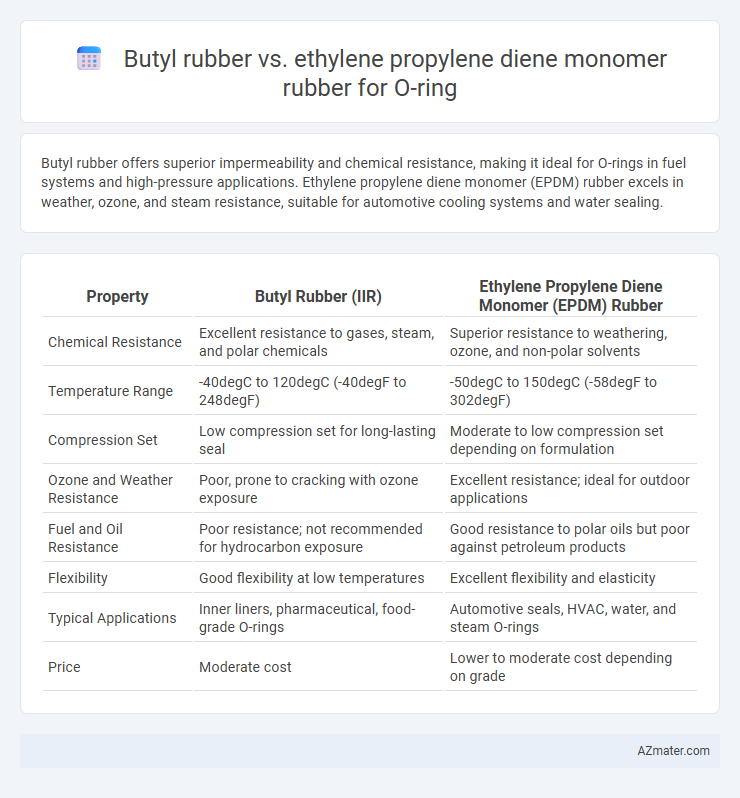
Butyl rubber offers superior impermeability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for O-rings in fuel systems and high-pressure applications. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber excels in weather, ozone, and steam resistance, suitable for automotive cooling systems and water sealing.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Butyl Rubber (IIR) | Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to gases, steam, and polar chemicals | Superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and non-polar solvents |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC (-40degF to 248degF) | -50degC to 150degC (-58degF to 302degF) |
| Compression Set | Low compression set for long-lasting seal | Moderate to low compression set depending on formulation |
| Ozone and Weather Resistance | Poor, prone to cracking with ozone exposure | Excellent resistance; ideal for outdoor applications |
| Fuel and Oil Resistance | Poor resistance; not recommended for hydrocarbon exposure | Good resistance to polar oils but poor against petroleum products |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility at low temperatures | Excellent flexibility and elasticity |
| Typical Applications | Inner liners, pharmaceutical, food-grade O-rings | Automotive seals, HVAC, water, and steam O-rings |
| Price | Moderate cost | Lower to moderate cost depending on grade |
Introduction to Butyl Rubber and EPDM for O-Rings
Butyl rubber, known for its excellent impermeability to gases and flexibility, is widely used in O-rings exposed to harsh chemicals and extreme conditions, offering superior resistance to ozone and weathering. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber provides outstanding heat, ozone, and steam resistance, making it ideal for O-rings in automotive cooling systems and water applications. Both materials deliver robust sealing performance, with butyl rubber excelling in gas-tight seals and EPDM preferred for thermal and environmental durability.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Butyl rubber, composed primarily of isobutylene with a small amount of isoprene, exhibits a saturated polymer backbone that provides excellent impermeability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for O-rings exposed to gases and various chemicals. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber contains ethylene, propylene, and a diene component, resulting in a saturated backbone with unsaturated side chains that enhance ozone, weather, and heat resistance, especially in applications requiring exposure to steam or polar substances. The distinct chemical compositions and molecular structures influence their sealing performance, with butyl rubber favored for its low gas permeability and EPDM preferred for its broader chemical and environmental durability.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Elasticity
Butyl rubber offers excellent impermeability and chemical resistance but has lower tensile strength and elasticity compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, which provides superior mechanical strength and flexibility. EPDM's enhanced elasticity and resilience make it ideal for O-rings subjected to dynamic stresses and extreme temperature variations. The superior tear resistance and elongation at break of EPDM ensure longer service life in sealing applications under mechanical strain.
