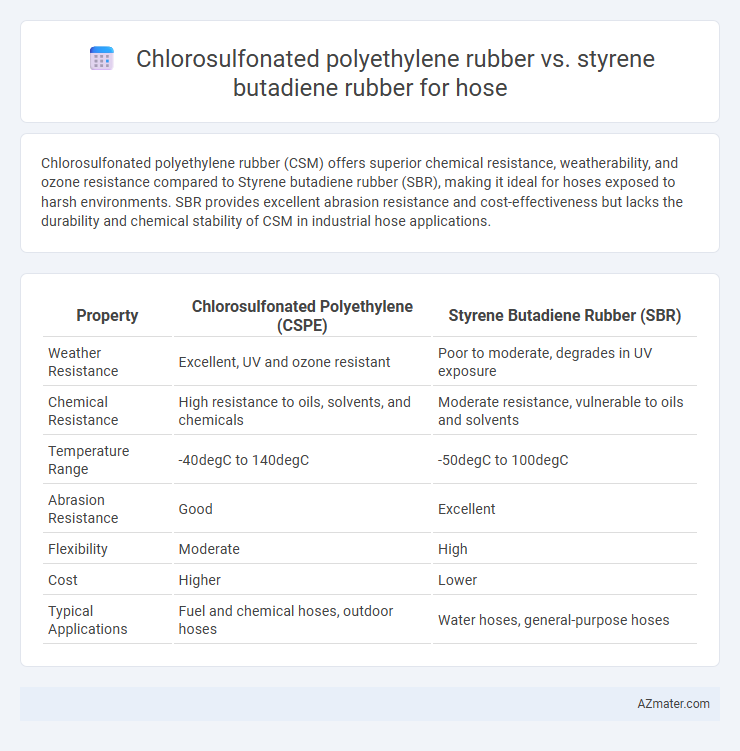
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) offers superior chemical resistance, weatherability, and ozone resistance compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making it ideal for hoses exposed to harsh environments. SBR provides excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness but lacks the durability and chemical stability of CSM in industrial hose applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene (CSPE) | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Weather Resistance | Excellent, UV and ozone resistant | Poor to moderate, degrades in UV exposure |
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to oils, solvents, and chemicals | Moderate resistance, vulnerable to oils and solvents |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 140degC | -50degC to 100degC |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Flexibility | Moderate | High |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Typical Applications | Fuel and chemical hoses, outdoor hoses | Water hoses, general-purpose hoses |
Introduction to Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene Rubber and Styrene Butadiene Rubber
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers exceptional resistance to ozone, weathering, and chemicals, making it highly suitable for hose applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) provides excellent abrasion resistance and moderate heat resistance, commonly used in general-purpose hoses requiring durability against mechanical wear. Understanding the chemical structure and performance properties of CSM and SBR is essential for selecting the appropriate elastomer in hose manufacturing.
Key Properties Comparison: CSM vs SBR
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers superior resistance to ozone, weathering, and chemicals compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making it ideal for harsh environments. SBR provides better abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, but its performance declines faster under UV exposure and aggressive chemical conditions. CSM's enhanced heat and oil resistance ensures longer hose life in industrial applications, while SBR remains popular for general-purpose hoses requiring moderate durability and flexibility.
Chemical Resistance: CSM vs SBR Performance
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), particularly against oils, weathering, ozone, and fuels. CSM maintains elasticity and physical integrity in aggressive chemical environments, making it ideal for hoses exposed to hydrocarbons and solvents. SBR, while cost-effective and abrasion-resistant, degrades faster in presence of oils, acids, and alkalis, limiting its use in chemically demanding hose applications.
Temperature Tolerance of CSM and SBR Hoses
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) hoses offer superior temperature tolerance, typically withstanding continuous exposure between -40degC to 130degC and short-term spikes up to 150degC, making them ideal for high-temperature industrial applications. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) hoses generally operate within a narrower temperature range of -40degC to 82degC, limiting their use in environments involving elevated heat. The enhanced thermal stability of CSM hoses ensures better resistance to heat aging and degradation compared to SBR hoses, promoting longer operational lifespan in demanding temperature conditions.
Abrasion and Wear Resistance Analysis
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) offers superior abrasion and wear resistance compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making it more suitable for hose applications subjected to harsh mechanical stress. CSM's densely cross-linked molecular structure and enhanced chemical stability contribute to its durability against surface wear and prolonged operational life. In contrast, SBR, while cost-effective, exhibits lower resistance to abrasive environments, leading to faster degradation under heavy friction and abrasive conditions in hose usage.
Flexibility and Handling in Hose Applications
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers superior flexibility and excellent ozone and chemical resistance, making it ideal for hoses exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) provides good abrasion resistance and moderate flexibility but tends to be less pliable than CSM, limiting its performance in applications requiring frequent bending or handling. For hose applications demanding enhanced flexibility and easier handling, CSM rubber outperforms SBR by maintaining elasticity and durability under dynamic stress.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber generally exhibits higher material costs compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) due to its superior chemical and weather resistance, making it a premium choice for hoses exposed to harsh environments. SBR remains more cost-effective and widely available, benefiting from large-scale production and extensive use in general-purpose hose applications. When selecting hose materials, budget constraints and local supply chain variability often prioritize SBR for economical projects, while CSM is preferred where durability and resistance justify the higher initial investment.
Environmental and Weather Resistance
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber offers superior resistance to ozone, UV exposure, and a wide range of chemicals compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making it highly suitable for outdoor hose applications subjected to harsh weather conditions. CSPE maintains flexibility and mechanical integrity at elevated temperatures and in aggressive environments, whereas SBR tends to degrade faster under prolonged UV radiation and ozone exposure. The enhanced durability of CSPE in environmental stress factors translates to a longer service life and reduced maintenance costs for hoses used in industrial and marine settings.
Typical Applications in Hose Manufacturing
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber excels in hose manufacturing for chemical transfer, fuel lines, and industrial hoses due to its superior resistance to chemicals, ozone, and weathering. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) is preferred in general-purpose hoses like water suction, discharge, and air hoses owing to its good abrasion resistance and flexibility at low costs. CSM hoses outperform SBR counterparts in harsh environments requiring long-term durability and resistance to aggressive substances.
Choosing the Right Rubber: CSM or SBR for Hose
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber exhibits superior resistance to chemicals, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for hoses exposed to harsh environmental conditions or aggressive fluids. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and good mechanical properties, suited for general-purpose hoses requiring flexibility and durability under moderate stress. Selecting CSM ensures enhanced longevity in demanding applications, while SBR delivers cost-effective performance in less aggressive environments.
Infographic: Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber vs Styrene butadiene rubber for Hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com