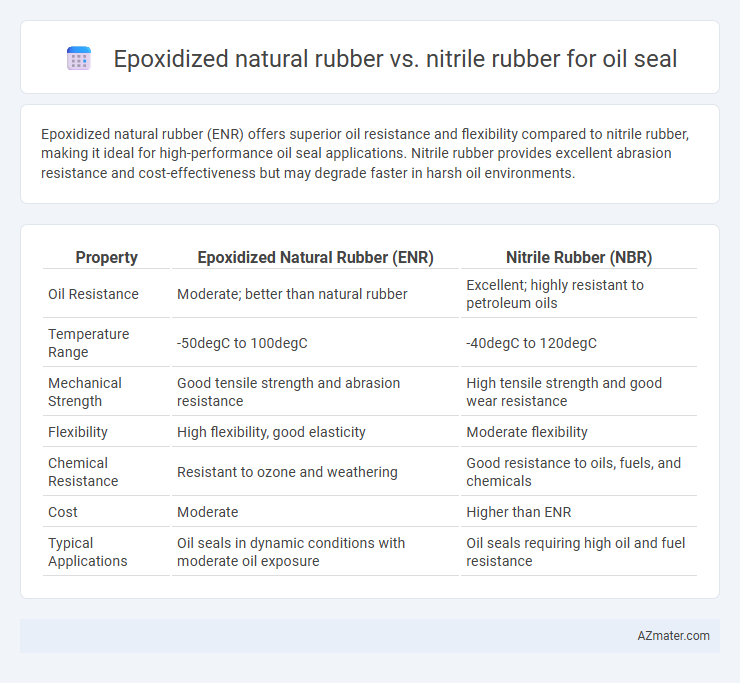
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior oil resistance and flexibility compared to nitrile rubber, making it ideal for high-performance oil seal applications. Nitrile rubber provides excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness but may degrade faster in harsh oil environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Resistance | Moderate; better than natural rubber | Excellent; highly resistant to petroleum oils |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 100degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Good tensile strength and abrasion resistance | High tensile strength and good wear resistance |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, good elasticity | Moderate flexibility |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to ozone and weathering | Good resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher than ENR |
| Typical Applications | Oil seals in dynamic conditions with moderate oil exposure | Oil seals requiring high oil and fuel resistance |
Introduction to Oil Seals and Material Selection
Oil seals require materials with excellent resistance to oil, heat, and mechanical wear to ensure long service life in dynamic environments. Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior elasticity and enhanced oil resistance compared to standard natural rubber, making it suitable for moderate oil sealing applications with improved flexibility. Nitrile rubber (NBR), known for its exceptional resistance to petroleum-based oils, high tensile strength, and temperature tolerance, is widely preferred for oil seals in demanding industrial and automotive settings.
Overview of Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR)
Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) is derived from natural rubber with epoxy groups introduced into its polymer chain to enhance oil and fuel resistance, outperforming standard natural rubber in sealing applications. ENR exhibits improved thermal stability, abrasion resistance, and barrier properties, making it suitable for oil seals exposed to harsh environments and hydrocarbon fluids. Compared to Nitrile Rubber (NBR), ENR offers better elasticity and eco-friendliness derived from renewable resources, although NBR generally provides superior oil and chemical resistance.
Overview of Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
Nitrile Rubber (NBR) is a synthetic elastomer widely used in oil seals due to its excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and other chemicals, making it ideal for automotive and industrial applications. Its superior tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and low gas permeability contribute to long-lasting performance in dynamic sealing environments. Compared to Epoxidized Natural Rubber, NBR offers enhanced thermal stability and chemical compatibility, especially in high-temperature oil sealing scenarios.
Oil Resistance: ENR vs NBR
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers improved oil resistance compared to standard natural rubber due to its polar epoxide groups, but it generally falls short when matched against nitrile rubber (NBR), which is specifically designed for superior resistance to oils, fuels, and hydrocarbons. NBR's molecular structure, rich in acrylonitrile content, provides exceptional resistance to swelling and degradation in contact with petroleum-based fluids, making it the preferred choice for oil seal applications in automotive and industrial systems. While ENR exhibits good elasticity and thermal stability, NBR dominates in terms of durability and chemical compatibility for continuous exposure to oils and lubricants.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits superior elasticity and higher tensile strength compared to nitrile rubber (NBR), making it more resistant to mechanical deformation in dynamic oil seal applications. Nitrile rubber demonstrates excellent abrasion resistance and better compression set characteristics, which contribute to enhanced durability under constant mechanical stress and oil exposure. The choice between ENR and NBR depends on the specific mechanical demands, with ENR favored for flexibility and resilience, while NBR excels in wear resistance and long-term sealing performance.
Temperature Performance Analysis
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) demonstrates superior high-temperature resistance compared to nitrile rubber (NBR), maintaining elasticity and mechanical strength up to approximately 150degC due to the presence of epoxide groups enhancing thermal stability. Nitrile rubber typically performs well within a temperature range of -40degC to 120degC but may exhibit reduced flexibility and accelerated degradation at higher temperatures, limiting its usage in extreme thermal environments. For oil seal applications subject to elevated temperatures, ENR offers enhanced durability and extended service life by resisting thermal decomposition and maintaining sealing integrity.
Chemical Compatibility with Lubricants
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits superior chemical compatibility with polar lubricants and synthetic oils due to its enhanced polarity from epoxy groups, making it resistant to swelling and degradation. Nitrile rubber (NBR) is highly compatible with a wide range of petroleum-based oils and mineral lubricants, offering excellent resistance to hydrocarbons but may degrade with certain polar or synthetic lubricants. Selecting between ENR and NBR for oil seals depends on the specific lubricant chemistry, with ENR preferred for polar or synthetic oils and NBR favored for conventional petroleum-based applications.
Wear and Aging Characteristics
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits superior wear resistance due to its enhanced tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to nitrile rubber (NBR), making it highly suitable for oil seal applications exposed to dynamic friction. ENR also shows improved aging characteristics, particularly oxidative and thermal stability, which prolongs seal life under high-temperature and harsh oil environments. In contrast, nitrile rubber offers good oil resistance but tends to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to heat and oxidative conditions, leading to reduced wear life and potential seal failure.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) tends to have higher raw material costs compared to nitrile rubber (NBR) due to specialized processing requirements, impacting overall oil seal production expenses. Nitrile rubber is widely available and produced in large volumes globally, ensuring steady supply and competitive pricing advantageous for oil seal manufacturing. The choice between ENR and NBR for oil seals hinges on balancing ENR's enhanced oil resistance and mechanical properties against NBR's cost-effectiveness and broader market accessibility.
Application Suitability for Oil Seals
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced oil resistance and improved mechanical properties compared to standard natural rubber, making it suitable for oil seals in moderate oil exposure and moderate temperature environments. Nitrile rubber (NBR) exhibits superior resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and other chemicals, with excellent abrasion and compression set resistance, making it the preferred choice for oil seals in high-temperature and aggressive chemical exposure applications. ENR is advantageous in applications requiring better elasticity and environmental resilience, while NBR is optimal for heavy-duty oil sealing in automotive, industrial, and aerospace sectors.
Infographic: Epoxidized natural rubber vs Nitrile rubber for Oil seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com