Temperature Resistance: Performance in Extreme Conditions
Butyl rubber O-rings offer excellent resistance to heat aging and retain flexibility at temperatures up to 120degC, making them suitable for moderate temperature applications. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) O-rings withstand a broader temperature range from -50degC to 150degC, maintaining performance in both extreme cold and heat conditions. EPDM's superior temperature resistance and resistance to weathering and ozone degradation make it ideal for outdoor and high-temperature environments compared to butyl rubber.
Chemical Compatibility and Resistance
Butyl rubber offers excellent resistance to polar solvents, acids, and alkalis, making it suitable for O-rings exposed to harsh chemicals and steam. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber excels in chemical compatibility with water, brake fluids, and dilute acids, while showing poor resistance to petroleum oils and hydrocarbons. For applications involving aggressive chemicals and oxidation, EPDM provides superior resistance, whereas Butyl rubber is preferred for ozone and weather exposure in O-ring seals.
Weathering, Ozone, and UV Stability
Butyl rubber exhibits excellent resistance to ozone, weathering, and UV exposure, maintaining its elasticity and sealing properties in harsh outdoor conditions. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber offers superior weathering, ozone, and UV stability compared to many other elastomers, making it highly suitable for O-rings exposed to sunlight and atmospheric aging. EPDM's enhanced durability under UV radiation and ozone ozone attack often results in longer service life for O-rings used in automotive, HVAC, and outdoor applications.
Applications in Industrial and Automotive Sectors
Butyl rubber offers exceptional impermeability to gases and excellent resistance to heat, chemicals, and weathering, making it ideal for automotive fuel system seals and industrial gas handling applications. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber excels in resistance to ozone, steam, and polar solvents, which suits its use in automotive cooling system O-rings and industrial water sealing systems. Both materials provide reliable sealing performance, but butyl rubber is preferred for fuel-related environments, while EPDM is favored where exposure to heat and weathering is critical.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Butyl rubber O-rings offer excellent cost-effectiveness due to their lower material costs and broad availability in various applications such as automotive and pharmaceutical sealing. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber O-rings, while slightly higher in price, provide superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and chemicals, making them a valuable investment for outdoor and industrial uses despite moderate availability. The choice between butyl and EPDM O-rings depends on budget constraints and specific environmental durability requirements.
Longevity and Maintenance Considerations
Butyl rubber O-rings exhibit superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and chemical exposure, contributing to extended longevity and reduced maintenance in sealing applications. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber offers excellent heat and steam resistance but may degrade faster when exposed to oils and hydrocarbons, necessitating more frequent inspections and replacements. Selecting Butyl rubber improves durability in harsh environments, while EPDM rubber requires careful maintenance to ensure optimal performance in specific chemical conditions.
Choosing the Right Material: Butyl Rubber vs EPDM for O-Rings
Butyl rubber offers excellent impermeability to gases, making it ideal for airtight O-ring applications, while EPDM excels in resistance to weathering, ozone, and a wide range of chemicals, which suits outdoor and automotive uses. The choice between Butyl and EPDM O-rings depends largely on the environmental conditions and chemical exposure, with Butyl preferred for gas sealing and EPDM favored for heat, water, and chemical resilience. Selecting the right material ensures optimal performance and longevity of O-rings in their specific sealing applications.
Infographic: Butyl rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene monomer rubber for O-ring
 azmater.com
azmater.com