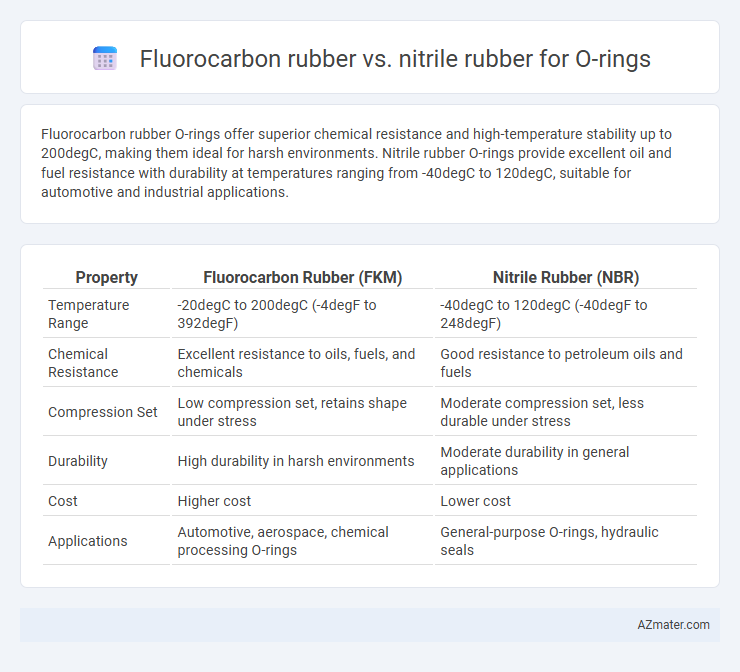
Fluorocarbon rubber O-rings offer superior chemical resistance and high-temperature stability up to 200degC, making them ideal for harsh environments. Nitrile rubber O-rings provide excellent oil and fuel resistance with durability at temperatures ranging from -40degC to 120degC, suitable for automotive and industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fluorocarbon Rubber (FKM) | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -20degC to 200degC (-4degF to 392degF) | -40degC to 120degC (-40degF to 248degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Good resistance to petroleum oils and fuels |
| Compression Set | Low compression set, retains shape under stress | Moderate compression set, less durable under stress |
| Durability | High durability in harsh environments | Moderate durability in general applications |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Applications | Automotive, aerospace, chemical processing O-rings | General-purpose O-rings, hydraulic seals |
Introduction to O-Ring Materials
O-ring materials such as fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) and nitrile rubber (NBR) are critical for sealing applications, offering distinct chemical and temperature resistance properties. Fluorocarbon rubber exhibits excellent resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and aggressive chemicals, making it suitable for automotive, aerospace, and chemical processing industries. Nitrile rubber provides superior resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels with a temperature range ideal for general-purpose sealing in hydraulic systems and fuel handling.
What is Fluorocarbon Rubber?
Fluorocarbon rubber, commonly known as Viton, is a high-performance elastomer renowned for its exceptional resistance to heat, chemicals, and oil, making it ideal for demanding O-ring applications. It exhibits superior durability in temperatures ranging from -20degC to 200degC and withstands aggressive fluids such as fuels, solvents, and acids, outperforming nitrile rubber in harsh environments. Fluorocarbon rubber's unique combination of chemical stability and mechanical strength ensures long-lasting seals in automotive, aerospace, and industrial settings.
What is Nitrile Rubber?
Nitrile rubber, also known as NBR or Buna-N, is a synthetic elastomer primarily composed of acrylonitrile and butadiene, widely used for O-rings due to its excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and other chemicals. Compared to fluorocarbon rubber (FKM), nitrile rubber offers superior resistance to petroleum-based fluids but has lower heat and chemical resistance, typically withstanding temperatures up to 120degC. Its cost-effectiveness and high tensile strength make nitrile rubber a preferred choice in automotive, industrial, and fuel system sealing applications where moderate temperature and chemical exposure occur.
Key Differences Between Fluorocarbon and Nitrile Rubber
Fluorocarbon rubber offers superior chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance up to 230degC, and excellent weathering properties compared to nitrile rubber, which performs well in oil resistance and abrasion but has a lower temperature range of approximately -40degC to 120degC. Nitrile rubber is generally more cost-effective and widely used for standard sealing applications involving hydrocarbons, while fluorocarbon rubber is preferred in aggressive chemical environments and high-heat scenarios. The choice between the two depends on the specific operational conditions, such as exposure to fuels, solvents, and extreme temperatures.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to nitrile rubber (NBR), particularly against high-temperature oils, fuels, and solvents such as aromatic hydrocarbons and chlorinated hydrocarbons. Nitrile rubber offers good resistance to aliphatic hydrocarbons, fuels, and certain greases but degrades quickly when exposed to ozone, ketones, and some acids. For O-rings used in aggressive chemical environments, fluorocarbon rubber provides enhanced durability and longevity, making it the preferred choice in aerospace, automotive fuel systems, and chemical processing industries.
Temperature Performance and Stability
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) exhibits superior temperature performance, maintaining stability from -26degC to 204degC, making it ideal for high-heat applications with strong resistance to heat aging and chemical exposure. Nitrile rubber (NBR) operates effectively within a narrower temperature range of approximately -40degC to 120degC and offers excellent resistance to oils and fuels but tends to degrade faster under prolonged high-temperature conditions. Fluorocarbon rubber's chemical inertness and low permeability provide exceptional dimensional stability and durability in harsh environments compared to nitrile rubber's more limited thermal resistance.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) offers superior mechanical properties such as high tensile strength and excellent resistance to compression set, making it ideal for O-rings exposed to harsh environments with high temperatures and aggressive chemicals. Nitrile rubber (NBR) provides good abrasion resistance and flexibility, but its mechanical durability declines significantly under prolonged exposure to heat, oils, and fuels compared to FKM. The chemical inertness and retention of elasticity of fluorocarbon rubber deliver enhanced durability and longer service life in dynamic sealing applications versus the more cost-effective but less durable nitrile rubber.
Cost Considerations for O-Rings
Fluorocarbon rubber O-rings generally have a higher cost due to their superior chemical resistance and temperature stability compared to nitrile rubber. Nitrile rubber O-rings provide a more cost-effective solution for applications involving oils and fuels but may degrade faster under extreme temperatures or harsh chemicals. Selecting between fluorocarbon and nitrile rubber O-rings involves balancing upfront material costs with long-term performance and replacement frequency.
Typical Applications of Each Material
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) O-rings excel in high-temperature environments and exposure to aggressive chemicals, making them ideal for automotive fuel systems, aerospace components, and chemical processing equipment. Nitrile rubber (NBR) O-rings are commonly used in applications involving petroleum-based oils, hydraulic fluids, and water sealing, such as automotive fuel systems, industrial machinery, and oil field equipment. Each material's chemical resistance and temperature tolerance guide its selection based on the specific operational demands of sealing applications.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your O-Ring Needs
Fluorocarbon rubber offers superior chemical resistance, high temperature tolerance up to 200-250degC, and excellent durability, making it ideal for O-rings used in automotive fuel systems or aerospace applications. Nitrile rubber provides good oil resistance, cost-effectiveness, and a temperature range of approximately -40degC to 120degC, which suits O-rings in general industrial or hydraulic sealing environments. Selecting the right rubber depends on exposure to chemicals, temperature requirements, and mechanical stress to ensure optimal O-ring performance and longevity.
Infographic: Fluorocarbon rubber vs Nitrile rubber for O-ring
 azmater.com
azmater.com