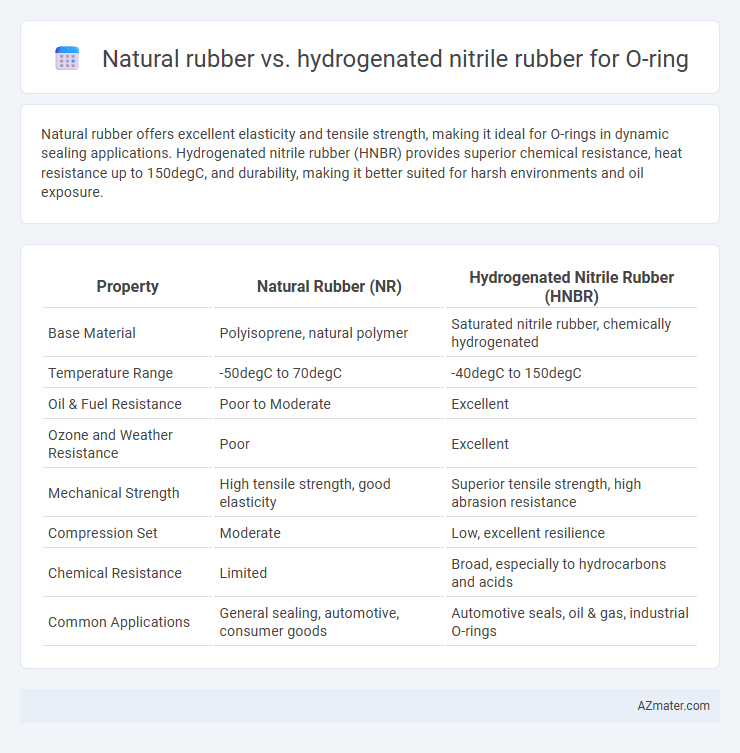
Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and tensile strength, making it ideal for O-rings in dynamic sealing applications. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior chemical resistance, heat resistance up to 150degC, and durability, making it better suited for harsh environments and oil exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Natural Rubber (NR) | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Base Material | Polyisoprene, natural polymer | Saturated nitrile rubber, chemically hydrogenated |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 70degC | -40degC to 150degC |
| Oil & Fuel Resistance | Poor to Moderate | Excellent |
| Ozone and Weather Resistance | Poor | Excellent |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, good elasticity | Superior tensile strength, high abrasion resistance |
| Compression Set | Moderate | Low, excellent resilience |
| Chemical Resistance | Limited | Broad, especially to hydrocarbons and acids |
| Common Applications | General sealing, automotive, consumer goods | Automotive seals, oil & gas, industrial O-rings |
Introduction to O-Ring Materials
Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity, tear resistance, and resilience, making it suitable for dynamic sealing applications, but it degrades quickly when exposed to oils, fuels, and high temperatures. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior chemical resistance, heat resistance up to 150degC, and enhanced abrasion resistance, making it ideal for automotive and industrial O-rings operating in harsh environments. Choosing between natural rubber and HNBR depends on factors like exposure to chemicals, temperature ranges, and mechanical stress in sealing applications.
What is Natural Rubber?
Natural rubber is an elastomer derived from the latex sap of rubber trees, primarily Hevea brasiliensis, known for its high tensile strength, flexibility, and excellent elasticity. It offers superior resistance to wear and tear but has limited resistance to oils, fuels, and certain chemicals, making it less suitable for harsh environments compared to hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR). Natural rubber O-rings are ideal for applications requiring good mechanical properties and resilience under moderate temperature and pressure conditions.
Properties and Performance of Natural Rubber O-Rings
Natural rubber O-rings exhibit excellent elasticity, high tensile strength, and superior flexibility at low temperatures, making them ideal for dynamic sealing applications. They offer outstanding resistance to abrasion, tear, and fatigue but show limited chemical resistance against oils, fuels, and solvents. Natural rubber is preferred in environments requiring resilience and mechanical performance but may degrade faster when exposed to hydrocarbons compared to hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR).
Understanding Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance, high tensile strength, and enhanced heat and ozone resistance compared to Natural Rubber, making it ideal for demanding O-ring applications in automotive and industrial environments. HNBR's hydrogenation process improves its resistance to oils, fuels, and harsh chemicals, extending the lifespan of O-rings in dynamic and static sealing conditions. Unlike Natural Rubber, HNBR maintains elasticity and durability at elevated temperatures up to 150degC, ensuring reliable sealing performance in extreme operational settings.
Key Advantages of HNBR O-Rings
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) O-rings offer superior chemical resistance, particularly against oils, fuels, and ozone, making them ideal for automotive and industrial applications. Their excellent thermal stability allows operation in a wide temperature range from -40degC to 150degC, outperforming natural rubber which degrades more rapidly under heat. HNBR O-rings also exhibit enhanced mechanical properties such as high tensile strength and abrasion resistance, providing longer service life and improved sealing reliability compared to natural rubber counterparts.
Chemical Resistance: Natural Rubber vs Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to natural rubber, particularly against oils, fuels, and various solvents, making it ideal for demanding industrial applications. Natural rubber tends to degrade quickly when exposed to hydrocarbons, ozone, and acids, limiting its use in harsh chemical environments. The enhanced stability and resistance of HNBR to oxidation and thermal degradation significantly extend the lifespan of O-rings in aggressive chemical conditions.
Temperature Tolerance Comparison
Natural rubber O-rings exhibit temperature tolerance typically ranging from -50degC to 70degC, making them suitable for moderate temperature applications. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) O-rings withstand a broader temperature range, from approximately -40degC up to 150degC, offering enhanced performance in high-heat environments. The superior thermal stability of HNBR enables reliable sealing in automotive and industrial applications where elevated temperatures are common.
Applications: When to Use Natural Rubber or HNBR O-Rings
Natural rubber O-rings excel in applications requiring excellent elasticity, low-temperature flexibility, and resistance to wear, making them ideal for automotive valves, seals in water systems, and general-purpose sealing where exposure to oils and chemicals is minimal. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) O-rings offer superior chemical, heat, and ozone resistance, making them suitable for high-temperature environments, automotive fuel systems, and industrial hydraulic seals that must withstand harsh chemicals and extreme temperatures up to 150degC. Choosing between natural rubber and HNBR O-rings depends on the specific service conditions, with natural rubber favored for cost-effective, flexible sealing and HNBR preferred in demanding industrial or automotive applications requiring enhanced durability and resistance.
Cost Considerations for O-Ring Selection
Natural rubber O-rings generally offer a lower initial cost compared to hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) due to simpler manufacturing processes and readily available raw materials. However, HNBR provides superior chemical resistance, heat stability, and durability, reducing long-term replacement and maintenance expenses in demanding applications. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including performance lifespan and environmental resistance, is crucial when selecting O-rings for industrial use.
Choosing the Right Material: Key Takeaways
Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for dynamic applications requiring flexibility. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior oil, heat, and chemical resistance, suitable for high-performance sealing in automotive and industrial environments. Selecting the right O-ring material depends on operating temperature, exposure to chemicals, and mechanical stress, with HNBR favored for harsh conditions and natural rubber for versatility and cost-effectiveness.
Infographic: Natural rubber vs Hydrogenated nitrile rubber for O-ring
 azmater.com
azmater.com