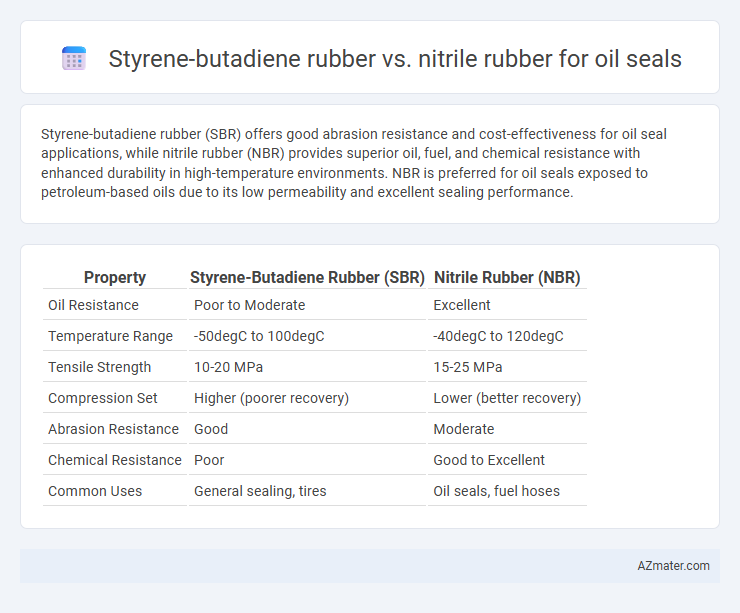
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers good abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness for oil seal applications, while nitrile rubber (NBR) provides superior oil, fuel, and chemical resistance with enhanced durability in high-temperature environments. NBR is preferred for oil seals exposed to petroleum-based oils due to its low permeability and excellent sealing performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Resistance | Poor to Moderate | Excellent |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 100degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Tensile Strength | 10-20 MPa | 15-25 MPa |
| Compression Set | Higher (poorer recovery) | Lower (better recovery) |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good | Moderate |
| Chemical Resistance | Poor | Good to Excellent |
| Common Uses | General sealing, tires | Oil seals, fuel hoses |
Introduction to Oil Seal Materials
Oil seal materials like Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) and Nitrile rubber (NBR) are critical for maintaining equipment reliability by preventing fluid leakage and contamination. Styrene-butadiene rubber offers excellent abrasion resistance and is cost-effective, but has limited resistance to oils and fuels, making it less ideal for high-exposure environments. Nitrile rubber, known for its superior oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, is widely preferred in oil seal applications where durability and sealing performance are essential under harsh operating conditions.
Overview of Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is a synthetic polymer widely used in oil seals due to its excellent abrasion resistance and aging stability under heat and oxidation. Its inherent resistance to wear and moderate resistance to oils and chemicals makes it a cost-effective choice for applications with limited exposure to aggressive fluids. SBR offers superior tensile strength and elasticity compared to natural rubber, but falls short against synthetic elastomers like Nitrile Rubber (NBR) in oil and fuel resistance, making it suitable for less demanding sealing environments.
Overview of Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
Nitrile Rubber (NBR), a synthetic rubber copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene, is widely preferred for oil seal applications due to its excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and other chemicals. Its high tensile strength and flexibility at low temperatures make it ideal for dynamic sealing environments, outperforming Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) in oil resistance and durability. NBR typically offers a temperature range of -40degC to 120degC, ensuring reliable sealing performance in automotive, industrial, and aerospace sectors.
Chemical Resistance: SBR vs NBR
Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers superior chemical resistance compared to Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), making it more suitable for oil seal applications exposed to fuels, oils, and hydrocarbons. NBR's molecular structure provides excellent resistance to mineral oils, gasoline, and aliphatic solvents, whereas SBR shows limited resistance, particularly to oils and fuels, leading to faster degradation. Therefore, NBR is preferred for oil seals requiring robust chemical stability in aggressive petroleum-based environments.
Temperature Tolerance Comparison
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) typically withstands temperatures ranging from -50degC to 100degC, making it suitable for moderate temperature oil seal applications. Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers superior temperature tolerance, functioning effectively between -40degC and 120degC, and can endure occasional peaks up to 150degC. The enhanced thermal resistance of Nitrile rubber makes it a preferred choice for oil seals exposed to higher temperatures and aggressive automotive or industrial environments.
Durability and Longevity in Oil Seals
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers moderate durability in oil seals, providing excellent abrasion resistance but limited chemical stability when exposed to petroleum-based oils. Nitrile rubber (NBR) outperforms SBR in longevity for oil seals due to its superior resistance to oil, fuel, and heat, maintaining elasticity and preventing swelling or degradation over extended periods. The enhanced chemical compatibility of nitrile rubber ensures longer service life and reduced maintenance in oil seal applications compared to styrene-butadiene rubber.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers a lower upfront cost compared to nitrile rubber (NBR) while providing adequate performance in dry and low-temperature applications. NBR delivers superior resistance to oil, fuel, and chemicals, reducing maintenance costs and extending the lifespan of oil seals in harsh environments. Cost-effectiveness analysis reveals that despite higher initial expenses, NBR's durability and reduced replacement frequency often result in lower total ownership costs for oil seal applications.
Application Suitability for Oil Seals
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers moderate resistance to abrasion and good flexibility, making it suitable for general-purpose oil seals in environments with low exposure to harsh chemicals or extreme temperatures. Nitrile rubber (NBR) exhibits superior resistance to petroleum oils, fuels, and synthetic fluids, with high tensile strength and excellent sealing performance under a wide temperature range (-40degC to 120degC), making it the preferred material for oil seals in automotive, industrial machinery, and hydraulic applications. The enhanced chemical resistance and durability of nitrile rubber ensure longer service life and better leakage prevention compared to SBR in oil seal applications.
Maintenance and Replacement Considerations
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers good abrasion resistance but exhibits lower oil and chemical resistance compared to nitrile rubber (NBR), leading to more frequent maintenance and earlier replacement in oil seal applications exposed to petroleum fluids. Nitrile rubber, with superior resistance to oils, fuels, and hydraulic fluids, extends the service life of oil seals and reduces downtime by minimizing degradation, swelling, and hardening under typical operating conditions. Maintenance schedules can be optimized by selecting NBR for seals in lubricated, oil-exposed environments, providing cost-effective longevity and reliability over SBR.
Conclusion: Choosing Between SBR and NBR for Oil Seals
NBR (Nitrile Butadiene Rubber) outperforms SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber) in oil resistance, making it the preferred choice for oil seals exposed to petroleum-based fluids. SBR offers superior abrasion resistance and low cost but lacks the chemical stability required for prolonged oil exposure. Therefore, NBR provides enhanced durability and sealing efficiency in oil seal applications subjected to oils and fuels.
Infographic: Styrene-butadiene rubber vs Nitrile rubber for Oil seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com