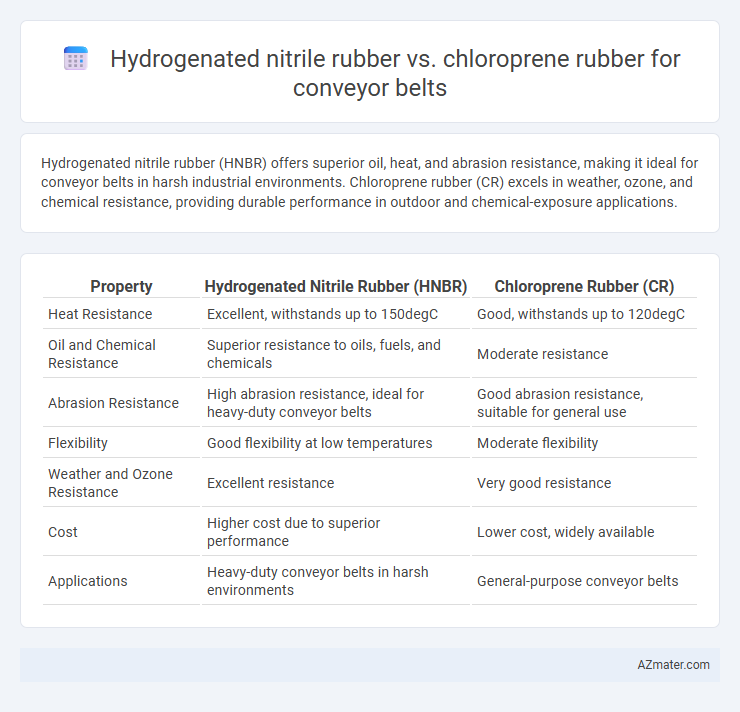
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior oil, heat, and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for conveyor belts in harsh industrial environments. Chloroprene rubber (CR) excels in weather, ozone, and chemical resistance, providing durable performance in outdoor and chemical-exposure applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) | Chloroprene Rubber (CR) |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Excellent, withstands up to 150degC | Good, withstands up to 120degC |
| Oil and Chemical Resistance | Superior resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Moderate resistance |
| Abrasion Resistance | High abrasion resistance, ideal for heavy-duty conveyor belts | Good abrasion resistance, suitable for general use |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility at low temperatures | Moderate flexibility |
| Weather and Ozone Resistance | Excellent resistance | Very good resistance |
| Cost | Higher cost due to superior performance | Lower cost, widely available |
| Applications | Heavy-duty conveyor belts in harsh environments | General-purpose conveyor belts |
Introduction to Conveyor Belt Materials
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) and chloroprene rubber (CR) are prominent materials used in conveyor belt manufacturing due to their distinct chemical and physical properties. HNBR offers excellent resistance to heat, oil, and abrasion, making it ideal for heavy-duty conveyor belts in industrial environments with exposure to harsh chemicals and high temperatures. Chloroprene rubber provides superior flexibility, weather resistance, and good mechanical strength, which suits conveyor belts used in outdoor or moderately abrasive conditions.
Overview of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, oil, and abrasion compared to Chloroprene rubber, making it ideal for conveyor belts in demanding industrial environments. Its enhanced chemical stability and mechanical properties ensure long-lasting performance under extreme conditions. HNBR's durability and resilience contribute to reduced maintenance and downtime in conveyor systems.
Overview of Chloroprene Rubber (CR)
Chloroprene Rubber (CR), also known as Neoprene, offers excellent resistance to oil, heat, and weathering, making it ideal for conveyor belt applications in harsh environments. Its balanced mechanical properties provide durability, flexibility, and resistance to abrasion, which ensures long service life in material handling systems. CR's chemical stability and resistance to ozone extend conveyor belt performance in diverse industrial settings.
Chemical Resistance: HNBR vs Chloroprene Rubber
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to chloroprene rubber, particularly against oils, fuels, and various solvents commonly encountered in conveyor belt applications. HNBR's enhanced resistance to heat and ozone also contributes to its durability in aggressive chemical environments, extending conveyor belt lifespan. Chloroprene rubber offers moderate chemical resistance but tends to degrade faster when exposed to harsh chemicals, making HNBR the preferred choice for demanding industrial settings.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and heat endurance compared to chloroprene rubber (CR), making it highly suitable for conveyor belts operating in high-stress environments. HNBR typically exhibits a tensile strength of 20-30 MPa and excellent resistance to oils, chemicals, and ozone, whereas CR provides moderate tensile strength around 10-20 MPa with good flexibility and weather resistance but lower chemical resilience. The enhanced mechanical durability and thermal stability of HNBR lead to longer conveyor belt life and reduced maintenance costs compared to CR in demanding industrial applications.
Temperature Stability and Performance
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior temperature stability, maintaining performance in a broader range from -40degC to 150degC, making it ideal for conveyor belts exposed to extreme heat and cold. Chloroprene rubber (CR) performs well within a narrower temperature range, typically from -40degC to 120degC, and provides excellent resistance to weathering and ozone. For conveyor belt applications demanding high temperature endurance and chemical resistance, HNBR delivers enhanced durability and consistent mechanical properties.
Abrasion and Wear Resistance
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior abrasion and wear resistance compared to chloroprene rubber (CR), making it ideal for conveyor belts subjected to harsh conditions and continuous friction. HNBR offers enhanced chemical stability and tensile strength, which contribute to prolonged belt life and reduced maintenance costs. Chloroprene rubber, while providing good overall durability, tends to wear faster under abrasive environments than hydrogenated nitrile rubber.
Cost and Availability Factors
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical and temperature resistance compared to chloroprene rubber (CR), but its higher production costs impact conveyor belt pricing. Availability of HNBR is more limited due to specialized manufacturing processes, whereas chloroprene rubber is widely produced and readily accessible, leading to lower overall procurement expenses. Cost-sensitive conveyor belt applications often favor chloroprene rubber for its balance of durability and availability despite lower performance metrics.
Industry Applications and Suitability
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to oils, chemicals, and high temperatures, making it ideal for conveyor belts in the automotive, oil, and chemical processing industries. Chloroprene rubber (CR) provides excellent weather, ozone, and abrasion resistance, suitable for outdoor conveyor belt applications in mining, agriculture, and general material handling. Selection depends on the operational environment; HNBR excels in harsh chemical exposure and heat, while CR is favored for durability under prolonged UV and ozone exposure.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Conveyor Belts
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, oil, and abrasion compared to chloroprene rubber (CR), making it ideal for conveyor belts operating in harsh industrial environments. Chloroprene rubber provides excellent weather, ozone, and chemical resistance, which suits applications exposed to outdoor conditions and moderate mechanical stress. Selecting the right rubber depends on specific conveyor belt requirements: HNBR is preferred for durability and chemical exposure, while CR is better for environmental resistance and flexibility.
Infographic: Hydrogenated nitrile rubber vs Chloroprene rubber for Conveyor belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com