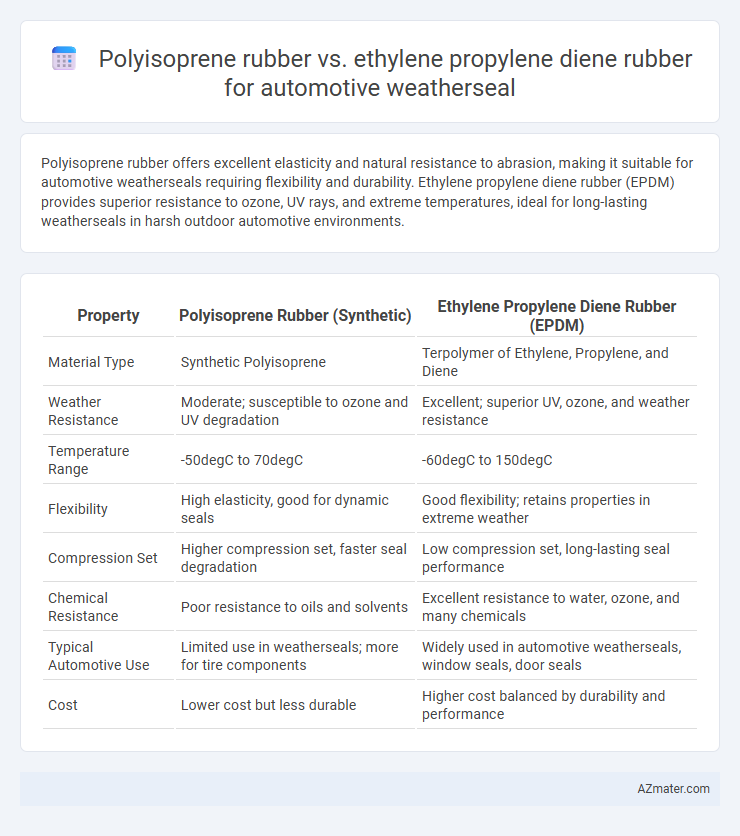
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent elasticity and natural resistance to abrasion, making it suitable for automotive weatherseals requiring flexibility and durability. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) provides superior resistance to ozone, UV rays, and extreme temperatures, ideal for long-lasting weatherseals in harsh outdoor automotive environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyisoprene Rubber (Synthetic) | Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic Polyisoprene | Terpolymer of Ethylene, Propylene, and Diene |
| Weather Resistance | Moderate; susceptible to ozone and UV degradation | Excellent; superior UV, ozone, and weather resistance |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 70degC | -60degC to 150degC |
| Flexibility | High elasticity, good for dynamic seals | Good flexibility; retains properties in extreme weather |
| Compression Set | Higher compression set, faster seal degradation | Low compression set, long-lasting seal performance |
| Chemical Resistance | Poor resistance to oils and solvents | Excellent resistance to water, ozone, and many chemicals |
| Typical Automotive Use | Limited use in weatherseals; more for tire components | Widely used in automotive weatherseals, window seals, door seals |
| Cost | Lower cost but less durable | Higher cost balanced by durability and performance |
Introduction to Automotive Weatherseal Materials
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent elasticity and natural rubber-like properties, making it suitable for automotive weatherseals requiring flexibility and resilience under varying temperatures. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber provides superior resistance to ozone, UV rays, and extreme weather conditions, enhancing durability and longevity in automotive sealing applications. Both materials are critical in automotive weatherseals, with EPDM favored for harsh environmental exposure and polyisoprene chosen for high elasticity and sealing performance.
Overview of Polyisoprene Rubber
Polyisoprene rubber, a synthetic elastomer with properties closely resembling natural rubber, offers excellent elasticity, tensile strength, and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for automotive weatherseal applications. Its superior resilience and low compression set ensure durable sealing performance against water, dust, and air infiltration in vehicle doors and windows. Compared to ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM), polyisoprene provides enhanced mechanical strength but may have reduced resistance to heat and ozone exposure.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM)
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber is a synthetic elastomer widely favored in automotive weatherseals due to its exceptional resistance to ozone, UV rays, heat, and aging, ensuring long-lasting durability in harsh environmental conditions. Its superior flexibility and excellent sealing capabilities maintain a tight barrier against water, dust, and air infiltration, enhancing vehicle cabin comfort and noise reduction. Compared to Polyisoprene rubber, EPDM offers enhanced chemical stability and temperature tolerance, making it the preferred choice for exterior automotive sealing applications.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Polyisoprene rubber exhibits excellent elasticity, tensile strength, and abrasion resistance, making it suitable for automotive weatherseals requiring flexibility and durability in moderate temperature ranges. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) offers superior resistance to ozone, UV, and extreme weather conditions, along with excellent thermal stability and aging resistance, crucial for long-term outdoor exposure in automotive applications. While polyisoprene provides better resilience to mechanical stress, EPDM's chemical inertness and weather resistance make it the preferred choice for automotive weatherseals exposed to harsh environmental elements.
Weathering Resistance: Polyisoprene vs EPDM
Polyisoprene rubber offers good elasticity but exhibits limited weathering resistance compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM), which excels in exposure to UV radiation, ozone, and extreme temperatures. EPDM's superior chemical structure provides long-lasting durability in harsh automotive weatherseal applications, effectively resisting cracking and degradation. Consequently, EPDM is generally preferred for automotive weatherseals requiring extended performance under diverse environmental conditions.
Performance Under Temperature Extremes
Polyisoprene rubber exhibits excellent flexibility and resilience at low temperatures, maintaining seal integrity without cracking in automotive weatherseals. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) offers superior resistance to heat aging and oxidation, sustaining performance at high temperatures up to 150degC. EPDM's balanced thermal stability and ozone resistance make it the preferred choice for prolonged exposure to extreme automotive climate conditions.
Chemical Resistance and Durability
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent elasticity and resilience but has limited chemical resistance, making it less suitable for exposure to automotive fluids such as oils, fuels, and solvents. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber provides superior chemical resistance against automotive chemicals, ozone, and UV radiation, ensuring prolonged durability in weatherseal applications. EPDM's robust resistance to heat and environmental aging makes it the preferred choice for automotive weatherseals requiring long-term performance in harsh chemical environments.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Polyisoprene rubber offers cost advantages in automotive weatherseals due to its lower raw material prices and easier processing, reducing overall manufacturing expenses. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) provides superior weather, ozone, and UV resistance, but its higher material cost and more complex cure systems increase production complexity and cost. Manufacturers often balance polyisoprene's cost-effectiveness with EPDM's durability requirements based on specific performance needs and long-term vehicle exposure.
Common Automotive Applications
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent elasticity and resistance to wear, making it ideal for automotive weatherseals in door seals, window channels, and trunk seals where flexibility and durability are crucial. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it the preferred choice for exterior weatherseals such as hood seals, windshield seals, and roof seals exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Both materials are widely used in automotive weatherseals, with polyisoprene favored for interior applications requiring softness and EPDM dominating in external applications due to superior environmental resistance.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Weatherseal Solutions
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent flexibility, resilience, and weather resistance, making it ideal for automotive weatherseals that require high elasticity and durability in varying temperatures. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber excels in UV, ozone, and chemical resistance, providing superior performance in harsh environmental conditions commonly exposed to vehicle exteriors. Selecting between polyisoprene and EPDM depends on specific weatherseal demands such as temperature tolerance, exposure to elements, and mechanical wear, ensuring optimal sealing performance and longevity.
Infographic: Polyisoprene rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene rubber for Automotive weatherseal
 azmater.com
azmater.com