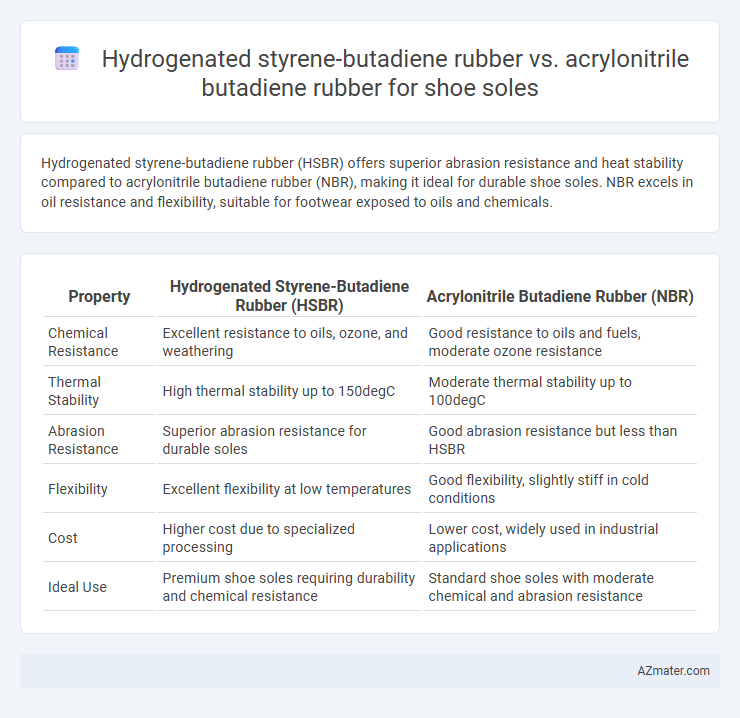
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and heat stability compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), making it ideal for durable shoe soles. NBR excels in oil resistance and flexibility, suitable for footwear exposed to oils and chemicals.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, ozone, and weathering | Good resistance to oils and fuels, moderate ozone resistance |
| Thermal Stability | High thermal stability up to 150degC | Moderate thermal stability up to 100degC |
| Abrasion Resistance | Superior abrasion resistance for durable soles | Good abrasion resistance but less than HSBR |
| Flexibility | Excellent flexibility at low temperatures | Good flexibility, slightly stiff in cold conditions |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialized processing | Lower cost, widely used in industrial applications |
| Ideal Use | Premium shoe soles requiring durability and chemical resistance | Standard shoe soles with moderate chemical and abrasion resistance |
Introduction to Synthetic Rubbers in Footwear
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) and acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) are key synthetic rubbers used in shoe sole manufacturing due to their distinct properties. HSBR offers enhanced heat resistance, abrasion resistance, and durability, making it ideal for high-performance athletic footwear requiring long-lasting soles. NBR provides superior oil and chemical resistance along with excellent flexibility, often favored in industrial and work footwear where exposure to oils and lubricants is common.
Chemical Structure: H-SBR vs NBR
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (H-SBR) features a partially or fully hydrogenated backbone that increases its resistance to heat, oxidation, and ozone compared to standard styrene-butadiene rubber, making it ideal for durable shoe soles with enhanced aging properties. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) contains acrylonitrile groups that provide excellent oil, fuel, and chemical resistance but can be less flexible at low temperatures due to its polar nitrile content. The saturated hydrocarbon backbone of H-SBR offers superior flexibility and weather resistance, while the polar nitrile groups in NBR deliver enhanced chemical resistance, influencing material selection based on the shoe sole's intended use environment.
Physical Properties Comparison
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) exhibits superior abrasion resistance and enhanced tensile strength compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), making it ideal for shoe soles requiring durability and wear resistance. NBR provides better oil and chemical resistance due to its high acrylonitrile content, which is advantageous in environments exposed to fuels and oils but typically shows lower flexibility and tear resistance than HSBR. The choice between HSBR and NBR shoe soles depends on the balance needed between mechanical strength and resistance to chemical exposure in specific footwear applications.
Abrasion Resistance and Durability
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior abrasion resistance compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), making HSBR a more durable choice for shoe soles subjected to frequent wear. The hydrogenation process enhances the polymer's stability against heat and oxidation, prolonging the lifespan of the sole in harsh conditions. NBR, while resistant to oil and chemicals, typically exhibits lower abrasion resistance and may wear faster under heavy mechanical stress.
Flexibility and Comfort in Shoe Soles
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior flexibility and excellent abrasion resistance, making it ideal for shoe soles requiring durability and smooth performance under variable temperatures. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), while providing high oil and chemical resistance, tends to be less flexible and can result in a stiffer sole with reduced cushioning, impacting overall comfort. For shoe soles prioritizing flexibility and comfort, HSBR delivers enhanced resilience and elasticity, ensuring a more comfortable, adaptive wear experience.
Oil and Chemical Resistance Performance
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior oil and chemical resistance compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), due to its saturated polymer backbone that resists hydrocarbon attack and oxidative degradation. NBR provides good resistance to oils and fuels, but its performance declines with exposure to aromatic and chlorinated solvents, limiting durability in harsh chemical environments. Shoe soles made with HSBR exhibit enhanced longevity and dimensional stability when subjected to oils, greases, and chemical contaminants, making HSBR a preferred choice for industrial and heavy-duty footwear applications.
Weather and Temperature Resistance
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior weather and temperature resistance compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), making it more suitable for shoe soles exposed to extreme conditions. HSBR exhibits excellent oxidative stability and resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and heat aging, maintaining flexibility in temperatures ranging from -50degC to 120degC. In contrast, NBR provides good oil and abrasion resistance but tends to harden and crack under prolonged UV exposure and extreme temperature variations.
Cost Efficiency and Production Considerations
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and aging stability compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), making it more cost-efficient for durable shoe soles with longer lifecycle performance. NBR, favored for its excellent oil and chemical resistance, generally incurs lower material costs and requires less complex processing, which can reduce initial production expenses. Production considerations highlight that HSBR demands higher curing temperatures and longer cycle times, potentially increasing manufacturing overhead compared to the faster, more versatile vulcanization process of NBR.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers improved durability and resistance to oxidation, leading to longer-lasting shoe soles that reduce waste over time compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR). NBR production generally involves higher energy consumption and releases more toxic byproducts, posing greater environmental challenges in manufacturing and disposal. Sustainable practices favor HSBR due to its enhanced lifecycle performance and lower ecological footprint in shoe sole applications.
Best Applications: Choosing the Right Rubber for Shoe Soles
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and thermal stability, making it ideal for high-performance athletic shoe soles that require durability and heat resistance. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) excels in oil and chemical resistance, making it more suitable for industrial or work boots frequently exposed to harsh environments. Selecting the right rubber depends on the specific performance requirements of the shoe, with HSBR favored for flexibility and durability in sports footwear and NBR preferred for protective, oil-resistant applications.
Infographic: Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber vs Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber for Shoe sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com