Thermally conductive rubber offers superior heat dissipation for electronic enclosure gaskets, enhancing device cooling and performance. Butyl rubber excels in sealing and chemical resistance but lacks the thermal conductivity needed for effective heat management in electronics.
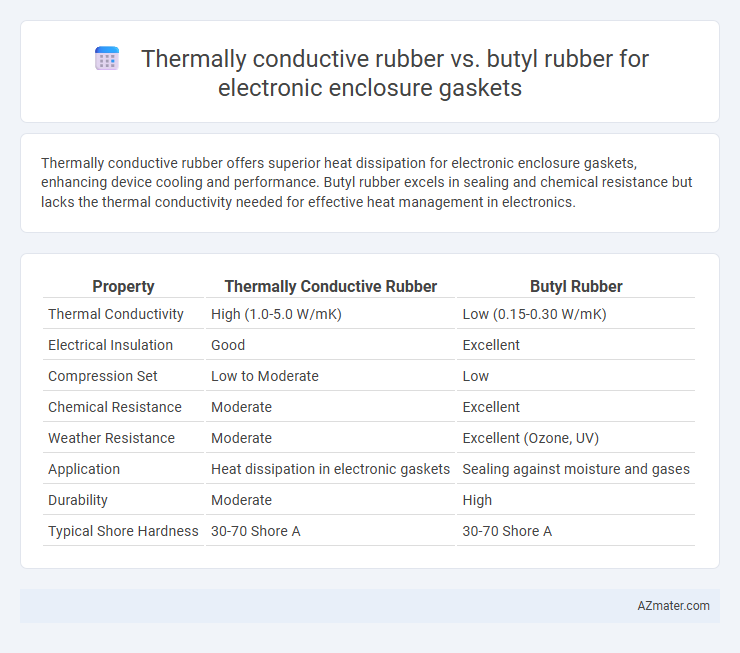
Table of Comparison
| Property | Thermally Conductive Rubber | Butyl Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | High (1.0-5.0 W/mK) | Low (0.15-0.30 W/mK) |
| Electrical Insulation | Good | Excellent |
| Compression Set | Low to Moderate | Low |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Weather Resistance | Moderate | Excellent (Ozone, UV) |
| Application | Heat dissipation in electronic gaskets | Sealing against moisture and gases |
| Durability | Moderate | High |
| Typical Shore Hardness | 30-70 Shore A | 30-70 Shore A |
Overview of Gasket Materials for Electronic Enclosures
Thermally conductive rubber offers superior heat dissipation properties, essential for managing thermal loads in electronic enclosures, while butyl rubber excels in moisture resistance and sealing against environmental contaminants. Both materials provide effective cushioning and vibration dampening, but thermally conductive rubber is preferred when thermal management is critical to device performance and longevity. Selection depends on balancing thermal conductivity needs with environmental sealing requirements to ensure optimal protection and functionality of electronic components.
What is Thermally Conductive Rubber?
Thermally conductive rubber is a specialized elastomer designed to efficiently dissipate heat from electronic components while maintaining electrical insulation and flexibility. It incorporates thermally conductive fillers such as silicone, graphite, or boron nitride to enhance thermal conductivity, making it ideal for electronic enclosure gaskets that require effective heat management. Unlike butyl rubber, which primarily provides excellent sealing and chemical resistance, thermally conductive rubber ensures optimal thermal performance to prevent overheating and improve device reliability.
Understanding Butyl Rubber in Electronic Applications
Butyl rubber, known for its excellent chemical resistance, low gas permeability, and strong electrical insulation properties, is widely used in electronic enclosure gaskets to protect sensitive components from moisture, dust, and environmental contaminants. Unlike thermally conductive rubber, which prioritizes heat dissipation, butyl rubber excels in sealing and cushioning, making it ideal for creating airtight, vibration-dampening seals in electronic housings. Its durability and stability under extreme temperatures ensure long-term reliability and protection in various electronic applications.
Key Thermal Properties: Conductive vs. Butyl Rubber
Thermally conductive rubber offers a significantly higher thermal conductivity, typically ranging from 1 to 5 W/m*K, compared to butyl rubber's poor conductivity near 0.2 W/m*K, enabling efficient heat dissipation in electronic enclosure gaskets. This property reduces hotspots and enhances device reliability by maintaining stable operating temperatures. Butyl rubber, while excellent for sealing and chemical resistance, lacks the thermal performance required for advanced heat management in electronic applications.
Electrical Insulation Capabilities Compared
Thermally conductive rubber offers superior heat dissipation while maintaining strong electrical insulation properties, making it ideal for electronic enclosure gaskets that require both thermal management and electrical isolation. Butyl rubber exhibits excellent electrical insulation but lacks significant thermal conductivity, limiting its use when efficient heat transfer is critical. Selecting thermally conductive rubber enhances device reliability by balancing insulation with effective heat dissipation in electronic applications.
Environmental Resistance Performance
Thermally conductive rubber offers superior heat dissipation and maintains performance under extreme temperatures, making it ideal for electronic enclosure gaskets exposed to high thermal stress. Butyl rubber provides excellent resistance to moisture, ozone, and chemical exposure, ensuring long-term sealing integrity in harsh environmental conditions. For applications demanding both thermal management and environmental resistance, thermally conductive rubber typically outperforms butyl rubber in thermal performance, while butyl rubber excels in UV and chemical durability.
Compression Set and Long-Term Sealing Integrity
Thermally conductive rubber offers superior heat dissipation with low compression set values, ensuring minimal permanent deformation under sustained pressure and excellent long-term sealing integrity in electronic enclosure gaskets. Butyl rubber, while effective for moisture and gas sealing, typically exhibits higher compression set, which can lead to gasket relaxation and compromised sealing performance over time. Selecting thermally conductive rubber enhances both thermal management and reliable, durable seal maintenance in electronics subjected to continuous thermal and mechanical stress.
Ease of Fabrication and Installation
Thermally conductive rubber offers superior ease of fabrication and installation for electronic enclosure gaskets due to its enhanced pliability and ability to conform tightly to complex shapes, ensuring effective heat dissipation. Butyl rubber, while providing excellent environmental sealing and chemical resistance, tends to be less flexible, making it more challenging to cut and fit precisely during installation. The comparative softness and thermal transfer properties of thermally conductive rubber streamline the gasket fabrication process and reduce labor time on-site.
Cost Implications for Large-Scale Manufacturing
Thermally conductive rubber offers superior heat dissipation properties essential for managing high-performance electronics, but it typically incurs higher material and processing costs compared to butyl rubber. Butyl rubber, known for its excellent sealing and chemical resistance, provides a more cost-effective solution in large-scale manufacturing where thermal management is less critical. Choosing between these materials depends on balancing upfront material expenses with the long-term benefits of thermal performance and product reliability in electronic enclosure gasket applications.
Choosing the Right Gasket: Application-Based Recommendations
Thermally conductive rubber offers superior heat dissipation properties, making it ideal for electronic enclosure gaskets in high-power devices where managing thermal buildup is critical for performance and longevity. Butyl rubber excels in providing excellent electrical insulation, chemical resistance, and weather sealing, suitable for enclosures exposed to harsh environmental conditions or requiring airtight protection. Selecting the right gasket depends on balancing thermal management needs with environmental resistance, ensuring optimal device reliability and protection.
Infographic: Thermally conductive rubber vs Butyl rubber for Electronic enclosure gasket
 azmater.com
azmater.com