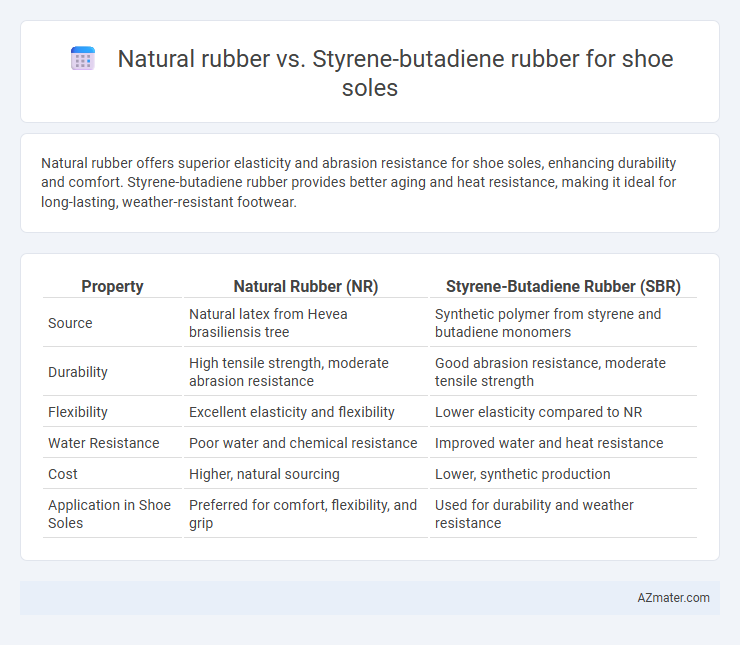
Natural rubber offers superior elasticity and abrasion resistance for shoe soles, enhancing durability and comfort. Styrene-butadiene rubber provides better aging and heat resistance, making it ideal for long-lasting, weather-resistant footwear.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Natural Rubber (NR) | Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural latex from Hevea brasiliensis tree | Synthetic polymer from styrene and butadiene monomers |
| Durability | High tensile strength, moderate abrasion resistance | Good abrasion resistance, moderate tensile strength |
| Flexibility | Excellent elasticity and flexibility | Lower elasticity compared to NR |
| Water Resistance | Poor water and chemical resistance | Improved water and heat resistance |
| Cost | Higher, natural sourcing | Lower, synthetic production |
| Application in Shoe Soles | Preferred for comfort, flexibility, and grip | Used for durability and weather resistance |
Introduction to Natural Rubber and Styrene-Butadiene Rubber
Natural rubber, derived from the latex of Hevea brasiliensis trees, offers excellent elasticity, high tensile strength, and superior abrasion resistance, making it ideal for durable shoe soles. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), a synthetic copolymer of styrene and butadiene, provides enhanced resistance to heat, aging, and abrasion, often favored for economical and weather-resistant footwear applications. Both materials serve crucial roles in shoe sole manufacturing, with natural rubber excelling in flexibility and comfort, while SBR delivers cost-effectiveness and durability in diverse environmental conditions.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Natural rubber (NR) consists primarily of polyisoprene with a cis-1,4 configuration, providing high elasticity and tensile strength due to its crystalline regions and flexible polymer chains. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is a synthetic copolymer of styrene and butadiene, featuring a random arrangement of vinyl and vinylidene units that offer enhanced abrasion resistance but lower elasticity compared to NR. The chemical structure of NR supports superior resilience and flexibility for shoe soles, while SBR's copolymeric composition delivers improved wear resistance and aging stability under various environmental conditions.
Production Process Differences
Natural rubber for shoe soles is obtained through latex extraction from Hevea brasiliensis trees, followed by coagulation, drying, and vulcanization, emphasizing eco-friendly and renewable sourcing. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is synthetically produced via emulsion polymerization of styrene and butadiene monomers, offering controlled molecular weight and consistent quality suited for industrial-scale manufacturing. The natural rubber process is slower and more variable, while SBR production allows for rapid, large-scale output with tailored polymer properties.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and superior abrasion resistance, making it highly durable for shoe soles under various conditions. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) provides enhanced wear resistance and aging stability, especially in wet environments, contributing to longer-lasting soles. Comparing durability, natural rubber excels in flexibility and resilience, while SBR outperforms in resistance to heat and oxidative degradation.
Comfort and Flexibility in Shoe Soles
Natural rubber offers superior elasticity and resilience, providing enhanced comfort and flexibility in shoe soles due to its high tensile strength and excellent stretch recovery. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) delivers good abrasion resistance and durability but tends to be less flexible and softer, resulting in reduced comfort during prolonged wear. Selecting natural rubber for shoe soles promotes better cushioning and adaptability to foot movement, essential for long-lasting comfort and flexibility.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Natural rubber, derived from latex sap of rubber trees, is biodegradable and renewable, making it a more sustainable choice for shoe soles compared to Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), which is petroleum-based and non-biodegradable. The cultivation of rubber trees promotes carbon sequestration and supports biodiversity, whereas SBR production relies on fossil fuels, contributing to higher greenhouse gas emissions and environmental pollution. Furthermore, natural rubber's biodegradability reduces long-term landfill waste, aligning with eco-friendly and circular economy principles essential for sustainable footwear manufacturing.
Cost and Market Availability
Natural rubber offers cost-effective pricing due to abundant natural sources, making it widely available for shoe sole manufacturing, especially in Southeast Asia. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), a synthetic alternative, typically incurs higher costs tied to petrochemical raw materials but benefits from stable supply chains regardless of geographic limitations. Market availability of natural rubber fluctuates with agricultural yield and climate impact, whereas SBR provides consistent, large-scale production suitable for mass-market shoe sole applications.
Performance in Various Weather Conditions
Natural rubber offers superior flexibility and excellent grip in wet conditions, making it ideal for shoe soles used in rainy or humid climates. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) provides enhanced abrasion resistance and better durability in cold and dry environments, maintaining its elasticity without cracking. Both materials exhibit distinct advantages, with natural rubber excelling in wet weather traction and SBR performing well under temperature fluctuations and wear.
Traction and Slip Resistance
Natural rubber offers superior traction and slip resistance for shoe soles due to its high elasticity and excellent grip on wet and dry surfaces. Styrene-butadiene rubber provides good abrasion resistance and durability but generally has lower traction compared to natural rubber, especially on slippery surfaces. Choosing natural rubber enhances footwear safety by reducing slip risks in diverse environmental conditions.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Shoe Soles
Natural rubber offers excellent flexibility, superior abrasion resistance, and enhanced grip, making it ideal for high-performance shoe soles requiring durability and comfort. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) provides better resistance to heat, aging, and chemicals, suitable for footwear exposed to harsh environments and prolonged wear. Choosing the right rubber depends on the shoe's intended use, balancing natural rubber's resilience and SBR's environmental toughness for optimal sole performance.
Infographic: Natural rubber vs Styrene-butadiene rubber for Shoe sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com