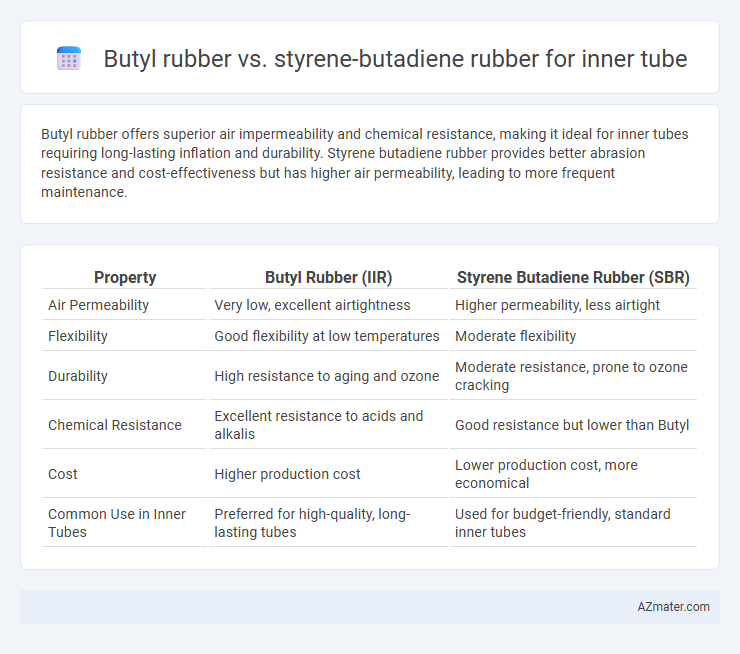
Butyl rubber offers superior air impermeability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for inner tubes requiring long-lasting inflation and durability. Styrene butadiene rubber provides better abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness but has higher air permeability, leading to more frequent maintenance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Butyl Rubber (IIR) | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Air Permeability | Very low, excellent airtightness | Higher permeability, less airtight |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility at low temperatures | Moderate flexibility |
| Durability | High resistance to aging and ozone | Moderate resistance, prone to ozone cracking |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to acids and alkalis | Good resistance but lower than Butyl |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower production cost, more economical |
| Common Use in Inner Tubes | Preferred for high-quality, long-lasting tubes | Used for budget-friendly, standard inner tubes |
Introduction to Inner Tube Materials
Inner tubes commonly use butyl rubber and styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) due to their distinct performance characteristics. Butyl rubber offers superior air retention and chemical resistance, making it ideal for long-lasting inflation in bicycle and automotive inner tubes. SBR provides enhanced abrasion resistance and flexibility but generally has higher air permeability, impacting its use in certain inner tube applications.
Overview of Butyl Rubber
Butyl rubber, characterized by its excellent impermeability to air and superior resistance to heat, chemicals, and weathering, is the preferred material for inner tubes due to its durability and low gas permeability. This synthetic rubber, derived from isobutylene with a small amount of isoprene, ensures minimal air loss and better tire pressure retention compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR). Its resilience against punctures and oxidation makes butyl rubber an optimal choice for maintaining inner tube integrity in various tire applications.
Overview of Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is a synthetic rubber widely used for inner tubes due to its excellent abrasion resistance and good aging stability compared to natural rubbers. Its molecular structure, combining styrene and butadiene monomers, provides a balance of heat resistance and elasticity, making SBR highly durable under varying temperature conditions. This material also offers superior resistance to wear and tear, ensuring longer service life for inner tubes in automotive and industrial applications.
Air Retention Capabilities
Butyl rubber exhibits superior air retention capabilities compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) due to its low permeability to gases, making it the preferred choice for inner tubes. The molecular structure of butyl rubber contains a high concentration of saturated hydrocarbons that significantly reduce air diffusion rates. In contrast, styrene butadiene rubber, while more cost-effective and abrasion-resistant, allows faster air leakage, resulting in more frequent inflation requirements.
Resistance to Weathering and Ozone
Butyl rubber exhibits superior resistance to weathering and ozone degradation compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making it highly durable for inner tubes in harsh environmental conditions. The impermeability and chemical stability of butyl rubber prevent cracking and deterioration caused by prolonged exposure to ultraviolet light and ozone. In contrast, SBR is more susceptible to ozone-induced cracking and weathering due to its unsaturated molecular structure.
Flexibility and Elasticity Comparison
Butyl rubber exhibits superior flexibility and excellent air retention, making it highly effective for inner tubes in maintaining shape under pressure variations. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) offers higher elasticity, which provides better shock absorption but may compromise long-term air impermeability. Choosing between butyl rubber and SBR depends on the required balance between flexibility, elasticity, and durability for inner tube performance.
Durability and Longevity
Butyl rubber offers superior air retention and chemical resistance, making it highly durable for inner tubes exposed to various environmental conditions. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) provides good abrasion resistance but has lower resilience against gases and chemicals, resulting in shorter lifespan compared to butyl. For inner tubes, butyl rubber significantly outperforms SBR in longevity due to its enhanced impermeability and resistance to aging.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Butyl rubber offers superior air impermeability and chemical resistance for inner tubes but comes at a higher production cost due to its complex synthesis and limited raw material availability. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) is more cost-effective with easier manufacturing processes, benefiting from abundant styrene and butadiene feedstocks and well-established production techniques. Manufacturers often balance the higher durability of butyl rubber inner tubes against the economical advantages of SBR to meet diverse market demands.
Performance in Different Environmental Conditions
Butyl rubber exhibits superior air retention and chemical resistance, making it ideal for inner tubes exposed to high temperatures and harsh chemicals. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and flexibility, performing well in lower temperature environments and rough terrains. Both materials balance durability and elasticity, but butyl rubber outperforms SBR in maintaining pressure and resisting ozone and weather aging.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Rubber for Inner Tubes
Butyl rubber offers superior air retention and chemical resistance, making it ideal for inner tubes requiring long-lasting inflation and durability. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) provides excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness but lacks the airtight characteristics of butyl rubber. Selecting the right rubber depends on balancing performance needs, with butyl rubber favored for high-performance inner tubes and SBR chosen for budget-friendly applications.
Infographic: Butyl rubber vs Styrene butadiene rubber for Inner tube
 azmater.com
azmater.com