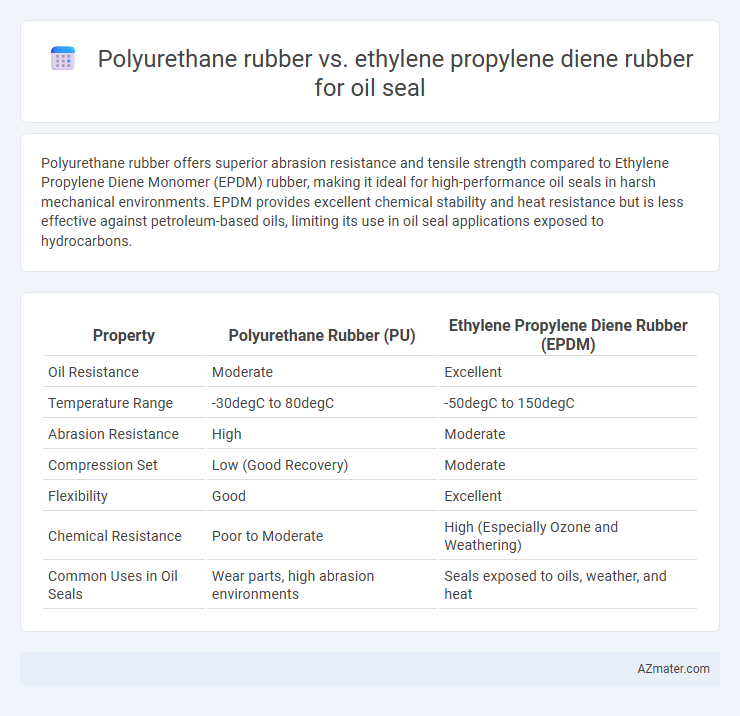
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and tensile strength compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, making it ideal for high-performance oil seals in harsh mechanical environments. EPDM provides excellent chemical stability and heat resistance but is less effective against petroleum-based oils, limiting its use in oil seal applications exposed to hydrocarbons.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane Rubber (PU) | Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Temperature Range | -30degC to 80degC | -50degC to 150degC |
| Abrasion Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Compression Set | Low (Good Recovery) | Moderate |
| Flexibility | Good | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Poor to Moderate | High (Especially Ozone and Weathering) |
| Common Uses in Oil Seals | Wear parts, high abrasion environments | Seals exposed to oils, weather, and heat |
Introduction to Oil Seal Materials
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and tensile strength, making it ideal for high-pressure oil seal applications where durability is critical. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering but has limited compatibility with petroleum-based oils and fuels. Selecting the appropriate oil seal material depends on application-specific factors such as chemical exposure, temperature range, and mechanical stress requirements.
Overview of Polyurethane Rubber (PU)
Polyurethane rubber (PU) offers superior abrasion resistance, high tensile strength, and excellent load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for oil seals in demanding mechanical environments. Its chemical resistance to oils, hydraulic fluids, and solvents ensures long-lasting performance and reduced maintenance in dynamic sealing applications. Compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM), PU provides enhanced durability and resistance to mechanical stress, extending the lifespan of oil seals in industrial machinery.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM)
Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for oil seals in automotive and industrial applications. EPDM offers superior flexibility and durability in temperatures ranging from -40degC to 150degC, outperforming many rubbers in harsh environmental conditions. Its resistance to polar substances and steam, combined with good electrical insulating properties, distinguishes EPDM as a robust material for sealing solutions where long-term reliability is essential.
Chemical Resistance: PU vs EPDM
Polyurethane (PU) rubber exhibits superior resistance to oils, fuels, and hydrocarbons, making it highly suitable for oil seals in harsh chemical environments. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber demonstrates excellent resistance to water, steam, and certain chemicals but performs poorly against petroleum-based oils and solvents. For oil seals exposed to aggressive oils and lubricants, PU outperforms EPDM in chemical resistance and durability.
Temperature Tolerance Comparison
Polyurethane rubber offers excellent temperature tolerance, typically ranging from -40degC to 90degC, making it suitable for moderate heat applications in oil seals. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) exhibits a wider temperature range, performing effectively from -50degC up to 150degC, which enhances its durability in both low and high-temperature environments. For oil seals exposed to extreme temperatures, EPDM provides superior thermal stability compared to polyurethane rubber.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Polyurethane rubber exhibits superior abrasion resistance, tensile strength, and tear resistance compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM), making it ideal for high-stress oil seal applications. EPDM offers excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and aging, but has lower mechanical strength and durability under oil exposure. For oil seals, polyurethane provides enhanced longevity and performance in dynamic sealing environments due to its high wear resistance and mechanical robustness.
Oil and Fluid Compatibility
Polyurethane rubber offers excellent abrasion resistance and high tensile strength, making it suitable for oil seals exposed to hydraulic fluids and petroleum-based oils. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in resistance to polar solvents, water, and some fuel oils but typically shows poor compatibility with petroleum-based oils and hydrocarbons. For oil seals in environments with significant exposure to engine oils or mineral oils, polyurethane provides superior fluid compatibility compared to EPDM.
Common Applications for PU and EPDM Oil Seals
Polyurethane rubber (PU) oil seals excel in hydraulic systems, heavy machinery, and automotive engines due to their superior abrasion resistance and high tensile strength. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) oil seals are widely used in water pumps, HVAC systems, and automotive cooling systems because of their excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering. PU is preferred for sealing petroleum-based oils, while EPDM is ideal for water and glycol-based fluids in oil seal applications.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and tensile strength but comes at a higher cost compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, which is generally more affordable and widely available. EPDM rubber is preferred for oil seals in non-petroleum applications due to its excellent resistance to weathering and ozone, while polyurethane is chosen for heavy-duty sealing where durability justifies the increased expense. Availability fluctuations of polyurethane can impact lead times, whereas EPDM's widespread production ensures more consistent supply and cost stability.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Oil Seal Performance
Polyurethane rubber offers exceptional abrasion resistance and high tensile strength, making it ideal for oil seals exposed to dynamic applications with heavy wear. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber excels in resistance to heat, ozone, and a wide range of chemicals, but its compatibility with oil and petroleum-based fluids is limited compared to polyurethane. Selecting the right rubber for oil seal performance depends on the specific operating environment, fluid type, and temperature range to ensure optimal durability and sealing efficiency.
Infographic: Polyurethane rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene rubber for Oil seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com