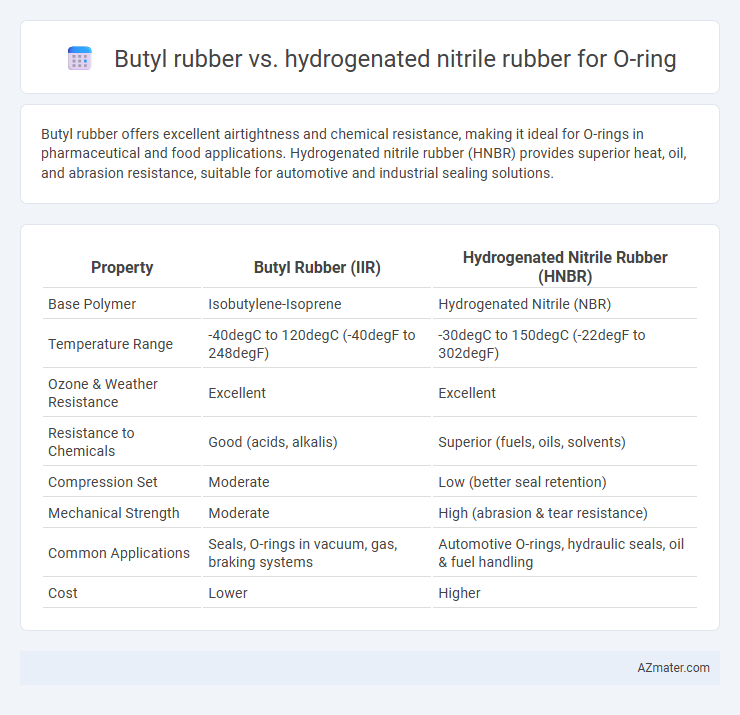
Butyl rubber offers excellent airtightness and chemical resistance, making it ideal for O-rings in pharmaceutical and food applications. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior heat, oil, and abrasion resistance, suitable for automotive and industrial sealing solutions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Butyl Rubber (IIR) | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Base Polymer | Isobutylene-Isoprene | Hydrogenated Nitrile (NBR) |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC (-40degF to 248degF) | -30degC to 150degC (-22degF to 302degF) |
| Ozone & Weather Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Resistance to Chemicals | Good (acids, alkalis) | Superior (fuels, oils, solvents) |
| Compression Set | Moderate | Low (better seal retention) |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate | High (abrasion & tear resistance) |
| Common Applications | Seals, O-rings in vacuum, gas, braking systems | Automotive O-rings, hydraulic seals, oil & fuel handling |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Butyl Rubber and Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber
Butyl rubber (IIR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent impermeability to gases, good chemical resistance, and outstanding flexibility at low temperatures, making it ideal for O-rings in sealing applications requiring airtightness. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior heat, ozone, and oil resistance due to hydrogenation of nitrile butadiene rubber, providing enhanced durability and mechanical properties in harsh environments. Both materials are widely used for O-rings, with butyl rubber favored for applications needing high gas impermeability and HNBR chosen where thermal and chemical resistance are critical.
Chemical Structure and Composition Differences
Butyl rubber (IIR) features a copolymer of isobutylene with a small amount of isoprene, resulting in a saturated hydrocarbon backbone with limited unsaturation, which imparts excellent impermeability and chemical resistance. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) is produced by hydrogenating nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), saturating its carbon-carbon double bonds and enhancing thermal stability and chemical resistance due to the presence of acrylonitrile units and saturated hydrocarbon segments. The key compositional difference lies in butyl rubber's isobutylene-based structure versus HNBR's hydrogenated copolymer of butadiene and acrylonitrile, driving their distinct performance in O-ring applications under aggressive chemical and thermal conditions.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Butyl rubber offers excellent airtightness, low gas permeability, and good resistance to ozone and weathering, making it ideal for O-rings in static sealing applications. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and higher temperature tolerance up to 150degC, suitable for dynamic O-rings exposed to oils, fuels, and harsh chemicals. Comparing key physical properties, butyl rubber has lower hardness (40-80 Shore A) and elongation (300-450%), whereas HNBR exhibits higher hardness (60-90 Shore A) and tensile strength (20-30 MPa), optimizing performance depending on the application requirements.
Temperature Resistance: Butyl vs HNBR
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior temperature resistance compared to butyl rubber, functioning effectively in ranges from -40degC to 150degC, while butyl rubber typically operates within -40degC to 120degC. HNBR maintains mechanical strength and chemical stability at higher temperatures, making it suitable for demanding automotive and industrial O-ring applications. In contrast, butyl rubber excels in low gas permeability but loses elasticity faster under elevated thermal conditions.
Chemical Compatibility: Performance in Harsh Environments
Butyl rubber exhibits excellent resistance to polar solvents, acids, and alkalis, making it suitable for applications involving exposure to harsh chemicals and weathering. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical compatibility with oils, fuels, and high-temperature fluids due to its enhanced saturation, providing resilience against swelling and degradation in aggressive environments. When selecting O-rings for harsh conditions, HNBR outperforms Butyl rubber in oil resistance and thermal stability, while Butyl excels in resistance to ozone and polar solvents.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Butyl rubber O-rings provide excellent resistance to compression set and maintain good elasticity, making them suitable for sealing applications under moderate mechanical stress. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) O-rings exhibit superior tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and oil resistance, resulting in enhanced mechanical durability and longer service life in harsh environments. HNBR outperforms butyl rubber in high-temperature stability and resistance to wear, ensuring optimal performance in dynamic sealing applications.
Compression Set and Elasticity Performance
Butyl rubber exhibits excellent compression set resistance due to its low gas permeability and high resilience, making it ideal for O-rings requiring long-term elasticity under static conditions. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior elasticity and higher resistance to heat, chemicals, and abrasion, resulting in improved compression set performance at elevated temperatures. Selecting between butyl and HNBR O-rings depends on the specific application environment, with butyl favored for sealing gases and HNBR preferred for dynamic sealing under harsh conditions.
Common Applications in O-Ring Sealing
Butyl rubber O-rings excel in applications requiring excellent impermeability to gases, such as in pharmaceutical and food processing equipment, due to their low permeability and chemical resistance. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) O-rings are preferred in automotive and industrial fluid sealing because of their superior resistance to heat, oil, and aggressive chemicals. Both materials provide reliable sealing solutions, with butyl rubber favored for its flexibility in low temperatures and HNBR chosen for high-performance environments demanding durability and chemical resistance.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Butyl rubber O-rings offer lower material costs and high availability due to widespread production and established supply chains, making them a cost-effective choice for standard sealing applications. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) O-rings typically have higher prices reflecting advanced chemical resistance and performance but may face limited availability depending on supplier and grade requirements. Cost and availability considerations drive selection between butyl rubber for economical and readily accessible O-rings versus HNBR when higher durability justifies premium pricing.
Choosing the Right Material for O-Rings: Butyl Rubber or HNBR
Butyl rubber offers excellent resistance to ozone, weathering, and chemicals, making it ideal for O-rings used in sealing applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior mechanical strength, improved heat resistance up to 150degC, and enhanced oil and fuel compatibility, which makes it suitable for high-performance automotive and industrial seals. Selecting between butyl and HNBR for O-rings depends on the specific application requirements such as temperature range, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress to ensure optimal sealing performance and durability.
Infographic: Butyl rubber vs Hydrogenated nitrile rubber for O-ring
 azmater.com
azmater.com