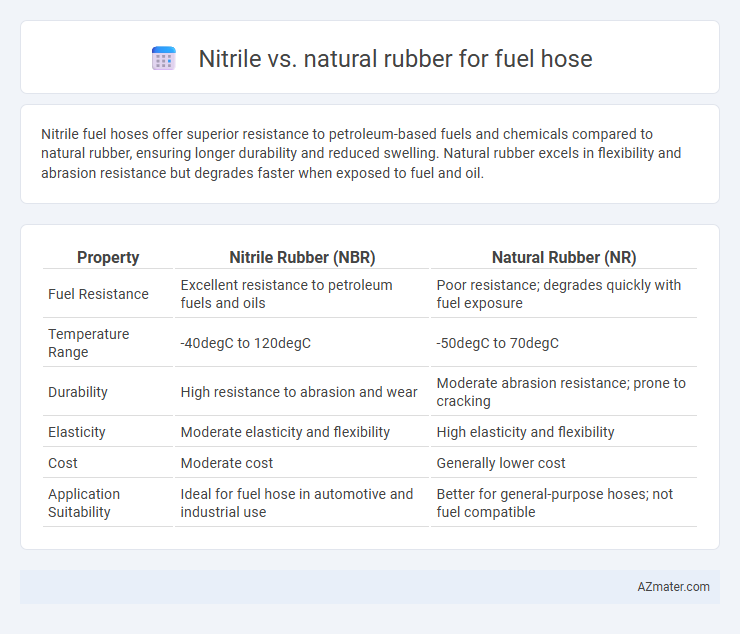
Nitrile fuel hoses offer superior resistance to petroleum-based fuels and chemicals compared to natural rubber, ensuring longer durability and reduced swelling. Natural rubber excels in flexibility and abrasion resistance but degrades faster when exposed to fuel and oil.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) | Natural Rubber (NR) |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Resistance | Excellent resistance to petroleum fuels and oils | Poor resistance; degrades quickly with fuel exposure |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -50degC to 70degC |
| Durability | High resistance to abrasion and wear | Moderate abrasion resistance; prone to cracking |
| Elasticity | Moderate elasticity and flexibility | High elasticity and flexibility |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Generally lower cost |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for fuel hose in automotive and industrial use | Better for general-purpose hoses; not fuel compatible |
Overview of Nitrile and Natural Rubber Materials
Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers exceptional resistance to fuels, oils, and chemicals, making it an ideal material for fuel hoses that require durability and chemical compatibility. Natural rubber provides excellent flexibility and tensile strength but has limited resistance to oils and fuels, often degrading when exposed to such substances. The choice between nitrile and natural rubber for fuel hoses depends primarily on the operational environment and the type of fluids conveyed.
Key Chemical Properties Affecting Fuel Resistance
Nitrile rubber (NBR) exhibits superior resistance to hydrocarbons due to its high acrylonitrile content, which enhances its fuel resistance by reducing swelling and degradation in contact with gasoline and diesel. In contrast, natural rubber lacks the polar nitrile groups, making it more susceptible to swelling, cracking, and breakdown when exposed to fuels and oils. The chemical structure of nitrile rubber provides greater barrier properties against aromatic and aliphatic hydrocarbons, making it the preferred material for fuel hoses requiring durability and chemical resistance.
Performance in Fuel Hose Applications
Nitrile rubber offers superior resistance to petroleum-based fuels and oils, making it an optimal choice for fuel hose applications where chemical durability is critical. Natural rubber provides excellent flexibility and mechanical strength but degrades faster when exposed to gasoline, diesel, and other hydrocarbons. The performance of nitrile in fuel hoses ensures longer service life and reduced maintenance due to its enhanced fuel and abrasion resistance properties.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Nitrile fuel hoses exhibit superior resistance to petroleum-based fuels, oils, and chemicals, enhancing durability compared to natural rubber counterparts prone to swelling and degradation when exposed to hydrocarbons. The synthetic structure of nitrile compounds contributes to an extended lifespan, maintaining flexibility and preventing cracking over prolonged fuel exposure. Natural rubber hoses generally offer better abrasion resistance but demonstrate shorter service life under continuous contact with fuel, making nitrile the preferred choice for demanding fuel hose applications.
Flexibility and Handling Differences
Nitrile fuel hoses exhibit superior flexibility compared to natural rubber, maintaining pliability across a broader temperature range, which enhances ease of handling during installation and maintenance. Natural rubber hoses tend to stiffen in cold conditions, reducing flexibility and complicating maneuverability in tight engine spaces. The chemical resistance of nitrile to hydrocarbons further supports consistent performance, making it the preferred choice for fuel applications requiring durable and flexible hoses.
Temperature Tolerance and Stability
Nitrile rubber offers superior temperature tolerance for fuel hoses, typically withstanding -40degC to 120degC, while natural rubber degrades faster under heat, limiting its range to approximately -50degC to 70degC. Nitrile's chemical structure provides enhanced stability against fuel exposure and high temperatures, reducing swelling and cracking over time. Natural rubber lacks the same resistance, making it less ideal for fuel hose applications requiring long-term thermal stability and durability.
Compatibility with Fuel Types and Additives
Nitrile rubber exhibits superior compatibility with a wide range of fuels, including gasoline, diesel, and ethanol blends, due to its excellent resistance to hydrocarbons and fuel additives like antioxidants and detergents. Natural rubber, while offering good flexibility and abrasion resistance, tends to degrade quickly when exposed to aromatic hydrocarbons and certain additives, limiting its use in complex fuel environments. Therefore, nitrile hoses are preferred for fuel lines requiring enhanced chemical resistance and durability against modern fuel formulations and additives.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Nitrile fuel hoses offer superior resistance to petroleum-based fuels and chemicals, reducing the risk of leaks and environmental contamination compared to natural rubber hoses, which can degrade faster when exposed to hydrocarbons. Nitrile's enhanced durability contributes to improved safety by minimizing hose failures and potential fire hazards in fuel systems. Natural rubber hoses, while biodegradable, lack the chemical resistance needed for long-term fuel handling, making nitrile the preferred choice for both environmental protection and operational safety.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Nitrile rubber offers a cost-effective solution for fuel hoses due to its widespread availability and resistance to petroleum-based fluids, often resulting in lower replacement and maintenance expenses compared to natural rubber. Natural rubber, while less expensive upfront in some markets, suffers from limited chemical resistance and shorter lifespan in fuel applications, leading to higher long-term costs. Market availability of nitrile is more consistent globally, ensuring better supply chain reliability for fuel hose manufacturers and consumers.
Choosing the Right Material for Fuel Hoses
Nitrile rubber excels in fuel hoses due to its superior resistance to petroleum-based fuels, oils, and chemicals, ensuring durability and preventing swelling or cracking. Natural rubber offers excellent flexibility and tensile strength but degrades faster when exposed to fuels and hydrocarbons, making it less suitable for long-term fuel hose applications. Selecting nitrile over natural rubber significantly enhances fuel hose performance and lifespan in automotive and industrial environments.
Infographic: Nitrile vs Natural rubber for Fuel hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com