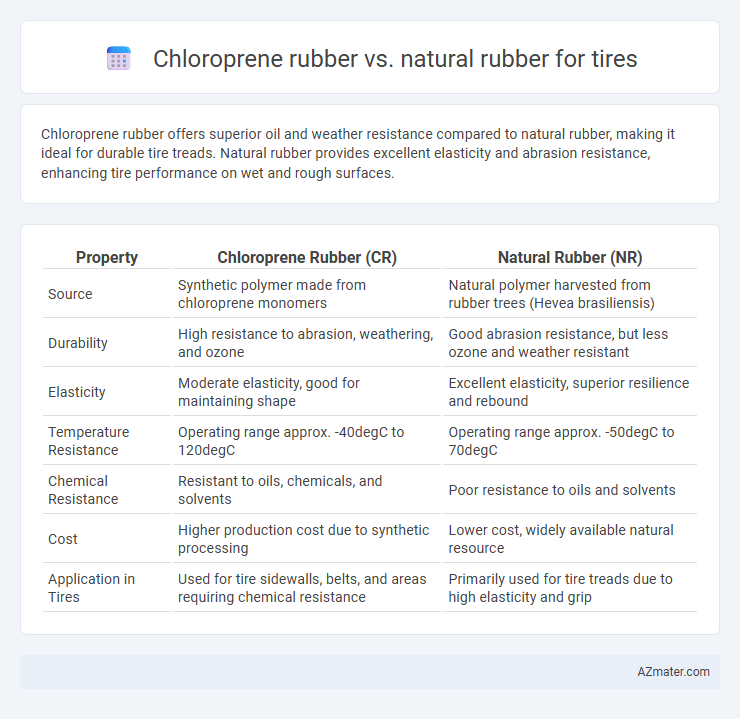
Chloroprene rubber offers superior oil and weather resistance compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for durable tire treads. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and abrasion resistance, enhancing tire performance on wet and rough surfaces.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chloroprene Rubber (CR) | Natural Rubber (NR) |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Synthetic polymer made from chloroprene monomers | Natural polymer harvested from rubber trees (Hevea brasiliensis) |
| Durability | High resistance to abrasion, weathering, and ozone | Good abrasion resistance, but less ozone and weather resistant |
| Elasticity | Moderate elasticity, good for maintaining shape | Excellent elasticity, superior resilience and rebound |
| Temperature Resistance | Operating range approx. -40degC to 120degC | Operating range approx. -50degC to 70degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to oils, chemicals, and solvents | Poor resistance to oils and solvents |
| Cost | Higher production cost due to synthetic processing | Lower cost, widely available natural resource |
| Application in Tires | Used for tire sidewalls, belts, and areas requiring chemical resistance | Primarily used for tire treads due to high elasticity and grip |
Introduction to Chloroprene Rubber and Natural Rubber
Chloroprene rubber (CR), also known as neoprene, is a synthetic elastomer noted for its excellent resistance to oil, chemicals, and weathering, making it suitable for tire applications requiring durability under harsh conditions. Natural rubber (NR) is a polyisoprene biopolymer derived from the latex of rubber trees, valued for its superior elasticity, tensile strength, and low heat build-up, which are critical properties in tire manufacturing. Both materials are essential in tire compounds, with CR providing enhanced chemical and abrasion resistance while NR offers unmatched resilience and flexibility.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Chloroprene rubber (CR) consists of polychloroprene polymers featuring chlorine atoms in its molecular chain, which provide enhanced resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering compared to natural rubber (NR). Natural rubber is primarily composed of cis-1,4-polyisoprene, a hydrocarbon polymer with a high degree of unsaturation, contributing to its excellent elasticity and tensile strength but lower resistance to environmental degradation. The presence of chlorine in chloroprene rubber's chemical structure imparts superior durability and thermal stability, making it more suitable for tire applications requiring chemical resistance and longer service life.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Chloroprene rubber (CR) undergoes a polymerization process using chloroprene monomers, producing a synthetic polymer with enhanced weather resistance and chemical stability, while natural rubber (NR) is sourced from latex sap of rubber trees through coagulation and drying. In tire manufacturing, CR requires specialized compounding with accelerators and vulcanizing agents to optimize its unique chlorine-containing polymer matrix, contrasting with the sulfur vulcanization process commonly applied to NR for improved elasticity and tensile strength. The manufacturing process of CR tires integrates heat-resistant and oil-resistant additives, leading to better performance in harsh environments compared to NR, which is preferred for its superior resilience and abrasion resistance.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Chloroprene rubber (CR) offers superior ozone and weather resistance compared to natural rubber (NR), making it ideal for tire applications exposed to harsh environments. CR exhibits better tensile strength and abrasion resistance, contributing to longer tire life and enhanced durability. In contrast, NR provides higher elasticity and resilience, resulting in improved traction and ride comfort but lower aging resistance.
Heat and Weather Resistance
Chloroprene rubber offers superior heat and weather resistance compared to natural rubber, making it more suitable for tire applications exposed to extreme temperatures and harsh environmental conditions. Its molecular structure provides enhanced resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and oxidation, which helps maintain tire integrity and performance over time. Natural rubber tends to degrade faster under prolonged heat and weather exposure, leading to reduced durability and increased maintenance requirements.
Performance in Wet and Dry Conditions
Chloroprene rubber offers superior resistance to abrasion and excellent wet traction, making it highly effective for tire performance in rainy or slippery conditions. Natural rubber provides exceptional elasticity and grip on dry surfaces, enhancing tire durability and handling in dry environments. Tires combining chloroprene rubber and natural rubber optimize performance across both wet and dry conditions by balancing traction, wear resistance, and flexibility.
Durability and Aging Characteristics
Chloroprene rubber exhibits superior durability and aging resistance compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for tire manufacturing in harsh environments. Its molecular structure provides enhanced resistance to ozone, weathering, and heat degradation, extending tire lifespan significantly. Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and tensile strength but degrades faster under UV exposure and oxidative conditions, leading to reduced durability in long-term use.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Chloroprene rubber (CR), known for its chemical resistance and durability, poses environmental challenges due to energy-intensive production and reliance on petrochemicals, contributing to higher carbon emissions compared to natural rubber (NR). Natural rubber, harvested from Hevea brasiliensis trees, offers a renewable, biodegradable option with lower carbon footprint and supports biodiversity when sourced sustainably through agroforestry practices. Sustainable tire manufacturing increasingly favors NR for its environmental benefits, but efforts to improve CR's eco-profile focus on bio-based feedstocks and cleaner processing technologies.
Cost and Market Availability
Chloroprene rubber typically incurs higher production costs due to its synthetic nature and complex manufacturing process, whereas natural rubber remains more cost-effective owing to abundant global plantations, especially in Southeast Asia. Market availability of natural rubber is generally more stable and widespread, supported by large-scale harvesting and established supply chains, while chloroprene rubber availability can be limited by raw material constraints and reliance on petrochemical feedstocks. Tire manufacturers often balance these factors, choosing natural rubber for cost efficiency and supply reliability, and chloroprene rubber for specialized performance benefits despite its higher expenses.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Tires
Chloroprene rubber offers superior oil resistance, weatherability, and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty and high-performance tires. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and abrasion resistance, enhancing ride comfort and traction in standard tire applications. Selecting the right rubber depends on balancing performance requirements, environmental conditions, and cost-effectiveness for specific tire uses.
Infographic: Chloroprene rubber vs Natural rubber for Tire
 azmater.com
azmater.com