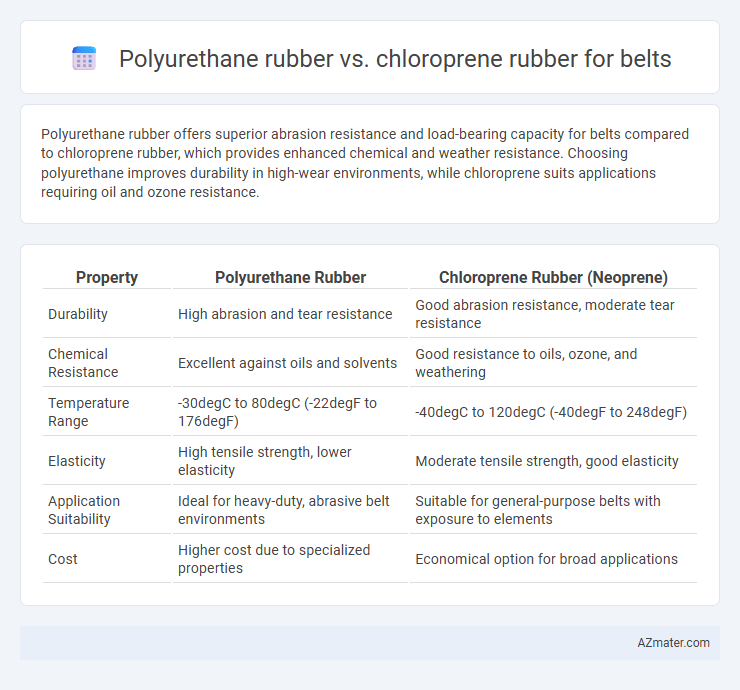
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity for belts compared to chloroprene rubber, which provides enhanced chemical and weather resistance. Choosing polyurethane improves durability in high-wear environments, while chloroprene suits applications requiring oil and ozone resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane Rubber | Chloroprene Rubber (Neoprene) |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High abrasion and tear resistance | Good abrasion resistance, moderate tear resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against oils and solvents | Good resistance to oils, ozone, and weathering |
| Temperature Range | -30degC to 80degC (-22degF to 176degF) | -40degC to 120degC (-40degF to 248degF) |
| Elasticity | High tensile strength, lower elasticity | Moderate tensile strength, good elasticity |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for heavy-duty, abrasive belt environments | Suitable for general-purpose belts with exposure to elements |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialized properties | Economical option for broad applications |
Introduction to Polyurethane and Chloroprene Rubber
Polyurethane rubber, known for its excellent abrasion resistance and high tensile strength, is widely used in industrial belts requiring durability and flexibility. Chloroprene rubber, also called neoprene, offers superior chemical resistance and weathering properties, making it ideal for belts exposed to oils, heat, and harsh environmental conditions. Both materials provide unique advantages in belt manufacturing, depending on the specific application requirements for performance and longevity.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Polyurethane rubber features a segmented block copolymer structure consisting of soft polyether or polyester segments linked by hard urethane groups, providing excellent abrasion resistance and flexibility for belts. Chloroprene rubber (CR) consists of chlorinated polydiene chains with a backbone of conjugated dienes, offering superior oil and weather resistance due to chlorine atoms enhancing chemical stability. The distinct chemical structures result in polyurethane belts excelling in durability and toughness, while chloroprene belts perform better under exposure to chemicals and environmental degradation.
Mechanical Properties Overview
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance, tensile strength up to 50 MPa, and excellent elasticity, making it ideal for high-wear belt applications. Chloroprene rubber, with tensile strength around 20-30 MPa and good resistance to oils and weathering, provides moderate flexibility and durability suitable for general-purpose belts. Polyurethane's enhanced mechanical properties enable longer service life under heavy loads, while chloroprene's balance of toughness and chemical resistance supports versatile operational environments.
Abrasion and Wear Resistance
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion and wear resistance compared to chloroprene rubber, making it ideal for conveyor belts subjected to heavy loads and rough friction. Its molecular structure provides excellent tensile strength and elasticity, ensuring longer service life in high-wear applications. Chloroprene rubber, while durable and resistant to weathering, generally exhibits lower abrasion resistance, limiting its effectiveness in extreme wear environments.
Flexibility and Elasticity Differences
Polyurethane rubber offers superior flexibility with excellent abrasion resistance, making it ideal for belts operating in high-stress environments requiring frequent bending. Chloroprene rubber exhibits moderate elasticity and better resistance to weathering and chemicals, providing durable performance in less dynamic applications. The elasticity of polyurethane allows for greater elongation and recovery, while chloroprene ensures consistent flexibility over a broad temperature range.
Temperature and Weather Resistance
Polyurethane rubber offers excellent temperature resistance, maintaining flexibility and durability in a range from -40degC to 90degC, making it ideal for environments with moderate heat variations. Chloroprene rubber excels in weather resistance, with superior performance against ozone, UV exposure, and harsh outdoor conditions, sustaining flexibility between -40degC and 120degC. For belt applications, polyurethane is preferred for abrasion resistance and moderate temperature stability, while chloroprene is favored for belts exposed to extreme weather and higher temperature fluctuations.
Oil, Chemical, and Solvent Resistance
Polyurethane rubber exhibits superior abrasion resistance and excellent oil resistance, making it ideal for belts exposed to hydraulic oils and lubricants. Chloroprene rubber (Neoprene) offers balanced chemical resistance, performing well against acids, alkalis, and mild solvents, but generally has lower oil resistance compared to polyurethane. For environments with frequent exposure to aggressive solvents and oils, polyurethane belts provide longer service life and better dimensional stability.
Cost and Availability
Polyurethane rubber belts typically offer higher abrasion resistance and longevity but come at a higher cost compared to chloroprene rubber belts. Chloroprene rubber is more widely available and generally less expensive, making it suitable for budget-conscious applications. Availability of chloroprene is greater globally due to established production, while polyurethane may have limited supply depending on regional manufacturers.
Typical Applications in Belt Manufacturing
Polyurethane rubber is extensively used in conveyor belts for handling abrasive materials due to its excellent resistance to wear, oil, and tear. Chloroprene rubber (neoprene) is preferred in industrial belts requiring good weather and ozone resistance, making it suitable for timing belts and power transmission belts exposed to outdoor environments. Both materials offer distinct advantages, with polyurethane suited for heavy-duty, high-abrasion applications and chloroprene favored for stability and durability under varied environmental conditions.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Belt
Polyurethane rubber offers exceptional abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for heavy-duty belts subjected to harsh environments and continuous wear. Chloroprene rubber provides superior chemical resistance and flexibility, suitable for belts exposed to oils, solvents, and extreme temperature variations. Selecting the right rubber depends on the belt's operational conditions, load requirements, and exposure to chemicals or temperature extremes, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Polyurethane rubber vs Chloroprene rubber for Belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com