Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility and waterproofing for pavement applications compared to styrene-butadiene rubber, which provides better abrasion resistance and durability. Choosing between them depends on specific performance needs such as elasticity or wear resistance in road surfaces.
Table of Comparison
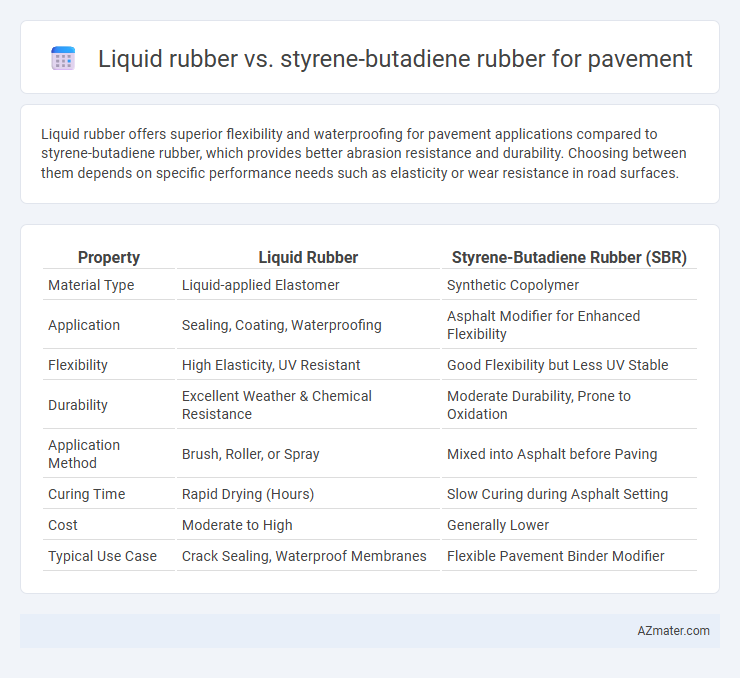
| Property | Liquid Rubber | Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Liquid-applied Elastomer | Synthetic Copolymer |
| Application | Sealing, Coating, Waterproofing | Asphalt Modifier for Enhanced Flexibility |
| Flexibility | High Elasticity, UV Resistant | Good Flexibility but Less UV Stable |
| Durability | Excellent Weather & Chemical Resistance | Moderate Durability, Prone to Oxidation |
| Application Method | Brush, Roller, or Spray | Mixed into Asphalt before Paving |
| Curing Time | Rapid Drying (Hours) | Slow Curing during Asphalt Setting |
| Cost | Moderate to High | Generally Lower |
| Typical Use Case | Crack Sealing, Waterproof Membranes | Flexible Pavement Binder Modifier |
Introduction to Liquid Rubber and Styrene-Butadiene Rubber
Liquid rubber is a versatile elastomer known for its strong adhesion, UV resistance, and waterproofing properties, making it ideal for flexible pavement coatings and crack sealing. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is a synthetic copolymer widely used in pavement applications due to its excellent abrasion resistance, tensile strength, and ability to improve asphalt durability. Both materials enhance pavement performance, but liquid rubber excels in elasticity and moisture resistance, while SBR provides enhanced mechanical strength and wear resistance.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Liquid rubber, primarily composed of hydrophobic polymers with flexible aliphatic chains, provides excellent adhesion and elongation properties ideal for pavement coatings. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) consists of styrene and butadiene monomers forming a copolymer with a random or block structure, delivering enhanced abrasion resistance and tensile strength in road surfaces. The chemical structure of liquid rubber enables superior elasticity and water resistance, while SBR's aromatic styrene units improve mechanical durability, making each suitable for specific pavement performance requirements.
Performance Characteristics in Pavement Applications
Liquid rubber exhibits superior flexibility and excellent adhesion properties, making it ideal for sealing cracks and waterproofing in pavement applications. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers high abrasion resistance and durability, enhancing the wear life of asphalt pavements under heavy traffic loads. The combination of liquid rubber's elasticity and SBR's toughness improves overall pavement resilience and longevity in varying environmental conditions.
Durability and Lifespan of Pavement Materials
Liquid rubber offers enhanced durability and extended lifespan for pavement materials due to its superior elasticity, UV resistance, and waterproofing properties, reducing cracking and weathering over time. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), while providing good abrasion resistance and flexibility, tends to degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure and harsh weather conditions, leading to increased maintenance requirements. Pavements treated with liquid rubber demonstrate significantly improved performance in high-traffic and extreme climate environments compared to those using SBR-based materials.
Flexibility and Elasticity under Traffic Loads
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility for pavement applications, allowing it to accommodate dynamic movements and temperature fluctuations without cracking. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) provides good elasticity, enhancing load distribution and resistance to deformation under traffic loads. The combination of liquid rubber's adaptability and SBR's resilient elasticity results in pavements with improved durability and extended service life.
Resistance to Weathering and Aging
Liquid rubber exhibits superior resistance to weathering and aging compared to styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) when used in pavement applications, due to its enhanced elasticity and UV stability. SBR tends to degrade more rapidly under prolonged exposure to sunlight, ozone, and temperature fluctuations, resulting in cracking and loss of flexibility. The molecular composition of liquid rubber allows it to maintain its protective properties and durability, thereby extending the service life of pavement surfaces.
Installation and Application Processes
Liquid rubber offers a seamless, quick-curing installation that involves spraying or rolling directly onto pavement, forming a flexible, waterproof membrane ideal for crack sealing and surface protection. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) requires mixing with aggregates and hot application, demanding careful temperature control and longer curing times to achieve durable, elastic pavement overlays. Liquid rubber's ease of application and minimal surface preparation contrast with SBR's more complex, labor-intensive process, influencing project timelines and maintenance requirements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Liquid rubber offers superior environmental benefits compared to styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) in pavement applications, primarily due to its non-toxic formulation and lower volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. Liquid rubber is derived from renewable resources and demonstrates excellent recyclability, reducing landfill waste and enhancing pavement lifecycle sustainability. In contrast, SBR, a synthetic polymer derived from petroleum, involves higher carbon emissions during production and presents challenges in biodegradability and end-of-life disposal.
Cost Considerations and Economic Benefits
Liquid rubber offers a cost-effective solution for pavement maintenance due to its lower material costs and longer lifecycle compared to styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), which often requires frequent reapplication. SBR's initial installation costs are higher, but its proven durability in heavy traffic areas can reduce long-term repair expenses. Evaluating total ownership costs, liquid rubber provides significant economic benefits by minimizing downtime and reducing labor expenses through faster application and curing times.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Pavement
Liquid rubber offers superior waterproofing and flexibility for pavement applications, enhancing durability and preventing cracks under varying weather conditions. Styrene-butadiene rubber provides excellent abrasion resistance and tensile strength, making it ideal for high-traffic areas requiring robust pavement performance. Selecting the right rubber depends on specific pavement needs, with liquid rubber favored for waterproofing and maintenance, while styrene-butadiene rubber excels in structural strength and wear resistance.
Infographic: Liquid rubber vs Styrene-butadiene rubber for Pavement
 azmater.com
azmater.com