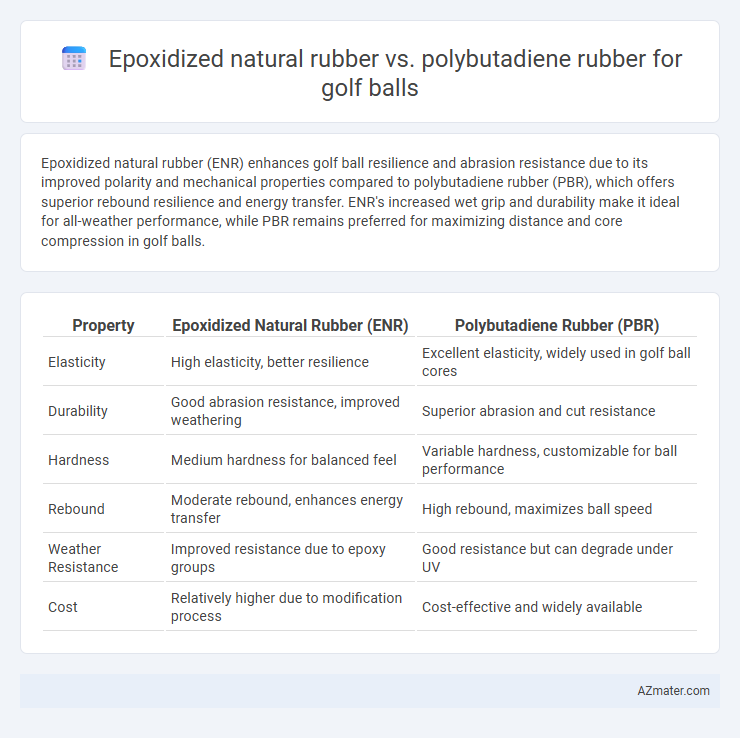
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) enhances golf ball resilience and abrasion resistance due to its improved polarity and mechanical properties compared to polybutadiene rubber (PBR), which offers superior rebound resilience and energy transfer. ENR's increased wet grip and durability make it ideal for all-weather performance, while PBR remains preferred for maximizing distance and core compression in golf balls.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) | Polybutadiene Rubber (PBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Elasticity | High elasticity, better resilience | Excellent elasticity, widely used in golf ball cores |
| Durability | Good abrasion resistance, improved weathering | Superior abrasion and cut resistance |
| Hardness | Medium hardness for balanced feel | Variable hardness, customizable for ball performance |
| Rebound | Moderate rebound, enhances energy transfer | High rebound, maximizes ball speed |
| Weather Resistance | Improved resistance due to epoxy groups | Good resistance but can degrade under UV |
| Cost | Relatively higher due to modification process | Cost-effective and widely available |
Introduction to Golf Ball Materials
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced abrasion resistance, improved resilience, and superior heat aging compared to traditional polybutadiene rubber (BR), making it a promising material for golf ball cores and covers. Polybutadiene rubber remains the industry standard due to its high rebound resilience and excellent energy transfer, crucial for achieving maximum distance. Selecting between ENR and BR depends on balancing factors like durability, spin control, and cost-effectiveness for optimal golf ball performance.
Overview of Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR)
Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) is a modified form of natural rubber with enhanced oil resistance, gas barrier properties, and mechanical strength, making it suitable for golf ball cores where durability and performance are critical. The epoxidation process introduces epoxy groups into the polymer chains, improving elasticity and resilience compared to conventional natural rubber. ENR's superior damping characteristics and abrasion resistance offer advantages over Polybutadiene Rubber (PBR), which is prized mainly for its high rebound but may lack the enhanced chemical resistance of ENR.
Overview of Polybutadiene Rubber (PBR)
Polybutadiene rubber (PBR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its exceptional abrasion resistance and high resilience, making it a popular choice in golf ball cores to enhance distance and durability. Its low glass transition temperature provides excellent elasticity and energy return, optimizing ball speed and performance. Compared to epoxidized natural rubber, PBR offers superior wear resistance and consistent molding properties, critical for maintaining structural integrity under repeated impact.
Physical and Mechanical Properties Comparison
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits superior abrasion resistance and higher tensile strength compared to polybutadiene rubber (PBR), making it ideal for enhancing golf ball durability and performance. ENR's improved elasticity and resilience contribute to better energy transfer on impact, while PBR offers lower hysteresis loss, providing enhanced distance through efficient energy return. The combination of ENR's enhanced mechanical properties and PBR's flexibility results in optimized golf ball performance, balancing control, distance, and wear resistance.
Performance Impact on Golf Ball Flight and Spin
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) enhances golf ball performance by providing superior resilience and energy return, resulting in increased ball speed and longer flight distances compared to polybutadiene rubber (PBR). ENR's improved elasticity and higher tensile strength contribute to greater spin control, allowing for better shot accuracy and enhanced greenside maneuverability. In contrast, PBR offers excellent durability but lower spin rates, which can limit the golfer's ability to execute precision shots with advanced ball flight dynamics.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Epoxidized natural rubber exhibits superior durability and wear resistance compared to polybutadiene rubber in golf ball applications, due to enhanced polymer chain interactions and oxidative stability. The epoxide groups in epoxidized natural rubber improve abrasion resistance and reduce surface degradation under repeated impact conditions. Polybutadiene rubber offers excellent resilience but is more prone to wear and surface cracking, making epoxidized natural rubber a preferred choice for long-lasting golf ball covers and cores.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced biodegradability and reduces reliance on petrochemical resources compared to polybutadiene rubber (PBR), which is derived from non-renewable fossil fuels. ENR's improved resistance to oxidation also extends golf ball lifespan, minimizing environmental waste and promoting sustainability in manufacturing. Conversely, PBR's environmental footprint is higher due to energy-intensive synthesis and limited end-of-life recyclability, making ENR a more eco-friendly alternative for golf ball production.
Cost Analysis and Manufacturing Considerations
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced abrasion resistance and elasticity compared to polybutadiene rubber (PBR), influencing raw material costs which are typically higher for ENR due to complex chemical modification processes. Manufacturing with ENR requires specialized compounding techniques to optimize cross-linking and maintain performance, potentially increasing production time and equipment investment relative to the more established and widely used PBR. Cost analysis reveals PBR's lower material and processing expenses make it a more economical choice for large-scale golf ball production, while ENR suits niche markets demanding superior durability and eco-friendly attributes despite higher overall manufacturing costs.
Industry Preferences and Market Trends
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) is gaining traction in the golf ball industry due to its superior resilience, enhanced abrasion resistance, and improved damping properties compared to polybutadiene rubber, commonly used for its high rebound and cost-effectiveness. Market trends indicate a growing preference for ENR in premium golf balls focused on durability and environmental sustainability, driven by increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly materials. Industry players are gradually adopting ENR to capitalize on its natural origin and performance benefits, reflecting a shift towards advanced rubber formulations in high-performance golf equipment.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Golf Balls
Epoxidized natural rubber offers enhanced abrasion resistance, superior resilience, and better wet-weather performance compared to polybutadiene rubber, making it ideal for golf ball covers that require durability and consistent distance. Polybutadiene rubber remains favored for core construction due to its high energy return and excellent compression properties, contributing significantly to ball velocity and control. Selecting the right rubber depends on balancing durability and playability, with epoxidized natural rubber being preferable for outer layers and polybutadiene rubber for cores to achieve optimal overall ball performance.
Infographic: Epoxidized natural rubber vs Polybutadiene rubber for Golf ball
 azmater.com
azmater.com