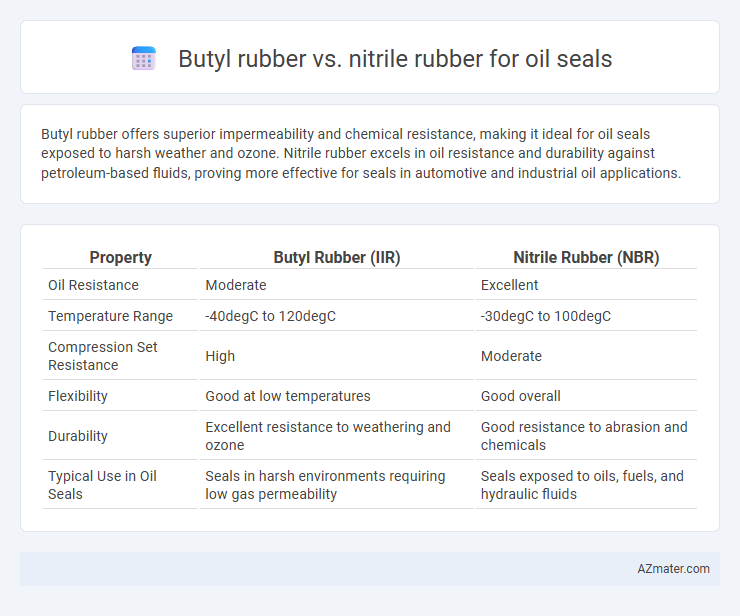
Butyl rubber offers superior impermeability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for oil seals exposed to harsh weather and ozone. Nitrile rubber excels in oil resistance and durability against petroleum-based fluids, proving more effective for seals in automotive and industrial oil applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Butyl Rubber (IIR) | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -30degC to 100degC |
| Compression Set Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Flexibility | Good at low temperatures | Good overall |
| Durability | Excellent resistance to weathering and ozone | Good resistance to abrasion and chemicals |
| Typical Use in Oil Seals | Seals in harsh environments requiring low gas permeability | Seals exposed to oils, fuels, and hydraulic fluids |
Introduction to Oil Seal Materials
Butyl rubber and nitrile rubber are commonly used materials for oil seals due to their excellent resistance to oil and chemicals. Butyl rubber offers superior impermeability and flexibility at low temperatures, making it ideal for applications requiring airtight seals and durability. Nitrile rubber provides outstanding resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels, combined with good abrasion resistance, making it the preferred choice for many dynamic sealing applications in automotive and industrial machinery.
Overview of Butyl Rubber
Butyl rubber is a synthetic elastomer renowned for its excellent impermeability to gases, making it ideal for oil seals that require airtight and durable performance. Its superior resistance to heat, ozone, and chemicals allows it to maintain elasticity and prevent leaks under harsh operating conditions. Compared to nitrile rubber, butyl offers enhanced weathering resistance but generally has lower oil and fuel resistance, making it best suited for sealing applications where gas impermeability and weather durability are prioritized.
Overview of Nitrile Rubber
Nitrile rubber (NBR), known for its excellent resistance to petroleum oils, fuels, and other hydrocarbons, is widely used in oil seal applications where durability against harsh fluids is critical. Compared to butyl rubber, nitrile offers superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for dynamic sealing conditions exposed to oils and greases. Its ability to maintain flexibility over a broad temperature range (-40degC to 120degC) enhances performance reliability in automotive, aerospace, and industrial oil seal components.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Butyl rubber offers excellent resistance to polar solvents, acids, and ketones, making it suitable for sealing applications exposed to harsh chemicals but shows limited resistance to oils and fuels. Nitrile rubber (NBR) excels in oil and fuel resistance due to its strong affinity for hydrocarbons, maintaining elasticity and sealing integrity in petroleum-based environments. For oil seals specifically, nitrile rubber provides superior chemical resistance against engine oils, hydraulic fluids, and greases compared to butyl rubber, which can degrade faster under these conditions.
Temperature Performance Differences
Butyl rubber exhibits superior resistance to heat aging and maintains flexibility at temperatures ranging from -40degC to 120degC, making it suitable for moderate temperature oil seal applications. Nitrile rubber offers a wider temperature range, typically from -40degC up to 100degC, with enhanced resistance to oil, fuel, and chemical exposure but can harden and lose elasticity faster under prolonged high-temperature conditions. Selecting between butyl and nitrile for oil seals depends on the specific temperature demands and chemical exposure in the operating environment.
Durability and Longevity
Butyl rubber offers excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and aging, making it highly durable for oil seal applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Nitrile rubber (NBR) provides superior resistance to petroleum oils, fuels, and many chemicals, significantly enhancing the longevity of oil seals in automotive and industrial settings. The choice between butyl and nitrile rubber depends on specific operating temperatures and chemical exposures, with nitrile generally preferred for oil resistance and butyl for superior environmental durability.
Cost Efficiency Analysis
Butyl rubber offers superior chemical resistance and flexibility at a lower cost than nitrile rubber, making it cost-efficient for oil seal applications with moderate temperature and chemical exposure. Nitrile rubber provides better abrasion and oil resistance, justifying its higher price in high-performance, demanding environments. Choosing between butyl and nitrile depends on the balance of upfront material costs against long-term durability and maintenance savings in specific oil sealing contexts.
Applications in Oil Seals
Butyl rubber offers excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and aging, making it ideal for oil seals in automotive and HVAC systems where exposure to harsh environmental conditions is common. Nitrile rubber provides superior resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and hydraulic fluids, making it the preferred choice for oil seals in engines, pumps, and fuel systems. Both materials are crucial in oil seal applications, with nitrile rubber dominating industries requiring strong chemical resistance and butyl rubber favored for sealing in harsh outdoor environments.
Pros and Cons of Butyl and Nitrile Rubber
Butyl rubber offers excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and chemicals, making it ideal for oil seals exposed to harsh environmental conditions, but it has lower oil and fuel resistance compared to nitrile rubber. Nitrile rubber provides superior oil, fuel, and abrasion resistance, enhancing durability in petroleum-based applications, yet it tends to degrade faster when exposed to ozone and weather. Choosing between butyl and nitrile rubber depends on the specific application requirements, balancing environmental exposure against oil and fuel resistance needs.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Oil Seal
Choosing the right material for your oil seal depends on the operating environment and chemical compatibility; butyl rubber offers excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and heat but has limited resistance to oils and fuels. Nitrile rubber, also known as NBR, is superior in resisting petroleum-based oils and fuels, making it the preferred choice for most oil seal applications in automotive and industrial machinery. Evaluating factors such as temperature range, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress ensures the optimal performance and longevity of the oil seal.
Infographic: Butyl rubber vs Nitrile rubber for Oil seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com