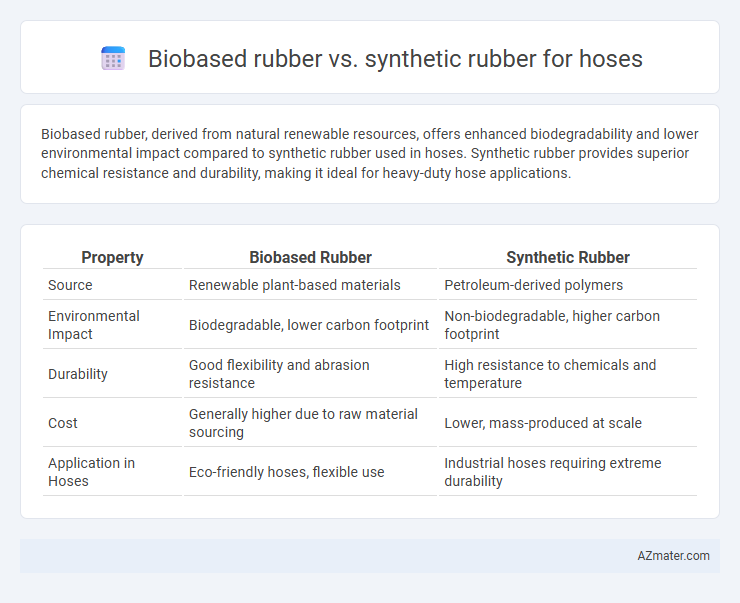
Biobased rubber, derived from natural renewable resources, offers enhanced biodegradability and lower environmental impact compared to synthetic rubber used in hoses. Synthetic rubber provides superior chemical resistance and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty hose applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Biobased Rubber | Synthetic Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Renewable plant-based materials | Petroleum-derived polymers |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, lower carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, higher carbon footprint |
| Durability | Good flexibility and abrasion resistance | High resistance to chemicals and temperature |
| Cost | Generally higher due to raw material sourcing | Lower, mass-produced at scale |
| Application in Hoses | Eco-friendly hoses, flexible use | Industrial hoses requiring extreme durability |
Introduction to Biobased and Synthetic Rubber
Biobased rubber, derived from natural sources such as Hevea brasiliensis latex and guayule plants, offers sustainable alternatives with renewable raw materials and lower environmental impact. Synthetic rubber, produced from petrochemical monomers like styrene and butadiene, delivers consistent performance, high abrasion resistance, and superior heat tolerance in hose applications. Hose manufacturers often select biobased rubber for eco-friendly properties while synthetic rubber remains preferred for durability and chemical resistance.
Key Raw Materials: Biobased vs Synthetic Rubber
Biobased rubber for hoses primarily relies on natural latex extracted from Hevea brasiliensis trees, providing a renewable and environmentally friendly raw material with inherent elasticity and degradation resistance. Synthetic rubber, such as styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) or nitrile rubber (NBR), is derived from petrochemical sources like butadiene and styrene, offering tailored chemical resistance and durability but with higher environmental impact. The choice between biobased and synthetic raw materials influences the hose's performance, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness in industrial applications.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Biobased rubber for hoses significantly reduces carbon footprint by utilizing renewable resources like natural latex, lowering greenhouse gas emissions compared to synthetic rubber derived from petroleum. The biodegradability of biobased rubber contributes to reduced environmental pollution and landfill waste, contrasting with synthetic rubber's persistence and potential microplastic contamination. Energy consumption during production is generally lower for biobased rubber, enhancing its sustainability profile relative to the energy-intensive synthesis of synthetic rubber.
Mechanical Performance and Durability
Biobased rubber for hoses exhibits competitive tensile strength and elasticity, often approaching the mechanical performance of synthetic rubber, which typically offers superior resistance to abrasion and higher tear strength. Durability in biobased rubber benefits from enhanced biodegradability and environmental resistance, but synthetic rubber usually outperforms in extreme temperature stability and chemical resistance. Advances in biobased formulations aim to close the gap, optimizing wear resistance and extending service life for demanding hose applications.
Flexibility and Temperature Resistance
Biobased rubber offers superior flexibility due to its natural polymer structure, making it ideal for applications requiring frequent bending or twisting. Synthetic rubber, such as EPDM or NBR, excels in temperature resistance, maintaining performance in extreme heat up to 150degC and cold conditions down to -40degC. Hose manufacturers often choose synthetic rubber for environments with fluctuating temperatures, while biobased rubber is preferred for sustainable, flexible hose solutions.
Cost Analysis: Biobased vs Synthetic Rubber
Biobased rubber for hoses typically incurs higher upfront costs due to limited production scale and raw material sourcing compared to synthetic rubber, which benefits from established manufacturing processes and economies of scale. Over the long term, biobased rubber may offer cost advantages through sustainability incentives and reduced environmental compliance expenses. Synthetic rubber remains more cost-effective for large-volume hose production but faces potential future cost increases linked to petrochemical price volatility and regulatory pressures.
Chemical Resistance in Hose Applications
Biobased rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to synthetic rubber in hose applications, particularly against fuels, oils, and solvents, enhancing durability and lifespan. Its natural polymer structure resists degradation from hydrocarbons and aggressive chemicals, making it suitable for eco-friendly and high-performance hoses. Synthetic rubber, while versatile, often requires additives to improve chemical resistance, which can compromise environmental sustainability and increase maintenance costs.
Industry Standards and Certifications
Biobased rubber hoses meet emerging industry standards such as ASTM D6814 and EN 13479, reflecting growing demand for sustainable materials without compromising durability and performance. Synthetic rubber hoses typically conform to established standards like ISO 1827 and SAE J517, ensuring resistance to chemicals, temperature extremes, and mechanical wear. Certifications such as FDA compliance for food-grade applications and REACH for chemical safety apply to both types, with biobased variants increasingly achieving eco-labels like USDA BioPreferred and Cradle to Cradle certification to verify environmental impact reduction.
Market Trends and Future Prospects
Biobased rubber is gaining significant traction in the hose market due to increasing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly materials, driven by regulatory pressures and consumer preference for green products. Synthetic rubber continues to dominate with its superior durability and cost-effectiveness, but innovations in biobased alternatives enhance performance and broaden application scopes in industrial hoses. Market forecasts indicate a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 7% for biobased rubber in hose manufacturing, highlighting expanding investments and technological advancements aimed at reducing carbon footprints.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Hose Manufacturing
Biobased rubber offers superior eco-friendly benefits and enhanced biodegradability compared to synthetic rubber, making it an excellent choice for sustainable hose manufacturing. Synthetic rubber provides greater abrasion resistance, chemical stability, and consistent performance under extreme temperatures, ideal for industrial hose applications requiring durability. Selecting the right rubber depends on specific hose requirements such as environmental impact, flexibility, resistance to oils or chemicals, and operational lifespan to optimize functionality and sustainability.
Infographic: Biobased rubber vs Synthetic rubber for Hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com