber
Liquid rubber is a versatile synthetic polymer known for its excellent elasticity, waterproofing, and chemical resistance properties, commonly used in coatings and adhesives. Isoprene rubber, a natural or synthetic elastomer derived from isoprene monomers, mimics the properties of natural rubber with high resilience, tensile strength, and flexibility, making it ideal for latex products. The primary difference lies in liquid rubber's application as a liquid form for seamless coatings, whereas isoprene rubber serves as the base material for solid latex products.
Key Differences Between Liquid Rubber and Isoprene Rubber
Liquid rubber offers enhanced flexibility and superior chemical resistance compared to isoprene rubber, which excels in elasticity and resilience due to its natural polyisoprene structure. Unlike isoprene rubber, liquid rubber is often easier to apply as a coating or sealant because of its viscous, pourable form, enabling seamless coverage for latex products. Isoprene rubber provides better tensile strength and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for durable latex applications requiring repeated stretching and wear.
Chemical Composition and Properties
Liquid rubber primarily consists of synthetic polymers such as styrene-butadiene or nitrile, offering superior abrasion resistance and chemical stability compared to natural isoprene rubber, which is composed of cis-1,4-polyisoprene with excellent elasticity and biodegradability. Isoprene rubber exhibits high tensile strength and flexibility due to its cis-1,4-polyisoprene molecular structure, whereas liquid rubber formulations can be tailored for enhanced durability and water resistance through copolymerization. The choice between liquid rubber and isoprene rubber for latex products depends largely on required performance criteria like mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and environmental impact.
Manufacturing Processes for Latex Products
Liquid rubber offers superior ease of processing in latex product manufacturing due to its low viscosity and ready-to-use formulation, enabling efficient dipping, coating, and molding techniques. Isoprene rubber requires a more complex synthesis process involving polymerization of isoprene monomers, which can impact production speed and consistency in latex goods. The choice of liquid rubber streamlines manufacturing with rapid curing and enhanced film formation, whereas isoprene rubber demands precise control over polymer structure to achieve desired elasticity and durability in end products.
Durability and Flexibility Comparison
Liquid rubber offers superior durability for latex products due to its enhanced resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and environmental factors, extending product lifespan significantly compared to isoprene rubber. Isoprene rubber maintains exceptional flexibility and elasticity, closely mimicking natural latex, which makes it ideal for applications requiring high stretch and comfort. The balance between durability and flexibility depends on product requirements, with liquid rubber excelling in toughness while isoprene provides better stretchability.
Applications in Various Industries
Liquid rubber exhibits excellent flexibility and chemical resistance, making it ideal for protective coatings and adhesives in automotive and electronics industries. Isoprene rubber, with its superior elasticity and durability, is widely used in medical devices, gloves, and elastic bands within healthcare and consumer goods sectors. Both materials offer unique properties tailored to specific latex product applications across diverse industrial fields.
Safety and Allergen Considerations
Liquid rubber, typically made from synthetic materials such as nitrile or silicone, offers a lower risk of allergic reactions compared to natural isoprene rubber, which contains natural proteins responsible for latex allergies. Isoprene rubber mimics the elasticity and softness of natural latex but is engineered to be hypoallergenic, reducing concerns related to Type I latex allergies. Safety evaluations highlight liquid rubber's chemical stability and resistance to contamination, making it a preferred choice for medical and consumer latex products requiring stringent allergen control.
Cost Analysis: Liquid Rubber vs Isoprene Rubber
Liquid rubber typically offers a lower initial cost compared to isoprene rubber, making it a cost-effective choice for latex product manufacturing. Isoprene rubber, while more expensive, provides superior resilience and durability, which can reduce long-term replacement and maintenance expenses. Analyzing total lifecycle costs reveals that liquid rubber suits budget-conscious projects, whereas isoprene rubber delivers enhanced performance value in demanding applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Liquid rubber derived from natural sources exhibits superior biodegradability compared to synthetic isoprene rubber, reducing long-term environmental pollution. The production of liquid rubber typically consumes less energy and results in lower greenhouse gas emissions due to its renewable feedstock origins. Isoprene rubber, often produced via petrochemical processes, generates significant carbon footprints and relies heavily on finite fossil resources, posing sustainability challenges.
Which Rubber is Best for Latex Products?
Liquid rubber and isoprene rubber both offer unique advantages for latex products, but isoprene rubber is often considered superior due to its closer chemical similarity to natural latex, providing enhanced elasticity and durability. Liquid rubber, typically synthetic, excels in applications requiring easy application and strong waterproofing but may lack the flexibility and natural feel of isoprene-based latex. For high-performance latex products such as gloves and medical devices, isoprene rubber delivers better comfort, tensile strength, and allergen reduction, making it the preferred choice.
Infographic: Liquid rubber vs Isoprene rubber for Latex product
 azmater.com
azmater.com