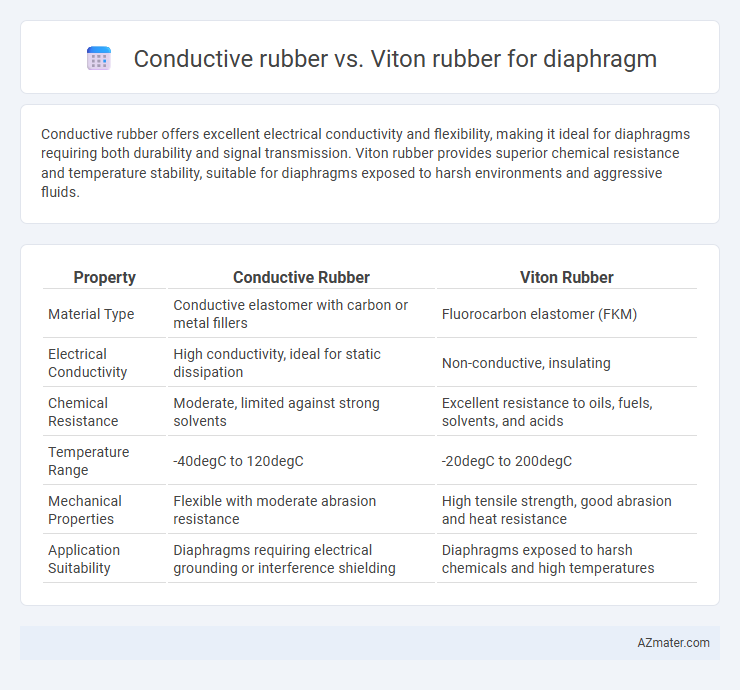
Conductive rubber offers excellent electrical conductivity and flexibility, making it ideal for diaphragms requiring both durability and signal transmission. Viton rubber provides superior chemical resistance and temperature stability, suitable for diaphragms exposed to harsh environments and aggressive fluids.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Conductive Rubber | Viton Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Conductive elastomer with carbon or metal fillers | Fluorocarbon elastomer (FKM) |
| Electrical Conductivity | High conductivity, ideal for static dissipation | Non-conductive, insulating |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate, limited against strong solvents | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, solvents, and acids |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -20degC to 200degC |
| Mechanical Properties | Flexible with moderate abrasion resistance | High tensile strength, good abrasion and heat resistance |
| Application Suitability | Diaphragms requiring electrical grounding or interference shielding | Diaphragms exposed to harsh chemicals and high temperatures |
Overview of Diaphragm Applications
Conductive rubber diaphragms are favored in electronic and sensor applications where static dissipation and electrical conductivity are critical, enabling accurate signal transmission and responsiveness. Viton rubber diaphragms excel in chemical processing, automotive, and aerospace industries due to their superior chemical resistance, high temperature tolerance, and exceptional durability against aggressive fluids. Selection between conductive rubber and Viton rubber depends heavily on the application's environmental exposure, electrical requirements, and mechanical demands.
Key Properties of Conductive Rubber
Conductive rubber used in diaphragms offers excellent electrical conductivity, ensuring efficient signal transmission and static dissipation in sensitive electronics. Its flexibility and durability provide superior resistance to wear, compression set, and environmental factors compared to Viton rubber, which is primarily valued for its chemical and heat resistance but lacks inherent conductivity. The combination of elasticity, electrical performance, and chemical resistance makes conductive rubber ideal for applications requiring both conductivity and mechanical resilience.
Key Properties of Viton Rubber
Viton rubber offers exceptional chemical resistance, high temperature tolerance up to 200degC, and excellent durability, making it ideal for diaphragm applications exposed to harsh environments. Its low permeability to gases and superior resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents outperform conductive rubber in maintaining diaphragm integrity. Viton's strong mechanical properties and resistance to compression set ensure reliable, long-lasting performance in demanding industrial and automotive systems.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Conductive rubber diaphragms offer superior electrical conductivity due to the incorporation of conductive fillers such as carbon black or metal particles, allowing efficient electron flow essential for applications requiring static dissipation or EMI shielding. Viton rubber, a fluorocarbon elastomer, provides excellent chemical resistance and thermal stability but is inherently non-conductive, limiting its use where electrical conductivity is critical. When selecting a diaphragm material, conductive rubber outperforms Viton in electrical conductivity, making it the preferred choice for electrical and electronic sealing environments.
Chemical Resistance Analysis
Conductive rubber diaphragms exhibit moderate chemical resistance and are particularly effective in applications involving conductive fluids or static dissipation, but may degrade when exposed to strong acids or solvents. Viton rubber excels in chemical resistance, with outstanding durability against a wide range of acids, oils, and high-temperature environments, making it ideal for aggressive chemical applications. Comparative analysis emphasizes Viton's superior chemical stability and longevity when used in diaphragms subjected to harsh chemical exposures.
Temperature Tolerance Comparison
Conductive rubber diaphragms typically withstand temperatures up to 120degC, making them suitable for moderate heat applications, while Viton rubber excels with a temperature tolerance range from -20degC to 200degC, providing superior resistance in high-heat environments. Viton's fluoropolymer composition ensures excellent chemical stability and durability under extreme thermal stress, outperforming conductive rubbers in longevity and performance. For applications requiring high temperature and chemical resistance, Viton rubber is the preferred choice over conductive rubber diaphragms.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility
Conductive rubber diaphragms exhibit superior mechanical strength due to their reinforced polymer matrix, making them highly resistant to tearing and deformation under pressure. Viton rubber offers excellent flexibility and chemical resistance, but its mechanical strength is generally lower compared to conductive rubber, leading to potential wear in high-stress applications. Selection depends on balancing the need for durability and flexibility, with conductive rubber favored for heavy-duty environments and Viton preferred where chemical resilience and flexibility are paramount.
Cost and Availability
Conductive rubber diaphragms typically cost more due to specialized materials and manufacturing processes but offer enhanced electrical properties essential for certain applications. Viton rubber, known for its chemical resistance and durability, is generally more affordable and widely available in various grades and sizes. Availability of Viton rubber is broader globally, whereas conductive rubber may require sourcing from specialized suppliers, impacting lead times and overall project costs.
Industry-Specific Recommendations
Conductive rubber is ideal for electronic and electrical industry diaphragms due to its excellent electrical conductivity, enabling effective shielding and grounding in sensitive components. Viton rubber, known for its superior chemical resistance and high-temperature tolerance, is preferred in chemical processing, automotive, and aerospace sectors where exposure to aggressive fluids and extreme conditions is common. Selecting conductive rubber enhances performance in ESD-sensitive environments, while Viton rubber ensures durability and reliability in harsh, high-temperature industrial applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Diaphragm
Conductive rubber offers excellent electrical conductivity and flexibility, making it ideal for applications requiring static dissipation or electromagnetic interference shielding in diaphragms. Viton rubber provides superior chemical resistance, high-temperature stability, and durability, suitable for harsh environments involving aggressive fluids or elevated temperatures. Selecting the right rubber depends on specific operational needs: prioritize conductive rubber for electrical performance and Viton rubber for chemical and thermal resilience in diaphragm applications.
Infographic: Conductive rubber vs Viton rubber for Diaphragm
 azmater.com
azmater.com